Abstract
From May 1990 to November 1994, 70 consecutive patients suffering from glioblastoma multiforme were treated following surgery with conventional radiotherapy and adjuvant IV BCNU administered alone or in combination with tamoxifen. Twenty-five patients received BCNU alone (control group A) while 24 patients also received 40 mg of tamoxifen (TMX) PO daily (group B) and 21 received 100 mg of TMX PO daily (group C). There were no significant differences between the 3 groups concerning age, type of resection and median post-operative Karnofsky performance status (KPS). Blood toxicity over grade II occurred in 33.5% of patients receiving TMX versus 12% of patients treated with BCNU alone (p<0.05).
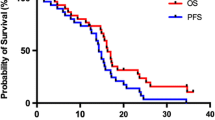
Deep venous thrombosis complications were observed in 4 patients of each TMX group, whereas they were not observed in the control group (p<0.04). Median time to tumor progression (MTTP) was 35 weeks in the control group and 27 weeks in both TMX groups B and C. Median survival time (MST) was 56, 66 and 51 weeks, respectively.
These results suggest that the addition of TMX to standard treatment of glioblastomas does not affect the time to tumor progression and overall survival but may increase the risk of deep venous thrombosis or nitrosourea-induced blood toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker MD, Alexander E Jr, Hunt WE, MacCarty CS, Mahaley MS Jr, Mealey J Jr, Norrell HA, Owens G, Ransohoff J, Wilson CB, Gehan EA, Strike TA: Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic 234 gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg 49: 333–343, 1978
Walker MD, Green SB, Byar DP, Alexander E Jr, Batzdorf U, Brooks WH, Hunt WE, MacCarty CS, Mahaley MS Jr, Mealey J Jr, Owens G, Ransohoff J 2nd, Robertson JT, Shapiro WR, Smith KR Jr, Wilson CB, Strike TA: Randomized comparisons of radiotherapy and nitrosoureas for the treatment of malignant glioma after surgery. N Engl J Med 303: 1323–1329, 1980
Muller H, Brock M, Ernst H: Long-term survival and recurrence-free interval in combined surgical, radio-and chemotherapy of malignant brain gliomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 87: 167–171, 1985
Kornblith PL, Walker M: Chemotherapy for malignant gliomas. J Neurosurg 68: 1–17, 1988
Ekstrand AJ, James CD, Cavenee WK, Seliger B, Pettersson RF, Collins VP: Genes for epidermal growth factor receptor, transforming growth factor alpha, and epidermal growth factor and their expression in human gliomas in vivo. J Neurosurg 73: 594–600, 1990
Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N, Kris R, Lax I, Soreq H, Whittle N, Waterfield MD, Ullrich A, Schlessinger J: Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature 313: 144–147, 1985
Couldwell WT, Antel JP, Yong VW: Protein kinaseCactivity correlates with the growth rate of malignant gliomas: Part II. Effects of glioma mitogens and modulators of protein kinase C. Neurosurg 33: 495–501, 1993
Baltuch GH, Couldwell WT, Villemure JG, Yong VW: Protein kinase C inhibitors suppress cell growth in established and low-passage glioma cell lines. A comparison between staurosporine and tamoxifen. Neurosurgery 33: 495–501, 1993
O'Brian CA, Liskamp RM, Solomon DH, Weinstein IB: Inhibition of protein kinase C by tamoxifen. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 4463–4465, 1986
Chouvet C, Vicard E, Frappart L, Falette N, Lefebvre MF, Saez S: Growth inhibitory effect of 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen on the BT-20 mammary cancer cell line. J Steroid Biochem 31: 655–663, 1988
O'Brian CA, Liskamp RM, Solomon DH, Weinstein IB: Triphenylethylenes: a new class of protein kinase C inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst 76: 1243–1246, 1986
