Abstract
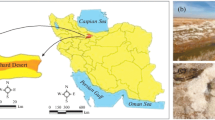
Halophilic archaea are multi-stress resistant organisms and their enzymes are of special interest as they are generally stable and functional under extreme conditions of temperature and low water activity. The search for novel extremozymes is an ongoing one because of their superior functionality in extreme conditions encountered in various industries. In this study, extremely halophilic archaea were isolated from two salterns (Marakkanam and Vedaranyam) in Tamil Nadu and from three salterns (Sinquetim, Siridao and Ribandar) in Goa, India. All isolates were Gram negative and their pigmentation ranged from light pink to bright orange. Characterization of the ten halophilic archaeal isolates was carried out by morphological, biochemical and molecular techniques. They spanned 6 different genera; Haloferax, Halorubrum, Halococcus, Haloarcula, Halogeometricum, and Haloterrigena. These extremely halophilic archaeal strains were screened for production of hydrolytic enzymes like amylase, esterase, lipase, protease, pectinase and cellulase. Amylase production by Halogeometricum sp. is being reported for the first time. All isolates showed at least one enzyme activity. Halococcus sp., Haloarcula sp., and Haloferax sp. were capable of producing three extracellular enzymes each. Cellulolytic activity was not observed in any of the isolates. Since these enzymes are inherently salt tolerant, they are very promising from the industrial point of view.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akmoussi-Toumi S, Khemili-Talbi S, Ferioune I, Kebbouche-Gana S (2018) Purification and characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant and detergent-stable lipase from Haloferax mediterranei CNCMM 50101. Int J Biol Macromol 116:817–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.05.087
Alsafadi D, Paradisi F (2013) Effect of organic solvents on the activity and stability of halophilic alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH2) from Haloferax volcanii. Extremophiles 17(1):115–122
Anderson I, Scheuner C, Göker M, Mavromatis K, Hooper SD, Porat I, Klenk HP, Ivanova N, Kyrpides N (2011) Novel insights into the diversity of catabolic metabolism from ten haloarchaeal genomes. PLoS One 6(5):e20237
Antunes A, Taborda M, Huber R, Moissl C, Nobre MF, da Costa MS (2008) Halorhabdus tiamatea sp. nov., a non-pigmented, extremely halophilic archaeon from a deep-sea, hypersaline anoxic basin of the Red Sea, and emended description of the genus Halorhabdus. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 58(1):215–220
Balkrishna SB (2015) Synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates by halophilic archaea and bacteria and their osmoadaptation. Doctoral dissertation, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani)
Bardavid RE, Oren A (2008) Dihydroxyacetone metabolism in Salinibacter ruber and in Haloquadratum walsbyi. Extremophiles 12(1):125–131
BBC Research (2012) In Report BIO030G—Global markets for enzymes in industrial applications. https://www.bccresearch.com/market-research/biotechnology/enzymes-industrial-applications-markets-bio030g.html
Birbir M, Calli B, Mertoglu B, Bardavid RE, Oren A, Ogmen MN, Ogan A (2007) Extremely halophilic Archaea from Tuz Lake, Turkey, and the adjacent Kaldirim and Kayacik salterns. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(3):309–316
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37(8):911–917
Burns DG, Janssen PH, Itoh T, Kamekura M, Li Z, Jensen G, Dyall-Smith ML (2007) Haloquadratum walsbyi gen. nov., sp. nov., the square haloarchaeon of Walsby, isolated from saltern crystallizers in Australia and Spain. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 57(2):387–392
Camacho RM, Mateos JC, González-Reynoso O, Prado LA, Córdova J (2009) Production and characterization of esterase and lipase from Haloarcula marismortui. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36(7):901–909
Chu X, He H, Guo C, Sun B (2008) Identification of two novel esterases from a marine metagenomic library derived from South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80(4):615–625
Cui HL, Tohty D, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2006) Halorubrum lipolyticum sp. nov. and Halorubrum aidingense sp. nov., isolated from two salt lakes in Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 56(7):1631–1634
Cui HL, Lin ZY, Dong Y, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2007) Halorubrum litoreum sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 57(10):2204–2206
De Rosa M, Trincone A, Nicolaus B, Gambacorta A (1991) Archaebacteria: lipids, membrane structures, and adaptation to environmental stresses. Life under extreme conditions. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 61–87
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70(4):484
Dyall-Smith M (2008) The halohandbook: protocols for halobacterial genetics. http://www.haloarchaea.com/resources/halohandbook/index.html. Accessed 31 Aug 2018
Elevi R, Assa P, Birbir M, Ogan A, Oren A (2004) Characterization of extremely halophilic Archaea isolated from the Ayvalik Saltern, Turkey. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(7):719–725
