Abstract
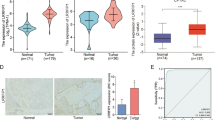
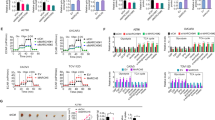
Asparagine-linked glycosylation protein 1 homolog (ALG1) participates in the initial stage of protein N-glycosylation and N-glycosylation has been implicated in the process of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression. However, whether ALG1 plays a role in human HCC remains unknown. In this study, the expression profile of ALG1 in tumorous and corresponding adjacent non-tumor tissues was analyzed. The relationship of ALG1 expression with clinical features and prognosis of HCC patients was also evaluated using immuno-histochemical method. Here we found ALG1 decreased in HCC tissues compared with adjacent normal liver tissues, which predicted an unfavorable prognosis. Combined with RNA interference, nascent proteome and glycoproteome were determined systematically in Huh7 cell line. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the differentially expressed proteins participating in the response of ALG1 knockdown were most significantly associated with cell–cell adhesion. Functional studies confirmed that knockdown of ALG1 reduced cell adhesion capacity, and promoted cell migration. Furthermore, down-regulation of H8N2 (on N-glycosite N651) and H5N4S2F1 (on N-glycosite N692) from N-cadherin was identified as a feature of ALG1 knockdown. Our findings revealed that ALG1 controlled the expression of glycosylated N-cadherin and played a role in HCC migration, with implications for prognosis.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Partial mass spectrometric data and analyzed result datasets have been deposited in iProX (http://www.iprox.org), which is an official member of ProteomeXchange Consortium. The project ID is IPX0003587000.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ALG1:
-
Asparagine-linked glycosylation protein 1 homolog
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- CDG:
-
Congenital disorders of glycosylation
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- siRNA:
-
Small interfereing RNA
- AHA:
-
Azidohomoalanine
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- BP:
-
Biological process
- H:
-
Hexose
- N :
-
N-Acetylhexosamine
- S:
-
Sialic acid
- F:
-
Fucose
References
Asano K, Duntsch CD, Zhou Q, Weimar JD, Bordelon D, Robertson JH, Pourmotabbed T (2004) Correlation of N-cadherin expression in high grade gliomas with tissue invasion. J Neurooncol 70:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:neon.0000040811.14908.f2
Asano K, Kubo O, Tajika Y, Huang MC, Takakura K, Ebina K, Suzuki S (1997) Expression and role of cadherins in astrocytic tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol 14:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478865
Bargellini I, Battaglia V, Bozzi E, Lauretti DL, Lorenzoni G, Bartolozzi C (2014) Radiological diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 1:137–148. https://doi.org/10.2147/JHC.S44379
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Cao X, Cao Z, Shao Y, Liu C, Yan G, Meng X, Zhang L, Chen C, Huang G, Shu H, Lu H (2021) Analysis of serum paraoxonase 1 using mass spectrometry and lectin immunoassay in patients with alpha-fetoprotein negative hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:651421. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.651421
Dieterich DC, Lee JJ, Link AJ, Graumann J, Tirrell DA, Schuman EM (2007) Labeling, detection and identification of newly synthesized proteomes with bioorthogonal non-canonical amino-acid tagging. Nat Protoc 2:532–540. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.52
Duan F, Wu H, Jia D, Wu W, Ren S, Wang L, Song S, Guo X, Liu F, Ruan Y, Gu J (2018) O-GlcNAcylation of RACK1 promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis. J Hepatol 68:1191–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.02.003
Gao XD, Nishikawa A, Dean N (2004) Physical interactions between the Alg1, Alg2, and Alg11 mannosyltransferases of the endoplasmic reticulum. Glycobiology 14:559–570. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwh072
Hu X, Chen R, Wei Q, Xu X (2022) The Landscape of alpha fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma: Where are we? Int J Biol Sci 18:536–551. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64537
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4:44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Lee SK, Li G, Yu SL, Alexander H, Alexander S (1997) The Dictyostelium discoideum beta-1,4-mannosyltransferase gene, mntA, has two periods of developmental expression. Gene 204:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00553-2
Li ST, Wang N, Xu S, Yin J, Nakanishi H, Dean N, Gao XD (2017) Quantitative study of yeast Alg1 beta-1, 4 mannosyltransferase activity, a key enzyme involved in protein N-glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1861:2934–2941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.09.023
Lipinski P, Bogdanska A, Socha P, Tylki-Szymanska A (2021) Liver involvement in congenital disorders of glycosylation and deglycosylation. Front Pediatr 9:696918. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.696918
Liu C, Song CQ, Yuan ZF, Fu Y, Chi H, Wang LH, Fan SB, Zhang K, Zeng WF, He SM et al (2014) pQuant improves quantitation by keeping out interfering signals and evaluating the accuracy of calculated ratios. Anal Chem 86:5286–5294. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac404246w
Liwosz A, Lei T, Kukuruzinska MA (2006) N-glycosylation affects the molecular organization and stability of E-cadherin junctions. J Biol Chem 281:23138–23149. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512621200
Lombard J (2016) The multiple evolutionary origins of the eukaryotic N-glycosylation pathway. Biol Direct 11:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13062-016-0137-2
Ma Y, McClatchy DB, Barkallah S, Wood WW, Yates JR 3rd (2017) HILAQ: A novel strategy for newly synthesized protein quantification. J Proteome Res 16:2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00005
Ma Y, McClatchy DB, Barkallah S, Wood WW, Yates JR 3rd (2018) Quantitative analysis of newly synthesized proteins. Nat Protoc 13:1744–1762. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-018-0012-y
Marques-da-Silva D, Dos Reis FV, Monticelli M, Janeiro P, Videira PA, Witters P, Jaeken J, Cassiman D (2017) Liver involvement in congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG). A systematic review of the literature. J Inherit Metab Dis 40:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-016-0012-4
