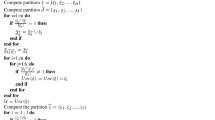Abstract
The rough set is a tool for the assessment of uncertainty, and the rough set reducts formation is the technique to remove uncertainty in the feature set for feature subset selection. This work uses uncertainty theory from the rough set perspective to find uncertainty optimization-based reducts (UOR). We formulate an algorithm based on uncertainty optimization to obtain reducts of the feature set for effectiveness and performance enhancement in feature selection. The average accuracy of the reducts found by the UOR algorithm is up to 96.66%. The proposed reduct approach is compared with the existing methods using the same numerical datasets. The comparison results show that the UOR method finds feature subsets of minimum sizes with similar classification accuracy compared to existing reduct methods.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1982) Variants of uncertainty. Cognition 11(2):143–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0277(82)90023-3
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01001956
Ahmed W, Beg M, Ahmad T (2020) A fuzzy rough set based fitting approach for fuzzy set-valued information system. Int J Inf Technol 12(4):1355–1364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-019-00304-y
Sadiq M, Devi VS (2021) A rough-set based approach for the prioritization of software requirements. Int J Inf Technol pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00749-0
Pawlak Z (2012) Rough sets: Theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. vol. 9. Springer, New York
Zhang X, Wu J, Yang X, Ou H, Lv T (2009) A novel pattern extraction method for time series classification. Optim Eng 10(2):253–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-008-9056-0
Wroblewski J (1995) Finding minimal reducts using genetic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the second annual join conference on information science. vol. 2; pp 186–189
Nguyen HS, Slezak D (1999) Approximate reducts and association rules. In: International Workshop on Rough Sets, Fuzzy Sets, Data Mining, and Granular-Soft Computing. Springer, pp 137–145
Zhang X, Miao D (2017) Three-way attribute reducts. Int J Approx Reason 88:401–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2017.06.008
Mafarja MM, Mirjalili S (2019) Hybrid binary ant lion optimizer with rough set and approximate entropy reducts for feature selection. Soft Comput 23(15):6249–6265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3282-y
Rodriguez-Diez V, Martinez-Trinidad JF, Carrasco-Ochoa JA, Lazo-Cortes MS, Olvera-Lopez JA (2020) MinReduct: a new algorithm for computing the shortest reducts. Pattern Recogn Lett 138:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.07.004
Cornejo ME, Medina J, Ramirez-Poussa E (2018) Characterizing reducts in multi-adjoint concept lattices. Inf Sci 422:364–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.08.099
Nandhini N, Thangadurai K (2019) An incremental rough set approach for faster attribute reduction. Int J Inf Technol pp 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-019-00326-6
Aven T, Renn O (2009) On risk defined as an event where the outcome is uncertain. J Risk Res 12(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669870802488883
Motro A, Smets P (1997) Uncertainty management in information systems: from needs to solutions. Springer, New York
Wiltbank R, Read S, Dew N, Sarasvathy SD (2009) Prediction and control under uncertainty: outcomes in angel investing. J Bus Ventur 24(2):116–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2007.11.004
Moradkhani M, Amiri A, Javaherian M, Safari H (2015) A hybrid algorithm for feature subset selection in high-dimensional datasets using FICA and IWSSr algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 35:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.03.049
Benitez-Caballero MJ, Medina J, Ramirez-Poussa E, Slezak D (2018) Bireducts with tolerance relations. Inf Sci 435:26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.12.037
Hosseini ES, Moattar MH (2019) Evolutionary feature subsets selection based on interaction information for high dimensional imbalanced data classification. Appl Soft Comput 82:105581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105581
Manikandan G, Abirami S (2021) An efficient feature selection framework based on information theory for high dimensional data. Appl Soft Comput 111:107729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107729
Polkowski L (2013) Rough sets in knowledge discovery 2: applications, case studies and software systems. vol. 19. Physica
Padula SL, Gumbert CR, Li W (2006) Aerospace applications of optimization under uncertainty. Optim Eng 7(3):317–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-006-9974-7
Romero VJ, Ayon DV, Chen CH (2006) Demonstration of probabilistic ordinal optimization concepts for continuous-variable optimization under uncertainty. Optim Eng 7(3):343–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-006-9978-3
Elishakoff I, Ohsaki M (2010) Optimization and anti-optimization of structures under uncertainty. World Scientific, Singapore
Rahal S, Li Z (2021) Norm induced polyhedral uncertainty sets for robust linear optimization. Optim Eng pp 1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-021-09659-3
Ziarko W (1993) Variable precision rough set model. J Comput Syst Sci 46(1):39–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0000(93)90048-2
Bubnicki Z (2001) Uncertain variables and their application to decision making problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A: Syst Hum 31(6):587–596. https://doi.org/10.1109/3468.983415
Liu B (2007) Uncertainty theory. Springer, New York, pp 205–234
Pawlak Z (2002) Rough sets and intelligent data analysis. Inf Sci 147(1–4):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-0255(02)00197-4
Sugeno M (1993) Fuzzy measures and fuzzy integrals-a survey. In: Readings in fuzzy sets for intelligent systems. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 251–257
Bohning D, Bohning W, Holling H (2008) Revisiting Youden’s index as a useful measure of the misclassification error in meta-analysis of diagnostic studies. Stat Methods Med Res 17(6):543–554. https://doi.org/10.1177/0962280207081867
Fisher RA (1936) The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann Eugen 7(2):179–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.1936.tb02137.x
Kumar A, Prasad PS (2021) Incremental fuzzy rough sets based feature subset selection using fuzzy min–max neural network preprocessing. Int J Approx Reason 139:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2021.09.006
Zhang X, Mei C, Chen D, Yang Y, Li J (2019) Active incremental feature selection using a fuzzy-rough-set-based information entropy. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(5):901–915. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2959995
Ni P, Zhao S, Wang X, Chen H, Li C, Tsang EC (2020) Incremental feature selection based on fuzzy rough sets. Inf Sci 536:185–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.04.038
Bazan JG, Nguyen HS, Nguyen SH, Synak P, Wroblewski J (2000) Rough set algorithms in classification problem. In: Rough set methods and applications. Springer, New York, pp 49–88
Bazan JG, Szczuka M (2005) The rough set exploration system. In: Transactions on Rough Sets III. Springer, New York, pp 37–56
Dua D, Graff C (2017) UCI machine learning repository. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/index.php
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the Department of Mathematics, National Institute of Technology Raipur (C. G.), India, for giving facilities, space, and an opportunity for the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, A.K., Shende, P. & Namdev, N. Uncertainty optimization based feature subset selection model using rough set and uncertainty theory. Int. j. inf. tecnol. 14, 2723–2739 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-022-00994-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-022-00994-x