Abstract
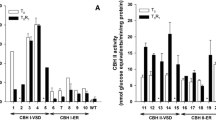
The genes encoding thermostable cellulases E2 and E3 of Thermomonospora fusca were expressed in plants under the control of the constitutive, hybrid Mac promoter. For both E2 and E3, the genes were modified so as to remove the sequence encoding the bacterial leader peptide. Western blot analysis indicated that expression levels of recombinant cellulase in tobacco lines ranged up to about 0.1% (E2) and 0.02% of soluble protein (E3). No phenotypic effect of cellulase expression was noted. Recombinant E2 expressed in either tobacco or alfalfa was active and retained heat stability. These findings are an important first step in the development of crop plants as a production system for cellulases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An G, Ebert PR, Mitra A, Ha SB: Binary vectors. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort RA (eds) Plant Molecular Biology Manual, pp. A3/1–A3/19. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands (1988).
Austin S, Bingham ET: The potential use of transgenic alfalfa as a bioreactor for the production of industrial enzymes. In: McKersie BD, Brown DCW (eds) Biotechnology and the Improvement of Forage Legumes, pp. 409–427, CAB International, Wallingford, UK (1996).
Austin S, Bingham ET, Mathews DE, Shahan MN, Will J, Burgess RR: Production and field performance of transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) expressing alpha-amylase and manganese-dependent lignin peroxidase. Euphytica 4: 1–13 (1995).
Austin S, Koegel RG, Matthews D, Shahan M, Straub RJ, Burgess R: Production of industrial enzymes in transgenic alfalfa. Ann NY Acad Sci 721: 234–242 (1994).
Belkacemi K, Turcotte G, Halleux Dd, Savoie P: Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Timothy Grass Pretreated by Ammonia Fiber Expolosion. In: Proceedings of the Third Liquid Fuel Conference (Nashville, TN). American Society of Agricultural Engineers (1996).
Calza RE, Irwin DC, Wilson DB: Purification and characterization of two _-1,4-endoglucanases from Thermomonospora fusca. Biochemistry 24: 7797–7804 (1985).
Cearley JA, Bolyard MG: Regeneration of Solanum tubersosum cv. Katahdin from leaf explants in vitro. Am Potato J 74: 125–129 (1997).
Comai L, Moran P, Maslyar D: Novel and useful properties of a chimeric plant promoter combining CaMV 35S and MAS elements. Plant Mol Biol 15: 373–381 (1990).
Delmer DP, Amor Y: Cellulose biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7: 987–1000 (1995).
Englard S, Seifter S: Precipitation Techniques. In: Deutscher MP (ed) Protein Purification, pp. 285–300. Academic Press, San Diego (1990).
Goddijn OJM, Pen J: Plants as bioreactors. Trends Biotechnol 13: 379–387 (1995).
Grohmann K, Wyman CE, Himmel ME: Potential for fuels from biomass and wastes. In: Proceedings of Emerging Technologies for Materials and Chemicals from Biomass, Washington. American Chemical Society (1990).
Halliwell N, Halliwell G: Biotechnological aspects of lignocellulose and biomass degradation. Outlook Agric 24: 219–225 (1995).
Hiatt A, Cafferkey R, Bowdish K: Production of antibodies in transgenic plants. Nature 342: 76–78 (1989).
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffman NL, Eicholtz D, Rogers SG, Farley RT: A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227: 1229–1231 (1985).
Irwin DC, Spezio M, Walker LP, Wilson DB: Activity studies of eight purified cellulases: specificity, synergism, and binding domain effects. Biotechnol Bioeng 42: 1002–1013 (1993).
Koegel RG, Straub RJ: Fractionation of alfalfa for food, feed, biomass, and enzymes. Trans ASAE 39: 769–774 (1996).
Kusnadi AR, Nokolov ZL, Howard JA: Production of recombinant proteins in transgenic plants: practical considerations. Biotechnol Bioeng 56: 473–484 (1997).
Loomis WD: Overcoming problems of phenolics and quinones in the isolation of plant enzymes and organelles. Meth Enzymol 31: 528–544 (1974).
Lynd LR, Cushman JH, Nichols RJ, Wyman CE: Fuel ethanol from cellulosic biomass. Science 251: 1318–1323 (1991).
McBride KE, Summerfeldt KR: Improved binary vectors for Agrobacterium mediated plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 14: 269–276 (1990).
Micallef MC, Austin S, Bingham ET: Improvement of transgenic alfalfa by backcrossing. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 31: 187–192 (1995).
Miceli A, Cuna D, Viggiano D, Leo PD: Integrated treatment of steam explosion and enzymatic hydrolysis to produce energetic and industrial products from lignocellulosic biomasses. Agro-Food-Ind Hi-Tech 7: 25–28 (1996). 318
Murashige T, Skoog F: A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497 (1962).
Sijmons PC, Dekker BMM, Schrammeijer B, Verwoerd TC, van den Elzen PJM, Hoekema A: Production of correctly processed human serum albumin in transgenic plants. Biotechnology 8: 217–221 (1990).
Spezio M, Wilson DB, Karplus PA: Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of a thermophilic endocellulase. Biochemistry 32: 9906–9916 (1993).
Teeri TT: Crystalline cellulose degradation: new insight into the function of cellobiohydrolases. Trends Biotechnol 15: 160–167 (1997).
Wright JD: Ethanol from lignocellulose: an overview. Energy Prog 8: 71–78 (1988).
Zhang S, Lao G, Wilson DB: Characterization of a Thermomonospora fusca exocellulase. Biochemistry 34: 3386–3395 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziegelhoffer, T., Will, J. & Austin-Phillips, S. Expression of bacterial cellulase genes in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Molecular Breeding 5, 309–318 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009646830403
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009646830403