McClatchy DB, Ma Y, Liem DA, Ng DCM, Ping P, Yates JR 3rd (2018) Quantitative temporal analysis of protein dynamics in cardiac remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 121:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.07.126
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL, El-Serag HB (2021) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 73(Suppl 1):4–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31288
Natu A, Singh A, Gupta S (2021) Hepatocellular carcinoma: understanding molecular mechanisms for defining potential clinical modalities. World J Hepatol 13:1568–1583. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1568
Ng BG, Shiryaev SA, Rymen D, Eklund EA, Raymond K, Kircher M, Abdenur JE, Alehan F, Midro AT, Bamshad MJ et al (2016) ALG1-CDG: clinical and molecular characterization of 39 unreported patients. Hum Mutat 37:653–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22983
Noor SI, Hoffmann M, Rinis N, Bartels MF, Winterhalter PR, Hoelscher C, Hennig R, Himmelreich N, Thiel C, Ruppert T et al (2021) Glycosyltransferase POMGNT1 deficiency strengthens N-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 296:100433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100433
Ramirez AS, Boilevin J, Lin CW, Ha Gan B, Janser D, Aebi M, Darbre T, Reymond JL, Locher KP (2017) Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of lipid-linked GlcNAc2Man5 oligosaccharides using recombinant Alg1, Alg2 and Alg11 proteins. Glycobiology 27:726–733. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwx045
Rexer TFT, Schildbach A, Klapproth J, Schierhorn A, Mahour R, Pietzsch M, Rapp E, Reichl U (2018) One pot synthesis of GDP-mannose by a multi-enzyme cascade for enzymatic assembly of lipid-linked oligosaccharides. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26454
Rohlfing AK, Rust S, Reunert J, Tirre M, Du Chesne I, Wemhoff S, Meinhardt F, Hartmann H, Das AM, Marquardt T (2014) ALG1-CDG: a new case with early fatal outcome. Gene 534:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.013
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Shao Y, Bao H, Ma L, Yuan W, Zhang L, Yao J, Meng P, Peng Y, Zhang S, Cao T, Lu H (2021) Enhancing comprehensive analysis of newly synthesized proteins based on cleavable bioorthogonal tagging. Anal Chem 93:9408–9417. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00965
Shu J, Dang L, Zhang D, Shah P, Chen L, Zhang H, Sun S (2019) Dynamic analysis of proteomic alterations in response to N-linked glycosylation inhibition in a drug-resistant ovarian carcinoma cell line. FEBS J 286:1594–1605. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14811
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Takahashi T, Honda R, Nishikawa Y (2000) Cloning of the human cDNA which can complement the defect of the yeast mannosyltransferase I-deficient mutant alg 1. Glycobiology 10:321–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/10.3.321
Takayama H, Ohta M, Iwashita Y, Uchida H, Shitomi Y, Yada K, Inomata M (2020) Altered glycosylation associated with dedifferentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a lectin microarray-based study. BMC Cancer 20:192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-6699-5
van Bergen W, Heck AJR, Baggelaar MP (2021) Recent advancements in mass spectrometry-based tools to investigate newly synthesized proteins. Curr Opin Chem Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.07.001
Wu Y, Liu Z, Xu X (2020) Molecular subtyping of hepatocellular carcinoma: a step toward precision medicine. Cancer Commun (lond) 40:681–693. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12115
Xiang Y, Karaveg K, Moremen KW (2016) Substrate recognition and catalysis by GH47 alpha-mannosidases involved in Asn-linked glycan maturation in the mammalian secretory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E7890–E7899. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1611213113
Xu Y, Chang R, Xu F, Gao Y, Yang F, Wang C, Xiao J, Su Z, Bi Y, Wang L, Zha X (2017) N-Glycosylation at Asn 402 stabilizes N-cadherin and promotes cell-cell adhesion of glioma cells. J Cell Biochem 118:1423–1431. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25801
Zhang S, Cao X, Gao Q, Liu Y (2017) Protein glycosylation in viral hepatitis-related HCC: characterization of heterogeneity, biological roles, and clinical implications. Cancer Lett 406:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.07.026
Zhang S, Cao X, Liu C, Li W, Zeng W, Li B, Chi H, Liu M, Qin X, Tang L et al (2019) N-glycopeptide signatures of IgA2 in serum from patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases. Mol Cell Proteomics 18:2262–2272. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA119.001722
Zhao H, Liang Y, Xu Z, Wang L, Zhou F, Li Z, Jin J, Yang Y, Fang Z, Hu Y et al (2008) N-glycosylation affects the adhesive function of E-cadherin through modifying the composition of adherens junctions (AJs) in human breast carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-435. J Cell Biochem 104:162–175. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21608
Acknowledgements
We thank openbiox community and Hiplot team (https://hiplot.com.cn) for providing technical assistance and valuable tools for data analysis and visualization. The authors thank Shu Zhang from Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China, for her generous support. We acknowledge the financial support of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0505100) and NSF of China (Grants 21974025 and 82121004) for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XC. Methodology: YS and PM. Visualization: ZC. Investigation: GY, JY, XZ. Software: CL. Data curation: LZ. Writing—original draft: HS. Writing—reviewing and editing: HL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University. Approval number was 2019(KY-E-086). The privacy rights of human subjects were also observed. No animal experimentation was performed.
Consent to Participate
Each participant provided written informed consent.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Shao, Y., Meng, P. et al. Nascent Proteome and Glycoproteome Reveal the Inhibition Role of ALG1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration. Phenomics 2, 230–241 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-022-00050-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-022-00050-5