Pollack IF, Randall MS, Kristofik MP, Kelly RH, Selker RG, Vertosick FT Jr.: Effect of tamoxifen on DNA synthesis and proliferation of human malignant glioma lines in vitro. Cancer Res 50: 7134–7138, 1990
Zhang W, Yamada H, Sakai N, Niikawa S, Nozawa Y: Enhancement of radiosensitivity by tamoxifen in C6 glioma cells. Neurosurgery 31: 725–729, 1992
Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG, Pollack IF, Arena V: The treatment of intracranial malignant gliomas using orally administered tamoxifen therapy: preliminary results in a series of 'failed' patients. Neurosurgery 30: 897–902, 1992
Couldwell WT, Weiss MH, DeGiorgio CM, Weiner LP, Hinton DR, Ehresmann GR, Conti PS, Apuzzo ML: Clinical and radiographic response in a minority of patients with recurrent malignant gliomas treated with high-dose tamoxifen. Neurosurgery 32: 485–489, 1993
Gelmann EP: Tamoxifen for the treatment of malignancies other than breast and endometrial carcinoma. Semin Oncol 24: S165-S170, 1997
Haiguang X, Goldthwait DA, Mapstone T: The identification of four protein kinase C isoforms in human glioblastoma cell lines: PKC alpha, gamma, and zeta. J Neurosurg 81: 734–740, 1994
Lam HY: Tamoxifen is a calmodulin antagonist in the activation of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 118: 27–32, 1984
O'Brian CA, Loannides CG, Ward NE, Liskamp RM: Inhibition of protein kinase C and calmodulin by the geometric isomers cis-and trans-tamoxifen. Biopolymers 29: 97–104, 1990
Fine RL, Sacchs CW, Safa A: Inhibition of MDR by tamoxifen: Mechanisms of action. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 34: A 1935, 1993 (abstr)
McClay EF, Albright KD, Jones JA, Christen RD, Howell SB: Tamoxifen modulation of cisplatin sensitivity in human malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Res 53: 1571–1576, 1993
Couldwell WT, Hinton DR, He S, Chen TC, Sebat I, Weiss MH, Law RE: Protein kinase C inhibitors induce apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. FEBS Lett 345: 43–46, 1994
Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG, Randall MS, KristofikMP, Rehn TJ: A comparison of the relative chemosensitivity of human gliomas to tamoxifen and n-desmethyltamoxifen in vitro. Neurooncol 19: 97–103, 1994
Vertosick FT Jr: The role of protein kinase C in the growth of human gliomas: implications for therapy. The Cancer Journal 5: 1992
Adam HK, Patterson JS, Kemp JV: Studies on the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen in normal volunteers. Cancer Treat Rep 64: 761–764, 1980
Fabian C, Sternson L, Barnett M: Clinical pharmacology of tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer: comparison of traditional and loading dose schedules. Cancer Treat Rep 64: 765–773, 1980
Lien EA, Solheim E, Lea OA, Lundgren S, Kvinnsland S, Ueland PM: Distribution of 4-hydroxy-Ndesmethyltamoxifen and other tamoxifen metabolites in human biological fluids during tamoxifen treatment. Cancer Res 49: 2175–2183, 1989
Lien EA, Wester K, Lonning PE, Solheim E, Ueland PM: Distribution of tamoxifen and metabolites into brain tissue and brain metastases in breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 63: 641–645, 1991
Baltuch G, Shenouda G, Langleben A, Villemure JG: High dose tamoxifen in the treatment of recurrent high grade glioma: a report of clinical stabilization and tumour regression. Can J Neurol Sci 20: 168–170, 1993
Couldwell WT, Hinton DR, Surnock AA, DeGiorgio CM, Weiner LP, Masri L, Law RE, Apuzzo MLJ, Weiss MH: Treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas with chronic oral high-dose tamoxifen. Clin Cancer Res 2: 619–622, 1996
Shenouda G, Preul M, Iangleben A: Phase I/Il trial of high-dose tamoxifen in patients with recurrent high-grade cerebral astocytomas: the McGill University experience (meeting abstract). Proc Ann Am Soc Clin Oncol 13: A489, 1994
