Abstract
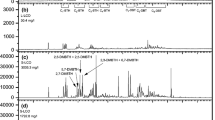
The desulfurization activity of the resting cells of Gordona sp. CYKS1 was strongly depended on harvest time and the highest value when the cells had been harvested in the early growth phase (0.12 mg sulfur g−1 cell−1 h−1). For the model oil, hexadecane containing dibenzothiophene, the specific desulfurization rate decreased as the reaction proceeded. Both the specific and the volumetric desulfurization rates were not significantly affected by the aqueous-to-oil phase ratio. The diesel oils, light gas oil and a middle distillate unit feed were desulfurized at higher rates (ca. 0.34 mg sulfur g−1 cell−1 h−1) than the model oil (0.12 mg sulfur g−1 cell−1 h−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang JH, Rhee S-K, Chang YK, Chang HN (1998) Desulfurization of diesel oils by a newly isolated dibenzothiophene-degrading Nocardia sp. strain CYKS2. Biotechnol. Progr. 14: 851–855
Denis-Larose C, Labbe D, Bergeron H, Jones AM, Greer CW, Al-Hawari J, Grossman MJ, Sankey BM, Lau PCK (1997) Conservation of plasmid-encoded dibenzothiophene desulfurization genes in several Rhodococci. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 2915–2919
Denome SA, Oldfield C, Nash LJ, Young KD (1994) Characterization of the desulfurization genes Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8 J. Bacteriol. 176: 6707–6716
Gallado ME, Fernandez A, Lorenzo VD, Garcia JL, Diaz E (1997) Designing recombinant Pseudomonas strains to enhance biodesulfurization. J. Bacteriol. 179: 7156–7160
Gallagher JR, Olson ES, Stanley DC (1993) Microbial desulfurization of dibenzothiophene: a sulfur-specific pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 107: 31–36
Izumi Y, Ohshiro T, Ogino H, Hine Y, Shimao M (1994) Selective desulfurization of Dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 223–226
Konishi J, Ishii Y, Onaka T, Okumura K, Suzuki M (1997) Thermophilic carbon-sulfur-bond-targeted biodesulfurization. App. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 3164–3169
Kropp KG, Andersson JT, Fedorak PM (1997) Bacterial transformation of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrodibenzothiophene and dibenzothiophene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 3032–3042
Lee MK, Senius HD, Grossman MJ (1995) Sulfur-specific microbial desulfurization of sterically hindered analogs of dibenzothiophene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4362–4366
Monticello DJ (1993) Biocatalytic desulfurization of petroleum and middle distillates. Environ. Progr. 12: 1–4
Nekodzuka S, Nakajimakambe T, Nomura N, Lu J, Nakahara H (1997) Specific desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Mycobacterium sp. strain G3. Biocata. Biotransf. 15: 17–27
Ohshiro TK, Hine Y, Izumi Y (1996) Regulation of dibenzothiophene degrading enzyme activity of Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 81: 121–124
Piddington CS, Kovacevich BR, Rambosek T (1995) Sequence and molecular characterization of a DNA region encoding the dibenzothiophene desulfurization operon of Rhodococcus sp. Strain IGTS8. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 468–475
Rhee S-K, Chang JH, Chang YK, Chang HN (1998) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel oils by a newly isolated Gordonastrain, CYKS2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2327–2331
Setti L, Rossi M, Lanzarini G, Pifferi PG (1992) The effect of nalkanes in the degradation of dibenzothiophene and of organic sulfur compounds in heavy oil by Pseudomonas sp. Biotechnol Lett. 14: 515–520
Setti L, Lanzarini G, Pifferi PG (1995) Dibenzothiophene biodegradation by a Pseudomonas sp. in model solutions. Process Biochem. 30: 721–728
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwan Chang, J., Keun Chang, Y., Cho, KS. et al. Desulfurization of model and diesel oils by resting cells of Gordona sp.. Biotechnology Letters 22, 193–196 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005637013879
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005637013879