Abstract
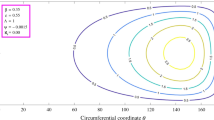
The lubrication mechanism and the performance parameters with consideration of wall slip and inertial force are studied in this paper. Based on the modified Reynolds equation, the finite difference method is used to study the lubrication mechanism and the performance. Effects of the wall slip and the inertial force on the performance parameters are obtained, and found in good agreement with the results of FLUENT. It is shown that the wall slip and the inertial force do not significantly change the distribution of the pressure, the load capacity and the friction force. The inertial force slightly increases the pressure and the load capacity by 1.2% and 4.8%, while the wall slip reduces them by 8.0% and 17.85%. The wall slip and the inertial force increase the friction by about 15.98%, 2.33%, respectively. Compared with the wall slip, the inertial force is smaller, but cannot be neglected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalin M., Polajnar M. The Effect of wetting and surface energy on the friction and slip in oil-lubricated contacts [J]. Tribology letter, 2013, 52(2): 185–194.
Neto C., Evans D. R., Bonaccurso E. et al. Boundary slip in Newtonian liquids: A review of experimental studies [J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2005, 68(12): 28–59.
Spikes H. A. The half-wetted bearing. Part 1: Extended Reynolds equation [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2003, 217(1): 1–14.
Spikes H. A. The half-wetted bearing. Part 2: Potential application in low load contacts [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology, 2003, 217(1): 15–26.
Spikes H., Granick S. Equation for slip of simple liquids at smooth solid surfaces [J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(12): 5065–5071.
Ma G. J., Wu C. W., Zhou P. Wall slip and hydrodynamics of two-dimensional journal bearing [J]. Tribology International, 2007, 40(7): 1056–1066.
Ma G. J., Wu C. W., Zhou P. Influence of wall slip on the hydrodynamic behavior of a two-dimensional slider bearing [J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2007, 23(6): 655–661.
Fortier A. E., Salant R. F. Numerical analysis of a journal bearing with a heterogeneous slip/no-slip surface [J]. Journal of Tribology, 2005, 127(4): 820–825.
Salant R. F., Fortier A. E. Numerical analysis of a slider bearing with a heterogeneous slip/no-slip surface [J]. Tribology Transaction, 2004, 47(3): 328–334.
Wang L. L., Lu C. H., Wang M. The numerical analysis of the radial sleeve bearing with combined surface slip [J]. Tribology International, 2012, 47: 100–104.
Wu C. W., Wu C. D., Ma G. J. Low friction and high load support capacity of slider bearing with a mixed slip surface [J]. Journal of Tribology, 2006, 128(4): 904–907.
Szeri A. Z. Fluid film lubrication: Theory and design [M]. New York, USA: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
Guo F., Wong P, Geng M. Occurrence of wall slip in ela-stohydrodynamic lubrication contacts [J]. Tribology Letter, 2009, 34(2): 103–111.
Wu C. W. Performance of hydrodynamic lubrication journal bearing with a slippage surface [J]. Industrial Lubrication Tribology, 2008, 60(6): 293–298.
Aurelian F., Patrick M., Mohamed H. Wall slip effects in (elasto) hydrodynamic journal bearings [J]. Tribology Intertational, 2011, 44(7): 868–877.
Hatzikiriakos S., Dealy J. Wall slip of molten high density polyethylene. I. Sliding plate rheometer studies [J]. Journal of Rheology, 1991, 35(4): 497–523.
Xie Z., Rao Z., Ta N. et al. Investigations on transitions of lubrication states for water lubricated bearing. Part I: Determination of friction coefficient and film thickness ratios [J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2016, 68(3): 404–415.
Xie Z., Rao Z., Ta N. et al. Investigations on transitions of lubrication states for water lubricated bearing. Part II: Further insight into the film thickness ratio lambda [J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2016, 68(3): 416–429.
Xie Z., Rao Z., Ta N. et al. Theoretical and experimental research on the friction coefficient of water lubricated bearing with consideration of wall slip effects [J]. Mechanics and Industry, 2016, 17(1): 106–119.
Yang J. Sharp interface direct forcing immersed boundary methods: A summary of some algorithms and applications [J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2016, 28(5): 713–730.
Zhang X., Yin Z., Gao G. et al. Determination of stiffness coefficient of hydrodynamic water-lubricated plain journal bearings [J]. Tribology International, 2015, 85: 37–47.
Illner T., Bartel D., Deters L. Determination of the transition speed in journal bearing consideration of bearing deformation [J]. Tribology Internaional, 2015, 82: 58–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
iography: Zhong-liang Xie (1988-), Male, Ph. D. Candidate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Zl., Ta, N. & Rao, Zs. The lubrication performance of water lubricated bearing with consideration of wall slip and inertial force. J Hydrodyn 29, 52–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60716-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60716-3