Abstract
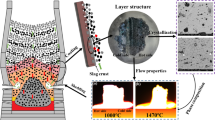
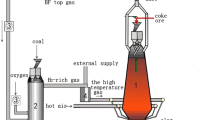
Based on the technology of gas-injection blast furnace (BF), the characteristics of primary slag formation with H2 addition were researched. The results indicate that, compared with traditional BF, the primary melt is formed at a lower temperature, which promotes the deformation of the solid burden particles. With the increase in temperature and H2 content, the quantity of formed melt containing FeO decreases sharply, corresponding to the crystallization of solid 2CaO·SiO2 during reduction. A wider softening range and narrower melting zone could be found in the gas-injection BF with a higher reduction potential. The permeability of burden layer is ameliorated as a result of decreased melt quantity. The influence of H2 on the high-temperature properties of burden is not so conspicuous when the H2 addition is from 10 to 15 vol.% against 5 to 10 vol.%. What is more, the slag shows a better liquidity with the decrease in basicity, owing to the transformation of melt composition from a primary phase field with high melting point to that with low melting point. The process of slag forming in gas-injection BF is characterized by earlier melt formation, less primary slag, higher melting temperature, better permeability and better liquidity, and the phase compositions of primary slag are close to those of final slag.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.D. Xu. Iron and Steel 45 (2010) No. 3, 1–12.
E.P. da Rocha, V.S. Guiherme, J.A. de Castro, Y. Sazaki, J.I. Yagi, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2 (2013) 255–262.
K.S. Abdel Halim, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 9, 40–46.
M.S. Chu, H. Nogami, J.I. Yagi, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 801–808.
J.M. Steer, R. Marsh, M. Greenslade, A. Robinson, Fuel 151 (2015) 40–49.
S.W. Du, C.P. Yeh, W.H. Chen, C.H. Tsai, J.A. Lucas, Fuel 143 (2015) 98–106.
C. Wang, M. Larsson, J. Lövgren, L. Nilsson, P. Mellin, W. Yang, H. Salman, A. Hultgren, Energy Procedia 61 (2014) 2184–2187.
W.H. Chen, C.L. Hsu, S.W. Du, Energy 86 (2015) 758–771.
G. Danloy, A. Berthelemot, M. Grant, J. Borlee, D. Sert, J. van der Stel, H. Jak, V. Dimastromatteo, M. Hallin, N. Eklund, N. Edberg, L. Sundqvist, B.E. Sköld, R. Lin, A. Feiterna, B. Korthas, F. Müller, C. Feilmayr, A. Habermann, Rev. Metall. 106 (2009) 1–8.
R. Schott, Iron Steel Technology 10 (2013) No. 3, 63–75.
P. Jin, Z. Jiang, C. Bao, S. Hao, X. Zhang, Resources, Conservation and Recycling 117 (2017) 58–65.
H.B. Luengen, M. Peters, P. Schmöle, Iron Steel Technology 9 (2012) 63–69.
Y.N. Qie, Q. Lyu, J.P. Li, C.C. Lan, X.J. Liu, ISIJ Int. 57 (2017) 404–412.
Q. Lyu, Y.N. Qie, X.J. Liu, C.C. Lan, J.P. Li, S. Liu, Thermochim. Acta 648 (2017) 79–90.
Q. Lü, F.M. Li, X.B. Li, L.F. Sun, Iron and Steel 43 (2008) No. 1, 17–21.
F.M. Li, Q. Lü, X.B. Li, Iron and Steel 42 (2007) No. 5, 12–15.
H. Guo, F.M. Li, Q. Lü, Journal of Hebei Institute of Technology 29 (2007) No. 1, 27–31.
I. Shigaki, S. Shirouchi, K. Tokutake, N. Hasegawa, ISIJ Int. 30 (1990) 199–207.
P.A. Tanskanen, S.M. Huttunen, P.H. Mannila, J.J. Härkki, Ironmak. Steelmak. 29 (2002) 281–286.
T. Nishimura, K. Higuchi, M. Naito, K. Kunitomo, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1316–1321.
M. Matsumura, M. Hoshi, T. Kawaguchi, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) 594–602.
X.W. An, J.S. Wang, R.Z. Lan, Y.H. Han, Q.G. Xue, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 5, 11–16.
T. Bakker, Softening in the blast furnace process, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands, 1999.
Y.N. Qie, Q. Lyu, X.J. Liu, J.P. Li, C.C. Lan, S.H. Zhang, C.J. Yan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 2622–2632.
K. Higuchi, M. Naito, M. Nakano, Y. Takamoto, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 2057–2066.
C.E. Loo, L.T. Matthews, D.P. O’dea, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 930–938.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1360205, 51674122) and Iron and Steel Research Foundation of Hebei (E2016209367).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qie, Yn., Lyu, Q., Lan, Cc. et al. Effect of H2 addition on process of primary slag formation in cohesive zone. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 132–140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00303-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00303-0