Abstract
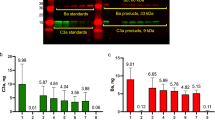
We have examined complement receptors on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and found that they express complement receptor 1 (CR1, CD35) and complement receptor 4 (CR4, CD11c/CD18), but not complement receptor 3 (CR3, CD11b/CD18). Binding of monoclonal antibodies against CR1 (CD35) and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) to HUVEC was demonstrated by flow cytometry. The presence of the corresponding mRNAs was confirmed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and sequencing of the amplified cDNA fragments. When HUVEC were treated with inflammatory mediators, chemotactic agents or the secretagogue phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), no change in reactivity to CR1 (CD35) or CR4 (CD11c/CD18) monoclonal antibodies was detected on the surface of the cells compared with untreated cells. The presence of CR1 (CD35) and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) on HUVEC indicates that endothelial cells (EC) have the potential to bind C3b and iC3b, respectively, which both mediate biological effects in the course of complement activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gulati, P., C. Lemercier, D. Guc, D. Lappin, and K. Whaley. 1993.Regulation of the synthesis of C1 subcomponents and C1-inhibitor.Behring Inst. Mitt. 93:196–203.
Brooimans, R. A., P. S. Hiemstra, A. A. J. Van der Ark, R. B. Sims, and M. R. Daha. 1989. Biosynthesis of complement factor H by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Regulation by T cell growth and IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 142:2024–2030.
Julen, N., H. Dauchel, C. Lemercier, R. B. Sims, M. Fontaine, and J. Ripoche. 1992. In vitro biosynthesis of complement factor I by human endothelial cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 22:213–217.
Berge, V., E. Johnson, K. Hogåsen, and G. Hetland. 1992. Human umbilical vein cells synthesize S-protein (vitronectin) in vitro.Scand. J. Immunol. 36:119–123.
Berge, V., E. Johnson, and K. Hogåsen. 1997. Clusterin and the terminal complement pathway synthesized by human umbilical vein endothelial cells are closely linked when detected on co-cultured agarose beads. APMIS 105:17–24.
Asch, A. S., T. Kinoshita, E. A. Jaffe, and V. Nussenzweig. 1986.Decay-accelerating factor is present on cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 163:221–226.
McNerney, T., L. Ballard, T. Seya, and J. P. Atkinson. 1989.Membrane cofactor protein of complement is present on human fibroblast, epithelial, and endothelial cells.J. Clin. Invest. 84:538–545.
Hamilton, K. K., Z. Ji, S. Rollins, B. H. Stewart, and P. J. Sims. 1990. Regulatory control of the terminal complement proteins at the surface of human endothelial cells: neutralization of a C5-9 inhibitor to antibody to CD 59. Blood 76:2572–2577.
Foreman, K. E., A. A. Vaporciyan, B. K. Bonish, M. L. Jones, K, J. Johnson, M. M. Glovsky, S. M. Eddy, and P. A. Ward. 1994. C5a-induced expression of P-selectin in endothelial cells. J. Clin.Invest. 94:1147–1155.
Andrews, B. S., M. Shadforth, P. Cunningham, and J. S. Davis IV. 1981. Demonstration of a Clq receptor on the surface of human endothelial cells. J. Immunol. 127(3):1075–1080.
Daha, M. R., A. M. M. Miltenburg, P. S. Hiemstra, N. Klar-Mohammed, L. A. van Es, and V. W. M. van Hinsbergh. 1988. The complement subcomponent Clq mediates binding of immune complexes and aggregates to endothelial cells in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 18(5):783–787.
Lozada, C., R. I. Levin, M. Huie, R. Hirschhorn, D. Naime, M. Whitlow, P. A. Recht, B. Golden, and B. N. Cronstein. 1995.Identification of Clq as the heat-labile serum cofactor required for immune complexes to stimulate endothelial expression of the adhesion molecules E-selectin and intercellular and vascular cell adhesion molecules 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 92:8378–8382.
Fearon, D. T. 1979. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 76:5867–5871.
Cornacoff, J. B., L. A. Hebert, W. L. Smead, M. E. Vanamann, D. J. Birmingham, and F. J. Waxman. 1983. Primate erythrocyte immune complex clearing mechanism. J. Clin. Invest. 71:236–241.
Ahearn, J. M. and D. T. Fearon. 1989. Structure and function of the complement receptors CR1 (CD35) and CR2 (CD21). Adv.Immunol. 46:183–219.
Klickstein, L. B., S. F. Barbashov, T. Liu, R. M. Jack, and A. Nicholson-Weller. 1997. Complement receptor type 1 (CR1, CD35) is a receptor for Clq. Immunity 7:345–355.
Ghiran, I., S. F. Barbashov, L. B. Klickstein, S. W. Tas, J. C. Jensenius, and A. Nicholson-Weller. 2000. Complement receptor 1/CD35 is a receptor for mannan-binding lectin. J. Exp. Med. 192(12):1797–1807.
Arnaout, M. A. 1990. Structure and function of the leukocyte adhesion molecules CD11/CD18. Blood 75:1037–1050.
Hynes, R. O. 1992. Integrins: versatility, modulation and signalling in cell adhesion. Cell. 69:11–25.
Myones, B. L., J. G. Dalzell, N. Hogg, and G. D. Ross. 1988.Neutrophil and monocyte cell surface p150,95 has iC3b-receptor (CR4) activity resembling CR3. J. Clin. Invest. 82:640–651.
