Abstract
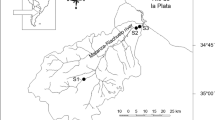
Cu, Cr, Pb, Zn and Fe in water, sediment and tissue of the emergent macrophyte Schoenoplectus californicus were studied in three coastal environments differing in aquatic chemistry and tide amplitude: a deltaic floodplain marsh, a coastal vegetated strip of the river and a tidal marsh at the south margin of the Río de la Plata Estuary. Metal content in water was not significantly different between the river and the floodplain marsh. Metal content in sediments showed higher values in the marshes than in the river, suggesting a retention in the marsh. Except for Cu, the highest metal content in sediments and water was observed in the tidal marsh. Pb in plants was undetectable. Metal content was higher in rhizomes, except Cr, which was mainly stored in stems. Rhizome metal content was higher in the river, probably related to the higher redox potential of its sediments. Inflorescence metal content was higher in the marshes: the highest Zn, Cr and Fe contents were measured in the tidal marsh; the highest Cu content was in the floodplain marsh, together with the highest organic matter content of the sediments. Zn, Cr and Fe increased in standing drying stems and in inflorescences in late fall. Inflorescences showed the highest metal content after seeds had been released.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, 1985. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water.Amer. Publ. Health Assoc., Washington, 1268 pp. 195
Baudo, R., E. Canziani, G. Galanti, P. Guilizzoni & G. Rapetti, 1985. Relationships between heavy metals and aquatic organisms in lake Messola hydrographic system, (Northern Italy). 6. Metal concentrations in two species of emergent macrophytes. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 43: 161–180.
Bettinelli, M., U. Baroni & N. Pastorelli, 1989. Determinazione diretta di elementi in traccia in matrici ambientali mediante imprego dell+ ETA-AAS Zeeman e midificazione di matrice. In Minoia, C. & S. Caroli (eds), Applicazioni dell'ETA-AAS Zeeman nel laboratorio chimico e tossicologico. Eddizioni Libreria Cortina, Padova (Vol. 1): 49–81.
Bonetto, C., L. de Cabo, N. Gabellone, A. Vinocur, J. Donadelli & F. Unrein, 1994. Nutrient dynamics in the deltaic floodplain of the Lower Paraná River. Arch. Hydrobiol. 131: 277–295.
Bryan, G.W. & W. J. Langston, 1992. Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: a review. Envir. Pollut. 76: 89–131.
Comish, M. F. & J. H. Ong, 1988. Trace metals. In Bodeck, I., J. W. Lyman, W. F. Rechl & D. Rosemblat (eds), Environmental Inorganic Chemistry. Pergamon Press, New York: 7.0/1–7.15/11.
D'Angelo, E.M. & K. R. Reddy, 1994. Diagenesis of organic matter in a wetland receiving hypereutrophic Lake Water: II. Role of inorganic electron acceptors in nutrient release. J. envir. Qual. 23: 937–943.
Gambrell, R. P., 1994. Trace and toxic metals in Wetlands - A Review. J. envir. Qual., 23: 883–891.
Gambrell, R. P., J. B. Wiesepape, W. H. Patrick & M. D. Duff, 1991. The effects of pH, redox, and salinity on metal release from a contaminated sediment. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 57–58: 359–367.
Jackson, L., J. Rasmussen, R. Peters & J. Kalff, 1991. Empirical relationships between the element composition of aquatic macrophytes and their underlying sediments. Biogeochemistry 12: 71–86.
Jackson, L., J. Kalff & R. Rasmussen, 1993. Sediment pH and redox potential affect the bioavailability of Al, Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn to rooted aquatic macrophytes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 50: 143- 148.
Mackereth, F., J. Heron & J. Talling, 1978. Water analysis: some revised methods for limnologists. Freshwater Biol. Assoc. Cd. Pub. No 36, 120 pp.
Masscheleyn, P., J. Pardue, R. DeLaune & W. H. Patrick, 1992.Chromium redox chemistry in a Lower Mississippi Valley Bottomland hardwood wetland. Envir. Sci. Technol. 26: 1217–1226.
Otte, M. L., S. J. Bestebroer, J. M. van der Linden, J. Rozema & R. A. Broekman, 1991. A survey of Zinc, Copper and Cadmium concentrations in salt marsh plants along the Dutch Coast. Envir. Pollut. 72: 175–189.
Otte, M. L., M. Haarsma, R. Broekman & J. Rozema, 1993. Relation between heavy metal concentrations in salt marsh plants and soil. Envir. Pollut. 82: 13–22.
Reddy, K. R., W. H. Patrick & C. Lindau, 1989. Nitrificationdenitrification at the plant root-sediment interface in wetlands. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 1004–1013.
Schecher, W. & D. McAvoy, 1991. MINEQL: a chemical equilibrium program for personal computers. Environmental Research Software, Edgewater.
SHN, 1996. Tablas de marea. Separata zona Río de la Plata. Servicio de Hidrografía Naval. Buenos Aires, 86 pp.
Sokal, R. & F. J. Rohlf, 1981. Introducción a la bioestadística. Reverté, Barcelona, 362 pp.
Statistica, 1993. Statistica for windows. Release 4.3. Copyright Statsoft Inc.
Strickland, J. & T. Parsons, 1972. A practical Handbook for seawater analysis. Bull. 167. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. Ottawa, 311 pp.
Villar, C., L. de Cabo & C. Bonetto, 1996. Macrophytic primary production and nutrient concentrations in a deltaic floodplain marsh of the Lower Paraná River. Hydrobiologia 330: 59–66.
Villar, C., M. Tudino, C. Bonetto, L. de Cabo, J. Stripeikis, L. d'Huicque & O. Troccoli, 1998. Heavy metals concentration in the Lower Paraná River and right margin of the Río de la Plata Estuary. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 26: 963–966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villar, C., Stripeikis, J., Tudino, M. et al. Trace metal concentrations in coastal marshes of the Lower Paraná River and the Río de la Plata Estuary. Hydrobiologia 397, 187–195 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003730306880
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003730306880