Elferink MGL, De Wit JG, Demel R, Driessen AJM, Konings WN (1992) Functional reconstitution of membrane proteins in monolayer liposomes from bipolar lipids of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem 267:1375–1381
Fang Z, Li J, Wang Q, Fang W, Peng H, Zhang X, Xiao Y (2014) A novel esterase from a marine metagenomic library exhibiting salt tolerance ability. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:771–780
Gattinger A, Günthner A, Schloter M, Munch JC (2003) Characterization of archaea in soils by polar lipid analysis. Eng Life Sci 23(1):21–28
Goh F, Leuko S, Allen MA, Bowman JP, Kamekura M, Neilan BA, Burns BP (2006) Halococcus hamelinensis sp. nov., a novel halophilic archaeon isolated from stromatolites in Shark Bay, Australia. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 56(6):1323–1329
Grant WD (2004) Life at low water activity. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 359(1448):1249–1267
Kakhki AM, Amoozegar MA, Khaledi EM (2011) Diversity of hydrolytic enzymes in haloarchaeal strains isolated from salt lake. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(4):705–714
Kamekura M (1999) Diversity of members of the family Halobacteriaceae. Microbiol Biogeochem Hypersaline Environ 13:26
Kamekura M, Kates M (1999) Structural diversity of membrane lipids in members of Halobacteriaceae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63(6):969–972
Karan R, Capes MD, Das Sarma S (2012) Function and biotechnology of extremophilic enzymes in low water activity. Aquat Biosyst 8:4
Karray F, Abdallah MB, Kallel N, Hamza M, Fakhfakh M, Sayadi S (2018) Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes produced by halophilic bacteria and archaea isolated from hypersaline lake. Molecular Biology Reports 45(5):1297–1309
Kates M (1977) The phytanyl ether-linked polar lipids and isoprenoid neutral lipids of extremely halophilic bacteria. Prog Chem Fats Other Lipids 15(4):301–342
Kates M (1993) Membrane lipids of archaea. New comprehensive biochemistry, vol 26. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 261–295
Kaur S, Purohit MK (2012) Rainfall Statistics of India, Indian Meteorological Department, Ministry of earth sciences. Report number: ESSO/IMD/HS/R.F. REP/02 (2013)/16
Konings WN, Albers SV, Koning S, Driessen AJ (2002) The cell membrane plays a crucial role in survival of bacteria and archaea in extreme environments. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81(1–4):61–72
Kumar S, Karan R, Kapoor S, Singh SP, Khare SK (2012) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing industrially important enzymes. Braz J Microbiol 43(4):1595–1603
Legat A, Denner E, Dornmayr-Pfaffenhuemer M, Pfeiffer P, Knopf B, Claus H, Stan-Lotter H (2013) Properties of Halococcus salifodinae, an isolate from Permian rock salt deposits, compared with halococci from surface waters. Life 3(1):244–259
Levin L, Herrmann C, Papinutti VL (2008) Optimization of lignocellulolytic enzyme production by the white-rot fungus Trametes trogii in solid-state fermentation using response surface methodology. Biochem Eng J 39(1):207–214
Li X, Yu HY (2014) Characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Haloarcula sp. G41 and its application for biodiesel production. Folia Microbiol 59(6):455–463
Litchfield CD, Irby A, Kis-Papo T, Oren A (2000) Comparisons of the polar lipid and pigment profiles of two solar salterns located in Newark, California, USA, and Eilat, Israel. Extremophiles 4(5):259–265
Liu XD, Xu Y (2008) A novel raw starch digesting α-amylase from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. YX-1: purification and characterization. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4315–4320
Madern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G (2000) Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 4(2):91–98
Mahadik ND, Puntambekar US, Bastawde KB, Khire JM, Gokhale DV (2002) Production of acidic lipase by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation. Process Biochem 38(5):715–721
Mani K, Salgaonkar BB, Braganca JM (2012) Culturable halophilic archaea at the initial and crystallization stages of salt production in a natural solar saltern of Goa, India. Aquat Biosyst 8(1):15
Markets and Markets (2014) In Report Code: FB 2277 industrial enzymes market by Types (Carbohydrase, Protease, Lipase), applications (food & beverages, cleaning agents, bio-fuel, animal feed), & Geography—Global Trends & Forecasts to 2018
Markets and Markets (2016) In Report Code: FB 2277 industrial enzymes market by type (Amylases, Cellulases, Proteases, Lipases, and Phytases), application (food and beverages, cleaning agents, and animal feed), source (microorganism, plant, and animal), and Region—Global Forecast to 2022
Martin DD, Ciulla RA, Roberts MF (1999) Osmoadaptation in archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(5):1815–1825
Minegishi H, Echigo A, Nagaoka S, Kamekura M, Usami R (2010) Halarchaeum acidiphilum gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately acidophilic haloarchaeon isolated from commercial solar salt. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 60(11):2513–2516
Moldoveanu N, Kates M, Montero CG, Ventosa A (1990) Polar lipids of non-alkaliphilic Halococci. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Lipids Lipid Metab 1046(2):127–135