Mantovani, A., S. Sozzani, A. Vecchi, M. Introna, and P. Allavena. 1997. Cytokine activation of endothelial cells: New Molecules for an old paradigm. Thrombosis and Heaemostasis 78:406–414.
Dauchel, H., N. Julen, C Lemercier, M. Daveau, D. Ozanne, M. Fontaine and J. Ripoche. 1990. Expression of complement alternative pathway proteins by endothelial cells. Differential regulation by interleukin-1 and glucocorticoids. Eur. J. Immunol. 20:1669–1675.
Wilson, M. E. and D. C. Morrison. 1982. Evidence for different requirements in physical state for the interacation of lipopolysaccharides with the classical and alternative pathways of complement.Eur. J. Biochem. 128:137–141.
Collard, C. D., C. Bukusoglu, A. Agah, S. P. Colgan, W. R. Reenstra, B. P. Morgan, and G. L. Stahl. 1999. Hypoxia-induced expression of complement receptor type 1 (CR1, CD35) in human vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 276:C450–C458.
Delibrias, C., E. Fischer, and M. D. Kazatchkine. 1998. Receptors for Human C3 fragments. In: The complement system. Rother, G.O. Till, and G. M. Hansch, eds: Heidelberg, pp. 211–220.
Jaffe, E. A., R. L. Nachman, and C. G. Becker. 1973. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphological and immunological criteria. J. Clin. Invest. 52:2745–2752.
Jakobsen, K. S., M. Haugen, S. Sæbøe-Larssen, K. Hollung, M. Espelund, and E. Hornes. 1994. Direct mRNA isolation using magnetic oligo (dT) beads: A protocol for all types of cell cultures, animal, and plant tissues. In: Advances in biomagnetic separation.Uhlen, M, E. Hornes, and Ø. Olsvik, eds: Eaton Publishing: pp. 61–71.
Hourcade, D., D. R. Miesner, J. P. Atkison, and V. M. Holers. 1988. Identification of an alternative polyadenylation site in the human C3b/C4b receptor (complement receptor type 1) transcriptional unit and prediction of a secreted form of complement receptor type 1. J. Exp. Med. 68:1255–1270.
Corbi, A. L., L. J. Miller, K. O'Connor, R. S. Larson, and T. Springer. 1987. cDNA cloning and complete primary structure of Langeggen, Berge, Johnson, and Hetland 110 the alpha subunit of a leukocyte adhesion glycoprotein, p150, 95.EMBO J. 6:4023–4028.
Cui, Y. C., P. C. Tai, K. C. Gatter, D. Y. Mason, and C. J. Spry. 1983. A vascular endothelial cell antigen with restricted distribution in human fetal, adult and malignant tissues. Immunol. 49:183–189.
Vermot-Desroches, C., D. Marchand, C. Roy, and J. Wijdenes. 1995. Heterogeneity of antigen expression among human umbilical cord vascular endothelial cell: identification of cell subsets by co-expression of haemopoietic antigens. Immunology Letters. 48:1–9.
Vita, N., S. Lefort, P. Sozzani, R. Reeb, S. Richards, L. K. Borysiewicz, P. Ferrara and M. O. Labeta. 1997. Detection and biochemical characteristics of the receptor for complexes of soluble CD14 and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 158:3457–3462.
Junghans, R. P. and C. L. Anderson. 1996. The protection receptor for IgG catabolism is the β 2-microglobulin-containing neonatal intestinal transport receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93(11):5512–5516.
Ryan, U. S., D. R. Schultz and J. W. Ryan. 1981. Fc and C3b receptors on pulmonary endothelial cells: induction by injury. Science. 214:557–558.
Cines, D. B., A. B. Lyss, M. Bina, R. Corkey, N. A. Kefalides, and H. M. Friedman. 1982. Fc and C3 receptors induced by herpes simplex virus on cultured human endothelial cells. J. Clin. Invest. 69:123–128.
Groger, M., G. Sarmay, E. Fiebiger, K. Wolff, and P. Petzelbauer. 1996. Dermal microvascular endothelial cells express CD32 receptors in vivo and in vitro. J. Immunol. 156:1549–1556.
Pascual, M., C. Daniellson, G. Steiger, and J. A. Schifferli. 1994. Proteolytic cleavage of CR1 on human erythrocytes in vivo: evidence for enhanced cleavage in AIDS. Eur. J. Immunol. 24:702–708.
Fleming, S. and D. B. Jones. 1989. Antigenic heterogeneity of renal endothelium. J. Pathol. 158:319–323.
Golenbock, D. T., R. R. Bach, H. Lichenstein, T. S. Juan, A. Thadavarthy, and C. F. Moldow. 1995. Soluble CD14 promotes LPS activation of CD14-deficient PNH monocytes and endothelial cells. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 125(5):662–671.
Frey, E. A., D. S. Miller, T. G. Jahr, A. Sundan, V. Bazil, T. Espevik, B. B. Finlay, and S. D. Wright. 1992. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 176(6):1665–1671.
Ingalls, R. R. and D. T. Golenbock. 1995. CD11c/CD18, a transmembrane signaling receptor for lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 181(4):1473–1479.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langeggen, H., Berge, K.E., Johnson, E. et al. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Express Complement Receptor 1 (CD35) and Complement Receptor 4 (CD11c/CD18) in vitro . Inflammation 26, 103–110 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015585530204
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015585530204