Abstract
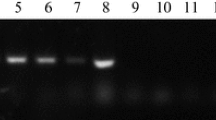
Xylella fastidiosa, the causal agent of Pierce's disease (PD) of grape, was isolated from diseased grapevines grown in Kosova, Yugoslavia. The Kosova isolate was a rod-shaped bacterium which showed a typically rippled cell wall under electron microscopy. ELISA comparisons indicated that the Kosova isolate was closely related to the U.S. PD strains and to several other strains of X. fastidiosa. When DNA extracted from diseased grapevines collected from Kosova was used as template in PCR with primer sets specific for X. fastidiosa, a band of about 730 bp diagnostic for PD bacteria was detected. DNA from the isolated Kosova bacteria and the type strain of PD yielded the same length of DNA fragment in PCR assay. The Kosova isolate was inoculated into young healthy grapevines through the roots with negative pressure applied to the shoots. Typical scald and scorch symptoms appeared on the leaves of the inoculated grapevines 40–80 days after inoculation. The same bacteria were reisolated from these inoculated diseased plants and used to reinoculate young grapevines. The reinoculated grapevines produced the same symptoms, thereby fulfilling Koch's postulates. This is the first confirmation that PD of grapes occurs in Europe.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Beretta MJG, Harakava R, Chagas CM, Derrick KS, Barthe GA, Ceccardi TL, Lee RF, Paradela O, Sagimori M and Ribeiro IA (1996) First report of Xylella fastidiosain coffee. Plant Dis 78: 821
Chang CJ and Walker, JT (1988) Bacterial leaf scorch of northern red oak: Isolation, cultivation, and pathogenicity of xylem limited bacterium. Plant Dis 72: 730-33
Chang CJ, Gernier M, Zreik L, Rossetti V and Bove JM (1993) Culture and serological detection of the xylem-limited bacterium causing citrus vainegated chlorosis and its identification as a strain of Xylella fastidiosa. Curr Microbiol 27: 137-142
Davis MJ, Purcell AH and Thompson SV (1978) Pierce's disease of grapevines: isolation of the causal bacterium. Science 199: 75-77
Davis MJ, Purcell AH and Thompson SV (1980) Isolation media for the Pierce's disease bacterium. Phytopathology 70: 425-29
French WJ, Christis RG and Stassi DL (1977) Recovery of rickettsia-like bacteria by vacuum infiltration of peach tissues affected with phony disease. Phytopathology 67: 945-948
French WJ and Kitajima EW (1978) Occurrence of plum leaf scald in Brazil and Paraguay. Plant Dis Reptr 62: 1035-1038
Goheen AC and Hopkins DL (1988) Pierce's disease. In: Pearson RC and Goheen AC (eds) Compendium of Grape Diseases. (pp. 44-45) APS Press, St. Paul
Goheen AC, Nyland G and Lowe SK (1973) Association of a rickettsia-like organism with Pierce's disease of grapevines and alfalfa dwarf and heat therapy of the disease in grapevines. Phytopathology 63: 341-345
Goheen AC, Raju BC, Lowe SK and Nyland G (1979) Pierce's disease of grapevine in Central America. Plant Dis Reptr 63: 788-792
Hartung JS, Beretta J, Belansky RH, Spisso J and Lee RF (1994) Citrus variegated chlorosis bacterium: axenic culture, pathogenicity and serological relationships with other strains of Xylella fastidiosa. Phytopathology 84: 591-597
Hearon SS, Sherald JL and Kostka SJ (1980) Association of xylem-limited bacteria with elm, sycamore, and oak leaf scorch. Can J Bot 58: 1986-93
Hopkins DL (1982) Relation of Pierce's disease bacteria to a wilt-type disease in citrus in the greenhouse. Phytopathology 72: 1090-1092
Hopkins DL (1989) Xylella fastidiosa: xylem-limited bacterial pathogen of plants. Ann Rev Phytopathol 27: 271-290
Hopkins DL and Mollenhauer HH (1973) Rickettsia-like bacterium associated with Pierce's disease of grapes. Science 179: 298-300
Hopkins DL, Mollenhauer HH and French WJ (1973) Occurrence of a rickettsia-like bacterium in the xylem of peach trees with phony disease. Phytopathology 63: 1422-23
Kitajima EW, Bakarcic M and Fernandez-Valiela MV (1975) Association of rickettsia-like bacteria with plum leaf scald disease. Phytopathology 65: 476-479
Kostka SJ, Tattar TA and Sherald JL (1986) Elm leaf scorch abnormal physiology in American elms infected with fastidious, xylem-inhabiting bacteria. Can J For Res 16: 1088-91
Leu LS and Su CC (1993) Isolation, cultivation, and pathogenicity of Xylella fastidiosa, the causal bacterium of pear leaf scorch disease in Taiwan. Plant Dis 77: 642-646
Lin CP and Chen TA (1985) Monoclonal antibodies against the aster-yellows agents. Science 227: 1233-1235
Lin CP and Chen TA (1986) Comparison of monoclonal antibodies and polyclonal antibodies in detection of the aster yellows mycoplasmalike organism. Phytopathology 76: 45-50
Minsavage GV, Thompson CM, Hopkins DL, Leite RMVBC and Stall RE (1994) Development of a polymerase chain reaction protocol for detection of Xylella fastidiosain plant tissue. Phytopathology 84: 456-461
Mircetish SM, Lowe SK, Moller WJ and Nyland G (1976) Etiology of almond leaf scorch disease and transmission of the causal agent. Phytopathology 66: 17-24
Purcell AH (1980) Environmental therapy for Pierce's disease of grapevines. Plant Dis 64: 388-90
Purcell AH and Finlay AH (1979) Evidence for non-circulative transmission of Pierce's disease bacterium by sharpshooter leafhoppers. Phytopathology 69: 393-395
Raju BC, Wells JM, Nyland G, Belansky RH and Lowe SK (1982) Plum leaf scald: isolation, culture, and pathogenicity of the causal agent. Phytopathology 72: 1460-1466
Rowhani A, Chay C, Golino DA and Falk BW (1993) Development of a polymerase chain reaction technique for the detection of grapevine fanleaf virus in grapevine tissue. Phytopathology 83: 749-753
Sherald JL, Hearon SS, Kostka SJ and Morgan DC (1983) Sycamore leaf scorch: culture and pathogenicity of fastidious xylem-limited bacteria from scorch-affected trees. Plant Dis 67: 849- 852
Sherald JL, Wells JM, Hurtt S and Kostka SJ (1987) Association of fastidious xylem-inhabiting bacteria with leaf scorch in red maple. Plant Dis 71: 930-933
Wells JM, Raju BC and Nyland G (1983) Isolation, culture and pathogenicity of the bacterium causing phony disease of peach. Phytopathology 73: 859-862
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berisha, B., Chen, Y., Zhang, G. et al. Isolation of Peirce's disease bacteria from grapevines in Europe. European Journal of Plant Pathology 104, 427–433 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008655621235
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008655621235