Abstract
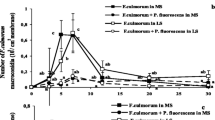
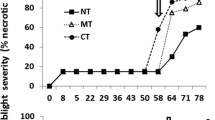
The seasonal population dynamics of Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli (Fsp) in naturally infested soil and the severity of Fusarium root rot were studied. Areas were sequentially planted (2 to 4 sowings) with the same legume crop (common bean, pigeonpea, sunn hemp, and jack bean) or cereal crop (corn, pearl millet and signalgrass) during the year, which were then compared to background bare soil. Counts of colony forming units (CFU) of Fsp populations during 12 sampling times spaced around one month were high at the first sowing and decreased in the bare soil and cereal crops. CFU reached zero after 9 months in the maize and pearl millet plots and after 11 months in the bare soil and signalgrass plots. The count of CFU in the legume plots peaked during the summer and decreased during the winter, in a pattern that followed monthly air temperatures. Disease severity was higher in common bean than in the other crops and tended to increase over time. Planting of legumes should be avoided in infested soil and cereal crops may be an option to reduce and even eradicate inoculum as part of an integrated disease management of Fusarium root rot.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abawi GS, Pastor-Corrales MA (1990) Root rots of beans in Latin America and Africa: diagnosis, research methodologies, and management strategies. CIAT, Cali
Berni RF, Silveira PM, Costa JLS (2002) Influência do preparo de solo e da rotação de culturas na severidade de podridões radiculares no feijoeiro comum. Pesq Agrop Trop 32:69–74
Burke DW, Hall R (1991) Fusarium root rot. In: Hall R (ed) Compendium of Bean Diseases. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 9–10
Costa G, Costa J (2004) Influência da densidade de inóculo de Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli na severidade da podridão radicular seca do feijoeiro. Pesq Agrop Trop 34:89–92
Hall R, Phillips LG (1992) Effects of crop sequence and rainfall on population dynamics of Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli in soil. Can J Bot 70:2005–2008
Lewis JA, Papavizas GC (1977) Effect of plant residues on chlamydospore germination of Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli and on Fusarium root rot of bean. Phytopathology 67:925–929
Mondal SN, Hyakumachi M (1998) Carbon loss and germinability, viability, and virulence of chlamydospores of Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli after exposure to soil at different pH levels, temperatures, and matric potentials. Phytopathology 88:148–155
Nicoli A, Zambolim L, Paula Júnior TJ, Vieira RF, Teixeira H, Carneiro JES (2012) Resistance of advanced common bean lines to Fusarium root rot. Trop Plant Pathol 37:393–398
Paula Júnior TJ, Lobo Júnior M, Sartorato A, Vieira RF, Carneiro JES, Zambolim L (2006) Manejo integrado de doenças do feijoeiro em áreas irrigadas - Guia Técnico. EPAMIG-CTZM, Viçosa
Paula Júnior TJ, Teixeira H, Vieira RF, Morandi MAB, Lehner MS, Lima RC, Carneiro JES (2012) Limitations in controlling white mold on common beans with Trichoderma spp. at the fall-winter season. Summa Phytopathol 38:337–340
Teixeira H, Paula Júnior TJ, Vieira RF, Silva MB, Ferro CG, Lehner MS (2012) Trichoderma spp. decrease Fusarium root rot in common bean. Summa Phytopathol 38:334–336
Toledo-Souza ED, Silveira PM, Lobo Junior M, Café Filho AC (2008) Sistemas de cultivo, sucessões de culturas, densidade do solo e sobrevivência de patógenos de solo. Pesq Agrop Brasileira 43:971–978
Toledo-Souza ED, Lobo Junior M, Silveira PM, Café Filho AC (2009) Interações entre Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli e Rhizoctonia solani na severidade da podridão radicular do feijoeiro. Pesq Agrop Trop 39:13–17
Van Schoonhoven A, Pastor-Corrales MA (1987) Standard system for the evaluation of bean germplasm. CIAT, Cali
Wood SN (2006) Generalized additive models: an introduction with R. Chapman and Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton
Acknowledgments
HT, MSL and RCL wish to thank FAPEMIG for their fellowships. TJPJ, EMDP and RFV wish to thank CNPq for their fellowships. This work was supported by FAPEMIG and CNPq grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Paul Esker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, H., Júnior, T.J.P., Vieira, R.F. et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil-borne inoculum and severity of Fusarium root rot of common beans affected by sequential planting of legume or cereal crops. Trop. plant pathol. 40, 335–338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-015-0047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-015-0047-3