Abstract
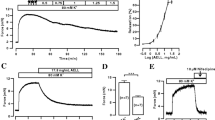
Medical plants, including Vitex agnus-castus L., Lamiaceae, were used in folk medicine for a long time; however, V. agnus-castus mechanisms of actions on trachea are not known. This study was attempted to give evidence for medicinal use of V. agnus-castus as a relaxant and to identify its underlying mechanisms. To this end, V. agnus-castus extract was extracted with ethanol and tested in rabbit tracheal smooth muscle using isolated organ baths. The V. agnus-castus extract (0.15–60 mg/ml) relaxed against acetylcholine-induced constriction in isolated rabbit tracheal smooth muscle, in vitro. Further, V. agnus-castus extract (0.15–75 mg/ml) shown relaxing effects in carbachol and high K-induced contraction of rabbit tracheal smooth muscle, implying antimuscarinic and calcium channel blocking activities. The addition (preincubation) of L-NAME (inhibitor of nitric oxide synthases), as well as indomethacin (cyclooxygenase inhibitor), inhibited (102%, 95% respectively) relaxing effects induced by V. agnus-castus extract precontracted with carbachol. On the other hand, bradykinin (stimulator of nitric oxide synthases) and zaprinast (phosphodiesterase inhibitor) further potentiated (40%, 41%, respectively) relaxing-induced effects by the V. agnus-castus extract. Our data suggest that V. agnus-castus extract airway-relaxing properties have muscarinic antagonism, are dependent on calcium blockade, and are at least partly mediated by the nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate- and cyclooxygenase-1-prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. These effects justify V. agnus-castus extract use in various respiratory disorders.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam G, Wahyuono S, Ganjar IG, Hakim L, Timmerman H, Verpoorte R (2002) Tracheospasmolytic activity of viteosin-A and vitexicarpin isolated from Vitex trifolia. Planta Med 68:1047–1049. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-35650
Bernareggi MM, Belvisi MG, Patel H, Barnes PJ, Giembycz MA (1999) Anti-spasmogenic activity of isoenzyme-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors in guinea-pig trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0702779
Berridge MJ (2008) Smooth muscle cell calcium activation mechanisms. J Physiol 586:5047–5061. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160440
Buels KS, Fryer AD (2012) Muscarinic receptor antagonists: effects on pulmonary function. Handb Exp Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-23274-9_14
Cabral RSA, Allard PM, Marcourt L, Young MCM, Queiroz EF, Wolfender JL (2016) Targeted isolation of indolopyridoquinazoline alkaloids from Conchocarpus fontanesianus based on molecular networks. J Nat Prod 79:2270–2278. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00379
Carbone L (2012a) Pain management standards in the eighth edition of the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 51:322–328
Carbone L (2012b) The utility of basic animal research. Hast Cent Rep. https://doi.org/10.1002/hast.101
Cheng YT, Yang CC, Shyur LF (2016) Phytomedicine - modulating oxidative stress and the tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Res 114:128–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.10.022
Cornélio Favarin D, Robison De Oliveira J, Jose Freire De Oliveira C, De Paula RA (2013) Potential effects of medicinal plants and secondary metabolites on acute lung injury. Biomed Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/576479
Fukahori M, Kobayashi S, Naraki Y, Sasaki T, Oka H, Seki M, Masada-Atsumi S, Hakamatsuka T, Goda Y (2014) Quality evaluation of medicinal products and health foods containing chaste berry (Vitex agnus-castus) in Japanese, European and American markets. Chem Pharm Bull 62:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.c13-00588
Insuela DBR, Daleprane JB, Coelho LP, Silva AR, Silva PMRE, Martins MA, Carvalho VF (2015) Glucagon induces airway smooth muscle relaxation by nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2. J Endocrinol 225:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-14-0648
Khan M, Shah AJ, Gilani AH (2015) Insight into the bronchodilator activity of Vitex negundo. Pharm Biol 53:340–344. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.919327
Kikuchi H, Yuan B, Nishimura Y, Imai M, Furutani R, Kamoi S, Seno M, Fukushima S, Hazama S, Hirobe C, Ohyama K, Hu XM, Takagi N, Hirano T, Toyoda H (2013) Cytotoxicity of Vitex agnus-castus fruit extract and its major component, casticin, correlates with differentiation status in leukemia cell lines. Int J Oncol 43:1976–1984. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2013.2133
Liu X, Farley JM (1996) Depletion and refilling of acetylcholine- and caffeine-sensitive Ca++ stores in tracheal myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:789–795
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA (1989) Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1709–1715. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6
