Abstract
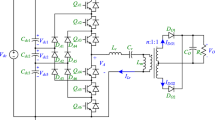
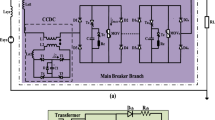
As a core piece of equipment in DC distribution networks, DC solid-state transformers (DCSSTs) are attracting more and more attention in academia and industry. Due to the limitations in terms of the electrical stress of the switches, the input series output parallel (ISOP) structure is adopted in DCSSTs. This paper proposed an improved DCSST topology based on a voltage balancing unit (VBU). This topology has the advantages of higher power density, reduced weight, and cascaded number without compromising efficiency, cost, or reliability. The working modes, mathematical models, and control strategy are analyzed. In addition, a start-up strategy and a parameter design method are proposed in this paper. Simulation and experimental results verify the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed solution. The proposed DCSST is a practical scheme for the application of DC distribution networks.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, J., Shanmei, C., Anwen, S.: A high efficiency two-stage inverter for photovoltaic grid-connected generation systems. J. Power Electron. 17(1), 200–211 (2017)
Katayama, N., Tosaka, S., Yamanaka, T., Hayase, M., Dowaki, K., Kogoshi, S.: New topology for dc–dc converters used in fuel cell–electric double layer capacitor hybrid power source systems for mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(1), 313–321 (2015)
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Yang, J., Zhao, N., Wang, Y., Zheng, T.Q.: A modified DC power electronic transformer based on series connection of full-bridge converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(3), 2119–2133 (2018)
Habib, S., Khan, M.M., Abbas, F., Ali, A., Faiz, M.T., Ehsan, F., Tang, H.: Contemporary trends in power electronics converters for charging solutions of electric vehicles. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 6(4), 911–929 (2020)
Xu, F., Guo, B., Xu, Z., Tolbert, L.M., Wang, F., Blalock, B.J.: Paralleled three-phase current-source rectifiers for high-efficiency power supply applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 20(1), 308–318 (2020)
Dam, D.-H., Lee, H.-H.: Battery–inductor–supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system for DC microgrids. J. Power Electron. 17(1), 200–211 (2017)
Wang, Y., Song, Q., Zhao, B., Li, J., Sun, Q., Liu, W.: Quasi-square-wave modulation of modular multilevel high-frequency DC converter for medium-voltage DC distribution application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(9), 7480–7495 (2017)
CIGRE WG C6.31.: Medium Voltage Direct Current (MVDC) Grid Feasibility Study. Technical Brochure no. 793 (2020)
Zhao, B., Song, Q., Liu, W., Sun, Y.: Overview of dual-activebridge isolated bidirectional dc–dc converter for high-frequency-link power-conversion system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(8), 4091–4106 (2014)
Doncker, R.W.A.A.D., Divan, D.M., Kheraluwala, M.H.: A threephase soft-switched high-power-density dc/dc converter for high-power applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 27(1), 63–73 (1991)
Zhu, L.: A novel soft-commutating isolated boost full-bridge ZVS-PWM dc-dc converter for bidirectional high power applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 21(2), 422–429 (2006)
Inoue, S., Akagi, H.: A bidirectional isolated dc-dc converter as a core circuit of the next-generation medium-voltage power conversion system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 22(2), 535–542 (2007)
Xie, Y., Sun, J., Freudenberg, J.S.: Power flow characterization of a bidirectional Galvanically isolated high-power dc–dc converter over a wide operating range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25(1), 54–66 (2010)
Zhao, B., Song, Q., Li, J., Liu, W., Liu, G., Zhao, Y.: High-frequency-link dc transformer based on switched capacitor for medium-voltage dc power distribution application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 31(7), 4766–4777 (2016)
Wang, Y., Song, Q., Sun, Q., Zhao, B., Li, J., Liu, W.: Multilevel MVDC link strategy of high-frequency-link DC transformer based on switched capacitor for MVDC power distribution. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(4), 2829–2835 (2017)
Bai, H., Mi, C.: Eliminate reactive power and increase system efficiency of isolated bidirectional dual-active-bridge DC-DC converters using novel dual-phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(6), 2905–2914 (2008)
Bai, H., Nie, Z., Mi, C.: Experimental comparison of traditional phase-shift, dual-phase-shift, and model-based control of isolated bidirectional dc-dc converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25(6), 1444–1449 (2010)
Krismer, F., Kolar, J.W.: Efficiency-optimized high-current dual active bridge converter for automotive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(7), 2745–2760 (2012)
Jain, A.K., Ayyanar, R.: PWM control of dual active bridge: comprehensive analysis and experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(4), 1215–1227 (2011)
Wu, K., Silva, C.W., Dunford, W.G.: Stability analysis of isolated bidirectional dual active full-bridge dc-dc converter with triple phaseshift control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 27(4), 2007–2017 (2012)
Shi, H., Wen, H., Chen, J., Hu, Y., Jiang, L., Chen, G., Ma, J.: Minimum-backflow-power scheme of DAB-based solid-state transformer with extended-phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 54(4), 3483–3496 (2018)
Zhao, B., Yu, Q., Sun, W.: Extended-phase-shift control of isolated bidirectional dc–dc converter for power distribution in microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 27(11), 4667–4680 (2012)
Li, X., Bhat, A.K.: Analysis and design of high-frequency isolated dual-bridge series resonant dc/dc converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25(4), 850–862 (2010)
Tian, S., Lee, F.C., Li, Q.: A simplified equivalent circuit model of series resonant converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 31(5), 3922–3931 (2015)
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Yang, J., Zhao, N., Wang, Y., Zheng, T.Q.: An LLC-LC type bidirectional control strategy for an LLC resonant converter in power electronic traction transformer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(11), 8595–8604 (2018)
Chen, Q., Wang, J., Ji, Y.: Control scheme of bidirectional LLC resonant DC-DC transformer for soft start and power conversion. Trans. China Electr. Soc. 29(8), 180–186 (2014). (in Chinese)
Jiang, T., Zhang, J., Wu, X., Sheng, K., Wang, Y.: A bidirectional LLC resonant converter with automatic forward and backward mode transition. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30(2), 757–770 (2014)
Shi, L., Liu, B., Duan, S.: Current sharing method based on optimal phase shift control for interleaved three-phase half-bridge LLC converter with floating y-connection. J. Power Electron. 19(4), 934–943 (2019)
Yeon, C., Kim, J., Park, M., Lee, I., Moon, G.: Improving the light-load regulation capability of LLC series resonant converter using impedance analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(9), 7056–7067 (2017)
Kim, C., Baek, J., Lee, J.: High-efficiency single-stage LLC resonant converter for wide-input-voltage range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(9), 7832–7840 (2018)
Martins, L.F., Stone, D., Foster, M.: Modelling of phase-shift modulated bidirectional CLLC resonant converter. IET Power Electron. 13(12), 2628–2637 (2020)
Zou, S., Lu, J., Mallik, A., Khaligh, A.: Bi-directional CLLC converter with synchronous rectification for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 54(2), 998–1005 (2018)
Zong, S., Fan, G., Yang, X.: Double voltage rectification modulation for bidirectional DC/DC resonant converters for wide voltage range operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(7), 6510–6521 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the State Grid Corporation of China Science and Technology Project: Research on the key technologies of high efficiency and compact multi-port DC transformer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zha, K., Tang, X. et al. Topology and start-up strategy for DC–DC transformers based on voltage balancing unit. J. Power Electron. 21, 1072–1083 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00247-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00247-3