Abstract
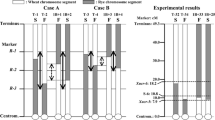
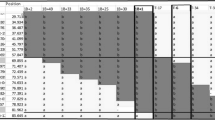
By crossing Aegilops mutica with Triticum dicoccum as a bridge species and backcrossing with common wheat as a recurrent pollen parent, male sterile alloplasmic line(s) were produced. In progeny of the crosses, a self fertile plant with 42 chromosomes was selected and named R 20. From this plant several lines that possessed Rf (fertility restoring) genes and/or powdery mildew resistant genes were obtained. Apparently, the system of sterility-fertility of pollen can be applied for hybrid wheat production. In addition, the disease resistance may be used in breeding. The male fertile lines possessed one or more Ae. mutica sat-chromosome(s), which show the ability to suppress the nucleolar organizing regions of chromosomes 1B and 6B of common wheat. The relation between the sat-chromosomes and male fertility restoration is not yet clear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kimber G. & K. Tsunewaki, 1988. Genome symbols and plasma types in the wheat group. Proc. 7th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Cambridge: 1209–1211.
Maan S.S., 1991. Nucleo-cytoplasmic genetics of wheat. Proc. ISCEW 'Nuclear and organellar genomes of wheat species', T. Sasakuma, T. Kinoshita (eds.), Yokohama, Japan: 175–194.
Navashin M.C., 1928. Amphiplastie-eine neue karyologische Erscheinung. Z.F.A.V. (Suppl.), in: R. Rieger, A. Mihaeles, 1958. Genetisches und Cytogenetisches Wörterbuch). 2: 1148
Ohta S., 1991. Phylogenetic relationship of Aegilops mutica Boiss. with the diploid species of concerning Aegilops-Triticum complex, based on the new method of genome analysis using its B-chromosomes. Memoirs of the College of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Japan 137: 116.
Panayotov I., 1980. New cytoplasmic male sterility in common wheat: their genetical and breeding considerations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 56:153–160.
Panayotov I., 1983. The cytoplasm in Triticinae. Proc. 6th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Kyoto: 481–497.
Panayotov I., 1991. The cytoplasm of Triticinae and wheat improvement. Proc. ISCEW "Nuclear and Organellar Genomes of Wheat Species", T. Sasakuma, T. Kinoshita (Eds.), Yokohama, Japan: 280–293.
Panayotov I., D. Gotsova, M. Savov, 1988. Chromosome location of Rf genes for Ae. mutica and Triticum timopheevi cytoplasms. Proc. 7th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Cambridge: 609–613.
Terachi T., 1991. Molecular evolution of mitochondrial genomes in Triticum and Aegilops. Proc. ISCEW "Nuclear and Organellar Genomes of Wheat Species", T. Sasaskuma, T. Kinoshita (Eds.), Yokohama, Japan: 123–130.
Tsunewaki K., 1991. A historical review of cytoplasmic studies in wheat. Proc. ISCEW "Nuclear and Organellar Genomes of Wheat Species", T. Sasakuma, T. Kinoshita (Eds.), Yokohama, Japan: 16–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panayotov, I., Tsujimoto, H. Fertility restoration and nor suppression caused by Aegilops mutica chromosomes in alloplasmic hybrids and lines. Euphytica 94, 145–149 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002955305001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002955305001