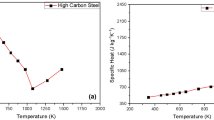
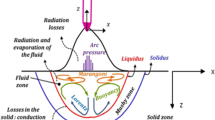
Abstract
Based on the extended application of COMSOL multiphysics, a novel dual heat source model for pulsed laser–gas tungsten arc (GTA) hybrid welding was established. This model successfully solved the problem of simulation inaccuracy caused by energy superposition effect between laser and arc due to their different physical characteristics. Numerical simulation for pulsed laser–GTA hybrid welding of magnesium alloy process was conducted, and the simulation indicated good agreements with the measured thermal cycle curve and the shape of weld beads. Effects of pulse laser parameters (laser-excited current, pulse duration, and pulse frequency) on the temperature field and weld pool morphology were investigated. The experimental and simulation results suggest that when the laser pulse energy keeps constant, welding efficiency of the hybrid heat source is increased by increasing laser current or decreasing pulse duration due to the increased ratio of the weld bead depth to width. With large laser currents, severe spatters tend to occur. For optimized welding process, the laser current should be controlled in the range of 150–175 A, the pulse duration should be longer than 1 ms, and the pulse frequency should be equal to or slightly greater than 20 Hz.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Song, J. Wang, J.W. Yu, L.M. Liu, Trans. China Weld. Inst. 37 (2016) No. 5, 69–72.
L.M. Liu, M.S. Chi, J.F. Wang, Mater. Mech. Eng. A 42 (2006) 82–86.
J. Shen, S. Li, D.J. Zhai, L.B. Wen, K. Liu, Y.C. Dai, Mater. Manuf. Process. 28 (2013) 1240–1247.
L.M. Liu, G. Song, G.L. Liang, J.F. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 390 (2005) 76–80.
X. Xie, J. Shen, F.B. Gong, D. Wu, T. Zhang, X. Luo, Y. Li, Adv. Manuf. Technol. 82 (2016) 75–83.
C. Shan, G. Song, L.M. Liu, Trans. China Weld. Inst. 29 (2008) No. 6, 57–60.
X.D. Qi ,G. Song, Mater. Des. 31 (2010) 605–609.
X.D. Qi, L.M. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. 44 (2009) 5725–5731.
M. Gao, S.W. Mei, Z.M. Wang, X.Y. Li, X.Y. Zeng, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212 (2012) 1338–1346.
G. Casalino, S.L. Campanelli, A.D. Ludovico, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 68 (2013) 209–216.
J. Chen, C.S. Wu, M.A. Chen, Mater. Manuf. Process. 16 (2014) 485–493.
L.M. Liu, M.S. Chi, J.F. Wang, Mater. Mech. Eng. 42 (2006) No. 2, 82–86.
R.S. Huang, L.M. Liu, G. Song, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 447 (2007) 239–243.
G. Song, Z.M. Luo, Opt. Laser Eng. 49 (2011) 82–88.
X.H. Zhan, Y.B. Li, W.M. Ou, F.Y. Yu, J. Chen, Y.H. Wei. Opt. Laser Technol. 85 (2016) 75–84.
L.C. Mo, B.N. Qian, X.M. Guo, S.F. Yu, Trans. China Weld. Inst. 22 (2001) No. 3, 93–96.
Y.B. Chen, L.Q. Li, J.F. Fang, X.S. Feng, L. Wu, China Weld. 12 (2003) No. 1, 62–66.
C. Carmignani, R. Mares, G. Tosell, Comput. Method Appl. Mech. Eng. 179 (1999) 197–217.
B. Tan, H.L. Zhang, D.G. Chen, G. Qi, J.C. Feng, C.F. Chen, Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 33 (2010) No. 2, 55–58.
V. Pavelic, Weld. J. 48 (1969) 295–305.
S. Wu, H.Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, X.H. Zhang, J. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 25 (2004) No. 1, 92–95.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (Grant Nos. 201602391 and 20170540460).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Zl., Liu, Lm., Lv, Xz. et al. Numerical simulation for pulsed laser–gas tungsten arc hybrid welding of magnesium alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 995–1002 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0122-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0122-3