Abstract
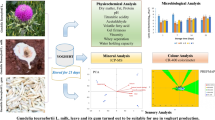
This study aimed to reveal the effect of salt reduction on the nutritional, functional and sensory aspects of doubanjiang through preparing three sets of doubanjiang fermentation (Sample H, Sample M and Sample L) with different salt concentrations. The results showed that fermentation with lower salt concentration led to significantly higher amino acids concentrations in doubanjiang, while the organic acids concentrations were also slightly increased. For biologically active compounds, the concentrations of total flavonoids, total phenols and five monomer isoflavones in Sample L were all significantly higher than those in Sample M and Sample H. Moreover, better anti-oxidant ability was observed in doubanjiang samples fermented with lower salt concentration. Bacillus and Millerozyma genus were found to be closely related to the formation of amino acids and biologically active compounds in doubanjiang, while organic acids were highly correlated with Cronobacter, Erwinia, Trabulsiella, Enterobacter and Millerozyma genus. Through sensory evaluation and electric tongue, unsatisfactory sensory characteristics, such as lighter color, strong acid taste and off-flavor, were found in lower salt fermented doubanjiang samples. This indicated that lower salt concentration favored the nutrition and function of doubanjiang while negatively influenced doubanjiang flavor. This study deepened our understanding of the roles of salt concentration on doubanjiang fermentation and provided guidance for the further development of low-salt doubanjiang.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information file.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Li Z, Rui J, Li X, Li J, Dong L, Huang Q, Huang C, Wang Z, Li L, Xuan P. Bacterial community succession and metabolite changes during doubanjiang-meju fermentation, a Chinese traditional fermented broad bean (Vicia faba L.) paste. Food Chem. 2017;218:534–42.
Wolfe BE, Dutton RJ. Fermented foods as experimentally tractable microbial ecosystems. Cell. 2015;161(1):49–55.
Niu C, Fan Z, Zheng F, Li Y, Liu C, Wang J, Li Q. Isolation and identification of gas-producing spoilage microbes in fermented broad bean paste. Food Control. 2018;84:8–16.
Shukla S, Park J, Kim D-H, Hong S-Y, Lee JS, Kim M. Total phenolic content, antioxidant, tyrosinase and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities of water soluble extracts of noble starter culture Doenjang, a Korean fermented soybean sauce variety. Food Control. 2016;59:854–61.
Kim MJ, Kwak HS, Kim SS. Effects of salinity on bacterial communities, Maillard reactions, isoflavone composition, antioxidation and antiproliferation in Korean fermented soybean paste (doenjang). Food Chem. 2018;245:402–9.
Soon AhK, Sung-Eun C, Kun-Young P. Anticancer effects of commercial doenjangs in azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis-associated colon cancer in C57BL/6J mice. Curr Dev Nutr. 2018;2(11):nzy035.
Niu C, Min S, Jia Y, Zhao J, Yang Y, Liu C, Zheng F, Li Q. Adaptive evolution of Aspergillus oryzae 3.042 strain and process optimization to reduce the formation of tyrosine crystals in broad bean paste. J Food Biochem. 2019;43(2):1–8.
Li W, Liu Y, Ye Y, Che Z, Wu T. Chemical profiling and metabolic mechanism of Pixian doubanjiang, a famous condiment in Chinese cuisine. LWT. 2021;4: 111274.
Mun E-G, Park JE, Cha Y-S. Effects of doenjang, a traditional Korean soybean paste, with high-salt diet on blood pressure in Sprague-Dawley rats. Nutrients. 2019;11(11):2745.
Chun BH, Kim KH, Sang EJ, Che OJ. The effect of salt concentrations on the fermentation of doenjang, atraditional Korean fermented soybean paste. Food Microbiol. 2020;86:122–31.
Devanthi P, Gkatzionis K. Soy sauce fermentation: microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification. Food Res Int. 2019;120:364–74.
Xie C, Zeng H, Qin L. Physicochemical, taste, and functional changes during the enhanced fermentation of low-salt Sufu paste, a Chinese fermented soybean food. Int J Food Prop. 2018;21(1):2714–29.
Qi Q, Huang J, Zhou R, Yang M, Wu C. Characterizing microbial community and metabolites of Cantonese soy sauce. Food Biosci. 2020;40: 100872.
Yang Y, Term CN, Shan W, Zheng F, Li Q. Physicochemical, flavor and microbial dynamic changes during low-salt doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation. Food Chem. 2021;4: 128454.
Zhao S, Niu C, Suo J, Zan Y, Wei Y, Zheng F. and Qi Li, Unraveling the mystery of “bask in daytime and dewed at night” technique in doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation. LWT. 2021;149(11): 111723.
Kong Y, Zhang L-L, Zhang Y-Y, Sun B-G, Sun Y, Zhao J, Chen H-T. Evaluation of non-volatile taste components in commercial soy sauces. Int J Food Prop. 2018;21(1):1854–66.
Feng K, Sun Q, Deng WQ, Zhang S, Qi-Sheng Z, Fan ZY, You JG, Heng LI. A HPLC method for determination of seven kinds of organic acids in broad bean paste with different fermentation year. Food Ferment Sci Technol. 2019;55(4):128–31.
