Abstract
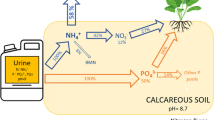
We have determined the temporal changes in the concentration of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and P and N components in soil solution following application of synthetic sheep urine (500 kg N ha-1) to a brown forest soil in boxes sown with Agrostis capillaris. Three contrasting defoliation treatments (no cutting, single cut before urine application and regular cutting twice per week) plus a fallow soil were studied. The synthetic urine contained 15N labelled urea and was P-free. Intact soil cores were taken after 2, 7, 14, 21 and 56 d and centrifuged to obtain soil solution. The urea in the synthetic urine was rapidly hydrolysed in the soil, increasing soil solution pH, DOC and total dissolved phosphorus (TDP) concentrations. For the regularly defoliated sward, DOC and P reached maximum concentrations (4000 mg DOC L-1 and 59 mg TDP L-1) on day 7. From their peak values, pH and DOC and P concentrations generally decreased with time and at day 56 were near those of the control. Concentrations of NH4 + and NO3 - in the no-urine treatments fluctuated and the greatest treatment differences were between the fallow soil and the soil sown with grass. Adding synthetic urine increased NH4 + concentrations during the first week, but NO3 - concentrations decreased. This was consistent with the 15N labelling of the NO3 - pool which required 3 weeks to reach that of 15NH4 +. Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) reached a maximum value at day 7 with a concentration of 409 mg N L-1. The DON in soil solution contained no detectable amounts of 15N label indicating that it was derived from sources in the soil. Differences in soil solution composition related to the effect of the other cutting treatments and the fallow treatment were small compared to the effect of synthetic urine addition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bramley R G V and White R E 1991 An analysis of variability in the activity of nitrifiers in a soil under pasture. I. Spatially dependent variability and optimum sampling strategy. Aust. J. Soil Res. 29, 95–108.
Bristow A W, Whitehead D C and Cockburn J E 1992 Nitrogenous constituents in the urine of cattle, sheep and goats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 59, 387–394.
Chen Y, Senesi N and Schnitzer M 1977 Information provided on humic substances by E4/E6 ratios. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 41, 352–358.
Childs E C 1969 An Introduction to the Physical Basis of SoilWater Phenomena. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, London. 493 p.
Clough T J, Ledgard S F, Sprosen M S and Kear M J 1998 Fate of 15N labelled urine on four soil types. Plant Soil 199, 195–203.
Crooke W M and Simpson W E 1971 Determination of ammonium in Kjeldahl digests of crops by an automated procedure. J. Sci. Food Agric. 22, 9–10.
Dawson L A, Grayston S J and Paterson E 2000 Effects of grazing on the roots and rhizosphere of grasses. In Grassland Ecophysiology and Grazing Ecology. Ed. G Lemaire. CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK. (In press).
De Klein C A M and Van Logtestijn R S P 1994 Denitrification and N2O emission from urine-affected grassland soil. Plant Soil 163, 235–242.
Fan M X and MacKenzie A F 1993 Interaction of urea with triple superphosphate in a simulated fertilizer band. Fert. Res. 36, 35–44.
Fraser P M, Cameron K C and Sherlock R R 1994 Lysimeter study of the fate of nitrogen in animal urine returns to irrigated pasture. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 45, 439–447.
Genstat 5 1995 Release 3.2, Lawes Agricultural Trust, Rothamsted Experimental Station, UK.
Hartikainen H and Koivunen M 1990 Mobilization of soil phosphorus as induced by urea hydrolysis. Trans. 14th Int. Congr. Soil Sci. II. pp. 204–209.
Hartikainen H and Yli-Halla M 1996 Solubility of soil phosphorus as influenced by urea. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 159, 327–332.
Haynes R J and Williams P H 1992 Changes in soil solution composition and pH in urine-affected areas of pasture. J. Soil Sci. 43, 323–334.
Haynes R J and Williams P H 1993 Nutrient cycling and soil fertility in the grazed pasture ecosystem. Adv. Agron. 49, 119–199.
Henriksen A and Selmer-Olsen A R 1970 Automatic methods for determining nitrate and nitrite in water and soil extracts. Analyst 95, 514–518.
Holland P T and During C 1977 Movement of nitrate-N and transformations of urea-N under field conditions. N.Z. J. Agric. Res. 20, 479–488.
Mawdsley J L and Bardgett R D 1997 Continuous defoliation of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) and white clover (Trifolium repens) and associated changes in the composition and activity of the microbial population of an upland grassland soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 24, 52–58.
Murphy J and Riley J P 1962 A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters Anal. Chim. Acta 27, 31–36.
Richards I R and Wolton K M 1975 A note on urine scorch caused by grazing animals. J. Brit. Grassland Soc. 30, 187–188.
Ron Vaz M D, Edwards A C, Shand C A and Cresser M 1992 Determination of dissolved organic phosphorus in soil solutions by an improved automated photo-oxidation procedure. Talanta 39, 1479–1487.
Schnitzer M 1978 Humic substances: chemistry and reactions. In Soil Organic Matter. Eds. M Schnitzer and SU Khan. pp 1–64. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam.
Schoenau J J and Bettany J R 1987 Organic matter leaching as a component of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur cycles in a forest, grassland, and gleyed soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. J. 51, 646–651.
Shand C A and Smith S 1997 Enzymatic release of phosphate from model substrates and P compounds in soil solution from a peaty podzol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 24, 183–187.
Somda Z C, Powell J M and Bationo A 1997 Soil pH and nitrogen changes following cattle and sheep urine deposition. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 28, 1253–1268.
Sørensen P and Jensen E S 1996 The fate of fresh and stored 15Nlabelled sheep urine and urea applied to a sandy and a sandy loam soil using different application strategies. Plant Soil 183, 213–220.
Thomas R J, Logan K A B, Ironside A D and Bolton G R 1988 Transformations and fate of sheep urine-N applied to an upland U.K. pasture at different times during the growing season. Plant Soil 107, 173–181.
Thompson R B and Fillery I R P 1998 Fate of urea nitrogen in sheep urine applied to soil at different times of the year in the pasturewheat rotation in south Western Australia. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 49, 495–510.
Williams B, Silcock D and Young M 1999a Seasonal dynamics of N in two Sphagnum moss species and the underlying peat treated with 15NH4 15NO3. Biogeochem. 45, 285–302.
Williams B L, Shand C A, Hill M, O'Hara C, Smith S and Young M E 1995 A procedure for the simultaneous oxidation of total soluble nitrogen and phosphorus in extracts of fresh and fumigated soils and litters. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 26, 91–106.
Williams B L, Shand C A, Sellers S and Young ME 1999b Impact of synthetic sheep urine on N and P in two pastures in the Scottish uplands. Plant Soil 214, 93–103.
Williams P H, Jarvis S C and Dixon E 1998 Emission of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide from soil under field and laboratory conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 30, 1885–1893.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shand, C., Williams, B., Smith, S. et al. Temporal changes in C, P and N concentrations in soil solution following application of synthetic sheep urine to a soil under grass. Plant and Soil 222, 1–13 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004799323646
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004799323646