Abstract
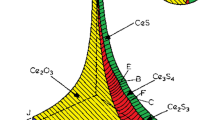
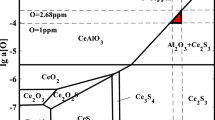
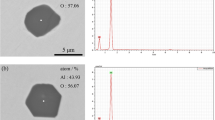
A coupled thermodynamic model of inclusions precipitation both in liquid and solid phase and microsegregation of solute elements during solidification of heat-resistant steel containing cerium was established. Then the model was validated by the SEM analysis of the industrial products. The type and amount of inclusions in solidification structure of 253MA heat-resistant steel were predicted by the model, and the valuable results for the inclusions controlling in 253MA steel were obtained. When the cerium addition increases, the types of inclusions transform from SiO2 and MnS to Ce2O3 and Ce2O2S in 253MA steel and the precipitation temperature of SiO2 and MnS decreases. The inclusions CeS and CeN convert to Ce2O3 and Ce2O2S as the oxygen content increases and Ce2O3 and CeN convert to Ce2O2S, Ce3S4, and MnS as the sulfur content increases. The formation temperature of SiO2 increases when the oxygen content increases and the MnS precipitation temperature increases when the sulfur content increases. There is only a small quantity of inclusions containing cerium in 253MA steel with high cleanliness, i. e., low oxygen and sulfur contents. By contrast, a mass of SiO2, MnS and Ce2O2S are formed in steel when the oxygen and sulfur contents are high enough. The condition that MnS precipitates in 253MA steel is 1. 2w[O] + w[S] > 0.01 % and SiO2 precipitates when 2w[O] + w[S] > 0. 017% (w[S] < 0.005%) and w[O] > 0.006% (w[S] > 0.005%).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- fi:
-
Activity coefficient
- e ji :
-
First-order interaction parameter
- γ ji , γ j,ki :
-
Second-order interaction parameters
- w[Cj], w[Ck]:
-
Mass fraction of components j and k, standard state
- CL:
-
Solute concentration in liquid, standard state
- CS:
-
Solute concentration in solid, standard state
- C[C]:
-
Concentration of carbon, standard state
- C0:
-
Solute concentration in each step, standard state
- C0(total):
-
Total solute concentration, standard state
- C0(inclusions):
-
Solute concentration in inclusions, standard state
- ΔGθ:
-
Standard Gibbs free energy
- ΔG:
-
Gibbs free energy
- A, B:
-
Constants for describing Gibbs free energy
- R:
-
Ideal gas constant, J/(mol • K)
- T:
-
Temperature, K
- TL, TS:
-
Temperature of liquidus and solidus, K
- Tstart, Tend:
-
Temperature of start and end of calculation, K
- DS:
-
Diffusion coefficient, m2/s
- α:
-
A constant related to the secondary dendrite arm space
- α′:
-
Revised α
- τ:
-
Distribution coefficient
- τγ/L:
-
Distribution coefficient between austenite phase and liquid phase
- D γS :
-
Diffusion coefficient in austenite phase
- fS:
-
Solid fraction
- λ:
-
Secondary dendrite arm space, m
- Φ:
-
Solidification rate, K/s
- tS:
-
Local solidification time, s
References
Y. K. Yao, M. W. Zhu, D. Y. Wang, C. J. Liu, M. F. Jiang, Chinese Rare Earth 25 (2004) No. 5, 17–19.
S. C. Zhao, F. Y. Shen, Q. Y. Han, G. L. Shao, Iron and Steel 17 (1982) No. 3, 24–31.
Z. S. Yu, W. Z. Zhao, Y. F. Xie, Q. H. Yu, Iron and Steel 19 (1984) No. 3, 18–24.
N. Kojola, S. Ekerot, M. Andersson, P. G. Jönsson, Ironmak. Steelmak. 38 (2011) 1–11.
I. H. Jung, S. A Decterov, A. D. Pelton, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 35 (2004) 493–507.
S. Choudhary, A. Ghosh, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 1819–1827.
Z. Z. Liu, K. J. Gu, K. K. Cai, ISIJ Int. 42 (2002) 950–957.
H. Q. Zhang, S. B. Zheng, Q. Zheng, Z. L. Liu, G. C. Jiang, Acta Metall. Sin. 42 (2006) 745–750.
C. J. Liu, L. Fang, Y. S Wang, M. F. Jiang, J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 28 (2007) 1410–1413.
R. J. Fruehan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 10 (1979) 143–148.
A. Vahed, D. Kay, Mater. Trans. B 7 (1976) 375–383.
V. R. Kalakota, Sulfur Removal Using Regenerahle Sorhents of Rare Earth/Transition Metal Oxides, Andhra University, Baton Rouge, 2008.
H. C. Wang, Y. C. Dong, Measurement and Calculation Methods of Metallurgical Thermodynamic Data, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2005.
N. Toker, L. Darken, A. Muan, Mater. Trans. B 22 (1991) 689–703.
S. Luo, M. Y. Zhu, C. Cai, Z. Z. Cai, Iron and Steel 45 (2010) No. 6, 31–36.
E. B. Yue, S. T. Chou, Y. Gan, J. Iron Steel Res. 18 (2006) No. 8, 49–52.
M. C. Zhang, S. D. Li, Q. Y. Zhang, J. P. Zhang, Journal Anhui University of Technology 29 (2012) 207–210.
G. B. Tang, X. Y. Wu, X. Yong, A. M. Bai, Z. D. Liu, Q. L. Yong, Heat Treatment Metals 33 (2008) No. 8, 67–72.
T. Clyne, W. Kurz, Mater. Trans. A 12 (1981) 965–971.
X. Y. Zhong, H. Q. Hu, C. M. Liu, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing (1984) No. 3, 16–21.
M. Wolf, Metall. Plant Technol. (1983) No. 2, 46–59.
R. Diederichs, W. Bleck, Steel Res. Int. 77 (2006) 202–209.
Y. M. Won, B. G. Thomas, Mater. Trans. A 32 (2001) 1755–1767.
A. C. Tas, M. Akinc, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76 (1993) 1595–1601.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Key Basic Research Program of China (2012CB626812); National Natural Science Foundation of China (51104039); Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Ministry of Education of China (NCET-11-0077)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yd., Liu, Cj., Li, Cl. et al. A coupled thermodynamic model for prediction of inclusions precipitation during solidification of heat-resistant steel containing cerium. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22, 457–463 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30027-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30027-3