Mejri F, Selmi S, Martins AI, Khoud HB, Baati T, Chaabene H, Njim L, Serralheiro ML, Rauter AP, Hosni K. Broad bean (Vicia faba L.) pods: a rich source of bioactive ingredients with antimicrobial, antioxidant, enzyme inhibitory, anti-diabetic and health-promoting properties. Food Funct. 2018;9:2051–69.
Gao X, Liu E, Zhang J, Yang M, Chen S, Liu Z, Ma H, Hu F. Effects of sonication during moromi fermentation on antioxidant activities of compounds in raw soy sauce. LWT. 2019;116: 108605.
Niu C, Yang L, Zheng F, Liu C, Wang J, Xu X, Li Q. Systematic analysis of the aroma profiles produced by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii Y-8 in different environmental conditions and its contribution to doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation with different salinity. LWT. 2022;158: 113118.
Cai W, Tang F, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Xue Y, Zhao X, Guo Z, Shan C. Bacterial diversity and flavor profile of Zha-chili, a traditional fermented food in China. Food Res Int. 2021;141: 110112.
Tian S, Qin Y, Han J. A new sensory sweetness definition and sweetness conversion method of five natural sugars, based on the Weber–Fechner law. Food Chem. 2019;281:78–84.
McKenna S, Meyer M, Gregg C, Gerber S. s-CorrPlot: an interactive scatterplot for exploring correlation. J Comput Graph Stat. 2016;25(2):445–63.
Li Z, Dong L, Huang Q, Wang X. Bacterial communities and volatile compounds in Doubanjiang, a Chinese traditional red pepper paste. J Appl Microbiol. 2016;120(6):1585–94.
Massey KA, Blakeslee CH, Pitkow HS. A review of physiological and metabolic effects of essential amino acids. Amino Acids. 1998;14(4):271–300.
Naveed M, Nadeem F, Mehmood T, Bilal M, Amjad F. Protease-A versatile and ecofriendly biocatalyst with multi-industrial applications: an updated review. Catal Lett. 2021;151:307–23.
Yang M, Huang J, Zhou R, Qi Q, Wu C. Characterizing the microbial community of Pixian doubanjiang and analysing the metabolic pathway of major flavour metabolites. LWT. 2021;143(2): 111170.
Jia Y, Niu CT, Lu ZM, Zhang XJ, Chai LJ, Shi JS, Xu ZH, Li Q. A bottom-up approach to develop simplified microbial community model with desired functions: application for efficient fermentation of broad bean paste with low salinity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020;86(12):1–12.
Bagchi TB, Chattopadhyay K, Sivashankari M, Roy S, Pal S. Effect of different processing technologies on phenolic acids, flavonoids and other antioxidants content in pigmented rice. J Cereal Sci. 2021;21: 103263.
Tepavčević L, Cvejić J, Poša M, Bjelica A, Miladinović J, Rizou M, Aldawoud T, Galanakis C. Classification and discrimination of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) genotypes based on their isoflavone content. J Food Comp Anal. 2020;95: 103670.
Silva L, Celeghini R, Chang YK. Effect of the fermentation of whole soybean flour on the conversion of isoflavones from glycosides to aglycones. Food Chem. 2011;128(3):640–4.
Vuong TV, Wilson DB. Glycoside hydrolases: catalytic base/nucleophile diversity. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010;107(2):195–205.
Kumari R, Sanjukta S, Sahoo D, Rai AK. Functional peptides in Asian protein rich fermented foods: production and health benefits. Syst Microbiol Biomanuf. 2022;2:1–13.
Sanjukta S, Padhi S, Sarkar P, Singh SP, Sahoo D, Rai AK. Production, characterization and molecular docking of antioxidant peptides from peptidome of kinema fermented with proteolytic Bacillus spp. Food Res Int. 2021;141: 110161.
Sanjukta S, Rai AK. Production of bioactive peptides during soybean fermentation and their potential health benefits. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2016;50:1–10.
Kim SS, Kwak HS, Kim MJ. The effect of various salinity levels on metabolomic profiles, antioxidant capacities and sensory attributes of doenjang, a fermented soybean paste. Food Chem. 2020;328: 127176.
Shim JM, Lee KW, Yao Z, Kim H-J, Kim JH. Properties of doenjang (soybean paste) prepared with different types of salts. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;26(9):1533–41.
Song DH, Chun BH, Lee S, Son SY, Reddy CK, Mun HI, Jeon CO, Lee CH. Comprehensive metabolite profiling and microbial communities of Doenjang (fermented soy paste) and Ganjang (fermented soy sauce): a comparative study. Foods. 2021;10(3):641.
Yue X, Li M, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zheng Y. Microbial diversity and function of soybean paste in East Asia: What we know and what we don’t. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2021;37:145–52.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the funding of Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education (KLIB-KF202104), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFD0400403) and Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No.111-2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, C., Xing, X., Zheng, F. et al. Effect of salt reduction on nutritional, functional and sensory aspects of Anhui-style doubanjiang, a traditional Chinese broad bean paste. Syst Microbiol and Biomanuf 3, 262–272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-022-00112-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-022-00112-9