Montalvo-Rodriguez RAFAEL, Vreeland RH, Oren A, Kessel M, Betancourt C, López-Garriga JUAN (1998) Halogeometricum borinquense gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel halophilic archaeon from Puerto Rico. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 48(4):1305–1312
Moreno ML, Mellado E, Garcia MT, Ventosa A (2007) Diversity of extreme halophiles producing hydrolytic enzymes in hypersaline habitats. Halophiles-2007 booklet, 59–60
Moshfegh M, Shahverdi AR, Zarrini G, Faramarzi MA (2013) Biochemical characterization of an extracellular polyextremophilic α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Halorubrum xinjiangense. Extremophiles 17:1–11
Müller-Santos M, de Souza EM, Pedrosa FDO, Mitchell DA, Longhi S, Carrière F, Krieger N (2009) First evidence for the salt-dependent folding and activity of an esterase from the halophilic archaea Haloarcula marismortui. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1791(8):719–729
Nayek A, Gupta PSS, Banerjee S, Mondal B, Bandyopadhyay AK (2014) Salt-bridge energetics in halophilic proteins. PLoS One 9(4):e93862
Oren A (2010) Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms. Environ Technol 31(8–9):825–834
Oren A, Duker S, Ritter S (1996) The polar lipid composition of Walsby’s square bacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138(2–3):135–140
Promchai R, Boonchalearn A, Visessanguan W, Luxananil P (2018) Rapid production of extracellular thermostable alkaline halophilic protease originating from an extreme haloarchaeon, Halobacterium salinarum by recombinant Bacillus subtilis. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 15:192–198
Rathod BN, Bhatt HH, Upasani VN (2016) Extracellular Hydrolases producing Haloarchaea from Marine Salterns at Okhamadhi, Gujarat, India. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 5(11):51–64
Reed CJ, Lewis H, Trejo E, Winston V, Evilia C (2013) Protein adaptations in archaeal extremophiles. Archaea. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/373275
Rodrigo-Baños M, Garbayo I, Vílchez C, Bonete MJ, Martínez-Espinosa RM (2015) Carotenoids from haloarchaea and their potential in biotechnology. Mar Drugs 13(9):5508–5532
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2009) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolyses from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J Ind Microbiol Biot 36(3):333–340
Sánchez-Porro C, Martin S, Mellado E, Ventosa A (2003) Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J Appl Microbiol 94(2):295–300
Shafiei M, Ziaee AA, Amoozegar MA (2010) Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel SDS and surfactant stable, raw starch digesting, and halophilic α-amylase from a moderately halophilic bacterium, Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. Process Biochem 45(5):694–699
Singh A, Singh AK (2017) Haloarchaea: worth exploring for their biotechnological potential. Biotech Lett 39(12):1793–1800
Sinha R, Khare SK (2012) Characterization of detergent compatible protease of a halophilic Bacillus sp. EMB9: differential role of metal ions in stability and activity. Bioresour Technol 145:357–361
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Thompson DH, Wong KF, Humphry-Baker R, Wheeler JJ, Kim JM, Rananavare SB (1992) Tetraether bolaform amphiphiles as models of archaebacterial membrane lipids: raman spectroscopy, phosphorus-31 NMR, x-ray scattering, and electron microscopy. J Am Chem Soc 114(23):9035–9042
Trigui H, Masmoudi S, Brochier-Armanet C, Maalej S, Dukan S (2011) Characterization of Halorubrum sfaxense sp. nov., a new halophilic archaeon isolated from the solar saltern of Sfax in Tunisia. Int J Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/240191
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol R 62(2):504–544
Wright AG (2006) Phylogenetic relationships within the order Halobacteriales inferred from 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1223–1227
Zafrilla B, Martínez-Espinosa RM, Alonso MA, Bonete MJ (2010) Biodiversity of Archaea and floral of two inland saltern ecosystems in the Alto Vinalopó Valley, Spain. Saline Syst 6(1):10
Zhang WJ, Cui HL (2014) Halorubrum salinum sp. nov., isolated from a marine solar saltern. Arch Microbiol 196(6):395–400
Zhang Y, Hao J, Zhang YQ, Chen XL, Xie BB, Shi M, Li PY (2017) Identification and characterization of a novel salt-tolerant esterase from the deep-sea sediment of the South China Sea. Front Microbiol 8:441
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by BITS Pilani Seed Grant 2013 to JB. DD would like to thank BITS Pilani, KK Birla Goa Campus for the fellowship. The authors thank Dr Hiroaki Minegishi, Bio-Nano Electronics Research Center, Tokyo University, Japan for identifying the haloarchaeal isolates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, D., Kalra, I., Mani, K. et al. Characterization of extremely halophilic archaeal isolates from Indian salt pans and their screening for production of hydrolytic enzymes. Environmental Sustainability 2, 227–239 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-019-00077-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-019-00077-x