Abstract
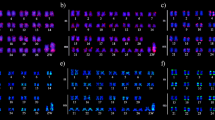
Several cytogenetic studies have shown that representatives of the family Cyperaceae have holocentric chromosomes. Despite their interesting chromosome morphology, the chromosome organization has not been studied. This paper reports on the number and distribution of 18S–5.8S–26S ribosomal RNA sites by fluorescence in situ hybridization in eight Brazilian species of Rhynchospora. The signal of the rDNA probe was always localized in the telomeric regions. A high degree of variation was observed in the number of labelled sites, ranging from 4–8 in karyotypes with 2n = 10 to 30 sites in a karyotype with 50 chromosomes. It is possible that the same mechanism involved in the multiplication of these regions in organisms with monocentric chromosomes also plays a role in the polymorphism observed in holocentric chromosomes of Rhynchospora. An interesting feature of most hybridization sites was their diffuse state observed through to early metaphase. The decondensed state probably reflects the later transcription of this region during the cell cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Honeycutt RL (1986) rDNA: evolution over a billion years. In: Dutta SK, ed. DNA Systematics II. Plant DNA. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp 81–125.
Braselton JP (1981) The ultrastructure of meiotic kinetochores of Luzula. Chromosoma 82: 143–151.
Brown GR, Amarasinghe V, Kiss G, Carlson JE (1993) Preliminary karyotype and chromosomal localization of ribosomal DNA sites in white spruce using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genome 36: 310–316.
Collet C (1984) Highly repeated DNA and holocentric chromosomes of the woodrush Luzula flaccida (Juncaceae). Can J Genet Cytol 26: 288–295.
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (1994) Mapping and organization of highly-repeated DNA sequences by means of simultaneous and sequential FISH and C-banding in 6x-Triticale. Chrom Res 2: 231–338.
Flavell RB, O'Dell M, Thompson WF (1988) Regulation of cytosine methylation in ribosomal DNA and nucleolus organizer expression in wheat. J Mol Biol 204: 523–534.
Garrido MA, Jamilena M, Lozano R, Ruiz Rejon C, Ruiz Rejon M, Parker JS (1994) rDNA site polymorphism and NOR inactivation in natural populations of Allium schoenoprasum. Genetica 94: 67–71.
Gerlach WL, Bedbrook JR (1979) Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res 7: 1869–1885.
Gustafson JP, Dera A, Petrovic S (1988) Expression of modified rye ribosomal RNA genes in wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3943–3945.
Håkansson A (1958) Holocentric chromosomes in Cyperaceae. Hereditas 11: 182–192.
Heilborn O (1924) Chromosome numbers and dimensions, species-formation and phylogeny in the genus Carex. Hereditas 5: 129–221.
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T, Anamthawat-Jónsson K, Leitch AR, Shi M, Leitch IJ (1991) In situ hybridization with automated chromosome denaturation. Technique 3: 109–106.
Hoshino T (1987) Karyomorphological studies on seven species of Japanese Rhynchospora (Cyperaceae). La Kromosomo 2: 1557–1561.
Hoshino T, Okamura K, Hong D, Dai Lun-kai, Nakata M, Tanaka R (1993) Cytological studies of Chinese Cyperaceae 1. Chromosome counts of nine species collected from Jilin. Liaoning and Hebei provinces (China). Jpn J Bot 68: 65–69.
Luceño M, Castroviejo S (1991) Agmatoploidy in Carex laevigata (Cyperaceae). Fusion and fission of chromosomes as the mechanism of cytogenetic evolution in Iberian populations. Pl Sys Evol 177: 149–159.
Luceño M, Vanzela ALL, Guerra M (1998) Cytotaxonomic studies in Brazilian Rhynchospora (Cyperaceae), a genus exhibiting holocentric chromosomes. Can J Bot (in press).
Pedersen C, Linde-Laursen I (1994) Chromosomal locations of four minor rDNA loci and a marker microsatellite sequence in barley. Chrom Res 2: 65–71.
Ray JH, Venketeswaran S (1979) DNA replication, 3H-cRNA in situ hybridization and C-banded patterns in the polycentric chromosomes of Luzula purpurea Link. Chromosoma 74: 337–346.
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1987) Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. Plant Mol Biol 9: 509–520.
Sakowicz T, Olszewska MJ (1997) DNA content, interphase AgNOR-area, number of 3HrDNA hybridization signals and the methylation level in coding rDNA sequence in different organs of Lupinus luteus L. Genetica 99: 67–72.
Schubert I, Wobus U (1985) In situ hybridization confirms jumping nucleolus organizing regions in Allium. Chromosoma 92: 143–148.
Schweizer D, Loidl J (1987) A model for heterochromatin dispersion and the evolution of C-band patterns. Chrom Today 9: 61–74.
Sheikh SA, Kondo K (1995) Differential staining with orcein, Giemsa, CMA and DAPI for comparative chromosome study of 12 species of Australian Drosera (Droseraceae). Am J Bot 82: 1278–1286.
Wachtler F, Hopman AH, Wiegant J, Schwarzacher HG (1986) On the position of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in interphase nuclei. Studies with a new, non-autoradiographic in situ hybridization method. Exp Cell Res 167: 227–240.
Vanzela ALL, Guerra M, Luceño M (1996) Rhynchospora tenuis Link (Cyperaceae), a species with the lowest number of holocentric chromosomes (n = 2). Cytobios 88: 219–228.
Zatsepina OV, Voit R, Grummt I, Spring H, Semenov MV, Trendelenburg MF (1993) The RNA polymerase I-specific transcription initiation factor UBF is associated with transcriptionally active and inactive ribosomal genes. Chromosoma 102: 599–611.
Zurita F, Sánchez A, Burgos M, Jiménez R, De la Guardia RD (1997) Interchromosomal, intercellular and interindividual variability of NORs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanzela, A.L.l., Cuadrado, A., Jouve, N. et al. Multiple Locations of the rDNA Sites in Holocentric Chromosomes of Rhynchospora (Cyperaceae). Chromosome Res 6, 345–350 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009279912631
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009279912631