Mullershausen F, Lange A, Mergia E, Friebe A, Koesling D (2006) Desensitization of NO/cGMP signaling in smooth muscle: blood vessels versus airways. Mol Pharmacol 69:1969–1974. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.105.020909
Neves RCS, Da Camara CAG (2016) Chemical composition and acaricidal activity of the essential oils from Vitex agnus-castus L. (Verbenaceae) and selected monoterpenes. An Acad Bras Cienc 88:1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201620140050
Rafieian-Kopaei M, Movahedi M (2017) Systematic review of premenstrual, postmenstrual and infertility disorders of Vitex agnus castus. Electron Physician 9:3685–3689. https://doi.org/10.19082/3685
Rani A, Sharma A (2013) The genus Vitex: a review. Pharmacogn Rev. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.120522
Romanucci V, Di Fabio G, D’Alonzo D, Guaragna A, Scapagnini G, Zarrelli A (2017) Traditional uses, chemical composition and biological activities of Sideritis raeseri Boiss. & Heldr. J Sci Food Agric 97:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7867
Saito M, Shibata O, Yamaguchi M, Yoshimura M, Makita T, Harada N, Niwa M, Sumikawa K (2004) Metoclopramide causes airway smooth muscle relaxation through inhibition of muscarinic M3 receptor in the rat trachea. Anesth Analg 98:1325–1329. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000111104.33104.51
Santana FPR, Pinheiro NM, Mernak MIB, Righetti RF, Martins MA, Lago JHG, Lopes FDTQDS, Tibério IFLC, Prado CM (2016) Evidences of herbal medicine-derived natural products effects in inflammatory lung diseases. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2348968
Schlemper V, Medeiros R, Ferreira J, Campos MM, Calixto JB (2005) Mechanisms underlying the relaxation response induced by bradykinin in the epithelium-intact guinea-pig trachea in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 145:740–750. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0706222
Siraskar B, Huang DY, Pakladok T, Siraskar G, Sopjani M, Alesutan I, Kucherenko Y, Almilaji A, Devanathan V, Shumilina E, Föller M, Munoz C, Lang F (2013) Downregulation of the renal outer medullary K+ channel ROMK by the AMP-activated protein kinase. Pflugers Arch 465:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1180-1
Sopjani M, Dërmaku-Sopjani M (2016) Klotho-dependent cellular transport regulation. Vitam Horm. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2016.02.003
Sopjani M, Konjufca V, Rinnerthaler M, Rexhepaj R, Dërmaku-Sopjani M (2016) The relevance of JAK2 in the regulation of cellular transport. Curr Med Chem 23:578–588. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666151207111707
Sopjani M, Shpetim S, Krasniqi B, Selmonaj M, Rinnerthaler M, Dermaku-Sopjani M (2017) Regulation of ion channels, cellular carriers and Na(+)/K(+)/ATPase by Janus kinase 3. Curr Med Chem 4:2251–2260. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170203122625
Stagos D, Portesis N, Spanou C, Mossialos D, Aligiannis N, Chaita E, Panagoulis C, Reri E, Skaltsounis L, Tsatsakis AM, Kouretas D (2012) Correlation of total polyphenolic content with antioxidant and antibacterial activity of 24 extracts from Greek domestic Lamiaceae species. Food Chem Toxicol 50:4115–4124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.08.033
Szabó LF (2008) Rigorous biogenetic network for a group of indole alkaloids derived from strictosidine. Molecules 13:1875–1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules13081875
Tesch BJ (2002) Herbs commonly used by women: an evidence-based review. Dis Mon 48:671–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-5029(02)90011-8
Weisskopf M, Schaffner W, Jundt G, Sulser T, Wyler S, Tullberg-Reinert H (2005) A Vitex agnus-castus extract inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in prostate epithelial cell lines. Planta Med 71:910–916. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-871235
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the research group of Prof. Jean Luc Wolfender, the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, EPGL, the University of Geneva, for acquiring orbitrap spectra.
Funding
This work was supported by the Small research project (Ref. nr. 2-3214/2, 2015, granted to M. Sopjani) financed by the Dpt. of Sci. and Tech. of the Republic of Kosova.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ST, BK, and DC: performed the day-by-day experimental work, revision; EB: paper draft improving and helping in study design; MS, SA, and MDS: designed the study, performed and supervised experimental work, extract preparation, statistical analysis, scientific writing, and paper drafting, revising, and final approval for publication.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Protection of Human and Animal Subjects
The authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Confidentiality of Data
The authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to Privacy and Informed Consent
The authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thaçi, S., Krasniqi, B., Cela, D. et al. Mechanisms Underlying the Tracheorelaxant Effect of Vitex agnus-castus Extract. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 30, 103–110 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-020-00009-5