Farina G, Mantica C, La Verde N, Vimercati C, Galassi B, Cobelli S, Tomiotti M, Scanni A: Toxicity of long term adjuvant treatment with tamoxifen (TAM) in breast cancer (BC). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 14: 139, Abs 257, 1995
Noguchi S, Koyama H, NomuraY, Tominaga T, Abe O: Late phase II study of TAT-59 (new antiestrogen) in advanced or recurrent breast cancer patients (a double-bind comparative study with tamoxifen citrate). Breast Cancer Res Treat 50(3); Abs 446, 21st Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, 12–15 Dec 1998
Smith DC, Trump DL: A phase I trial of high-dose oral tamoxifen and CHOPE. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 36: 65–68, 1995
Pritchard KI, Paterson AHG, Fiine S, Paul NA, Zee B, Shepherd LE, Abu Z, Ragaz J, Knowling M, Levine MN et al. study-group. Randomized trial of cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil chemotherapy added to tamoxifen as adjuvant therapy in postmenopausal women with node-positive estrogen and/or progesterone receptorpositive breast cancer: A report of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 15: 2302–2311, 1997
Healey B, Tormey DC, Gray R: Arterial and venous thrombotic events in ECOG adjuvant breast cancer trials. ProcAm Soc Clin Oncol 6: 54, Abstr 208, 1987
Fornander T, Rutqvist LE, Cedermark B, Glas U, Mattsson A, Skoog L, Somell A, Theve T, Wilking N, Askergren J: Adjuvant tamoxifen in early-stage breast cancer: effects on intercurrent morbidity and mortality. J Clin Oncol 9: 1740–1748, 1991
Enck RE, Rios CN:Tamoxifen treatment of metastatic breast cancer and antithrombin III levels. Cancer 53: 2607–2609, 1984
Jordan VC, Fritz NF, Tormey DC: Long-term adjuvant therapy with tamoxifen: effects on sex hormone binding globulin and antithrombin III. Cancer Res 47: 4517–4519, 1987
Auger MJ, Mackie MJ: Effects of tamoxifen on blood coagulation. Cancer 61: 1316–1319, 1988
Bertelli G, Pronzato P, Amoroso D, CusimanoMP, Conte PF, Montagna G, Bertolini S, Rosso R: Adjuvant tamoxifen in primary breast cancer: influence on plasma lipids and antithrombin III levels. Breast Cancer Res Treat 12: 307–310, 1988
Thoron L and Arbit E: Hemostatic changes in patients with brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 22: 87–100, 1994
Kaiser-Kupfer MI, Lippman ME: Tamoxifen retinopathy. Cancer Treat Rep 62: 315–320, 1978
Stuart NS, Philip P, Harris AL, Tonkin K, Houlbrook S, Kirk J, Lien EA, Carmichael J: High-dose tamoxifen as an enhancer of etoposide cytotoxicity. Clinical effects and in vitro assessment in p-glycoprotein expressing cell lines. Br J Cancer 66: 833–839, 1992
Millward MJ, Lien EA, Robinson A, Cantwell BM: Highdose (480 mg per day) tamoxifen with etoposide: a study of a potential multi-drug resistance modulator. Oncology 51: 79–83, 1994
Trump DL, Smith DC, Ellis PG, Rogers MP, Schold SC, Winer EP, Panella TJ, Jordan VC, Fine RL: High-dose oral tamoxifen, a potential multidrug-resistance-reversal agent: phase I trial in combination with vinblastine. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 1811–1816, 1992
Chang SM, BarkerFG2nd, Huhn SL, NicholasMK, Page M, Rabbitt J, Prados MD: High dose oral tamoxifen and subcutaneous interferon alpha-2a for recurrent glioma. J Neuro-Oncol 37: 169–176, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Napolitano, M., Keime-Guibert, F., Monjour, A. et al. Treatment of Supratentorial Glioblastoma Multiforme with Radiotherapy and a Combination of BCNU and Tamoxifen: A Phase II Study. J Neurooncol 45, 229–235 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006390414555
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006390414555