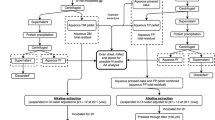
Abstract
With protein contents higher than 20% (dry weight), some red or green seaweeds are potential sources of commercially useful plant proteins. However, the presence of anionic or neutral polysaccharides in large quantities in the cell wall strongly hinders the solubilization of proteins during the application of classical extraction procedures. A present this limits the study and industrial use of seaweed proteins. This short paper is a discussion about the use of enzymes degrading the cell wall polysaccharides as an alternative method to improve the extraction and the solubilization of algal proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano H, Noda H (1990) Proteins from protoplasts from red alga Porphyra yezoensis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 56: 1859–1864.
Amano H, Noda H (1992) Proteins of protoplasts from several seaweeds. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58: 291–299.
Fleurence J (1999) Seaweed proteins: biochemical, nutritional aspects and potential uses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 10: 25–28.
Fleurence J, Le Coeur C, Mabeau S, Maurice M, Landrein A (1995) Comparison of different extractive procedures for proteins from the edible seaweeds Ulva rigida and Ulva rotundata. J. appl. Phycol. 7: 577–582.
Fleurence J, Massiani L, Guyader O, Mabeau S (1995) Use of enzymatic cell wall degradation for improvement of protein extraction from Chondrus crispus, Gracilaria verucosa and Palmaria palmata. J. appl. Phycol. 7: 393–397.
Fujiwara-Arasaki T, Mino T, Kuroda M (1984) The protein value in human nutrition of edible marine algae in Japan. Hydrobiologia 116/117: 513–516.
Horie Y, Sugase K, Horie K (1995) Physiological differences of soluble and insoluble dietary fibre fractions of brown algae and mushrooms in pepsin activity in vitro and protein digestibility. Asian Pacific J. Clin. Nut. 4: 251–255.
Lahaye M, Vigouroux J (1992) Liquefaction of dulse (Palmaria palmata (L.) Kuntze) by a commercial enzyme preparation and a purified endo-b-1,4-D-xylanase. J. appl. Phycol. 4: 329–337.
Polne-Fuller M, Gibor A (1987) Tissue culture of seaweeds. In Bird KT, Benson PH (eds), Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 219–239.
Rice EL, Crowden RK (1987) An improved method for the extraction and electrophoresis of proteins and active enzymes from fucalean macroalgae (Phaeophyta). Phycologia 26: 235–246.
Saga N, Sakai Y (1984) Isolation of protplasts from Laminaria and Porphyra. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fisheries 50: 1085.
Serot T, Courcoux T, Guillemineau F (1994) Extraction and partial characterization of protein from the green alga Ulva sp. Sciences des Aliments 4: 301–309.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fleurence, J. The enzymatic degradation of algal cell walls: a useful approach for improving protein accessibility?. Journal of Applied Phycology 11, 313–314 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008183704389
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008183704389