Abstract
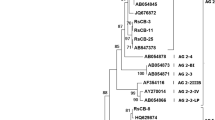
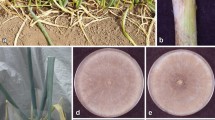
In Argentina, more than 60 % of the tobacco crops are grown in the northwestern part of the country and where Rhizoctonia solani leads to a reduction in crop yield and quality. In this study, 35 isolates of Rhizoctonia were obtained from 32 tobacco fields in northwestern Argentina and characterized by both morphological and molecular approaches. Based on the variability in the ITS region, isolates were identified as R. solani (80 %), Waitea circinata var. zeae (Rhizoctonia zeae) (8 %) and binucleate Rhizoctonia (8 %). Most isolates of R. solani belonged to the anastomosis groups (AGs) AG 4 HG-I (44 %), AG 2-1 (41 %) and AG 4 HG-III (13 %). Isolates of binucleate Rhizoctonia belonged to AG-F and AG-P of Ceratobasidium sp. Morphological variability was higher within isolates of AG 2-1 and AG 4 HG-III than within those of AG 4 HG-I. Aggressiveness of the isolates towards tobacco seedlings was assessed in the greenhouse. Isolates of AG 2-1 were the most aggressive on leaves, causing target spot, whereas isolates of AG 4 HG-I were the most aggressive on stems and roots, causing damping-off.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfenas A, Valverde E, Gomeide E, Ferreira A, Murilo F, Pereira F, Rogeiro J, Grassi L, Maffia L, Pereira O, Alfenas P, Gonçalves R, Gonçalves R, D’Arc R, Dos Santos W (2007) Métodos em Fitopatologia. Brasil. Ed. Universidade de Visçosa, Visçosa
Bacharis C, Gouziotis A, Kalogeropoulou P, Koutita O, Tzavella-Klonari K, Karaoglanidis G (2010) Characterization of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates associated with damping-off disease in cotton and tobacco seedlings in Greece. Plant Dis 94:1314–1322
Carling D (1996) Grouping in Rhizoctonia solani by hyphal anastomosis reaction. In: Sneh B, Jabaji-Hare S, Neate S, Dijst G (eds) Rhizoctonia Species: taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 37–47
Ceresini PC, Shew HD, Vilgalys RJ, Cubeta MA (2002) Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 from potato and tobacco in North Carolina. Mycologia 94:437–449
Csinos AS, Stephenson MG (1999) Evaluation of fungicides and tobacco cultivar resistance to Rhizoctonia solani incited target spot, damping-off and sore shin. Crop Prot 18:373–377
Food and Agriculture Organization-FAO (2012) Production Crops 2012. http://www.faostat.fao.org/site/567/default.aspx#ancor.html. Accessed 3 Oct 2014
Garcia MG, Ramos ER, Chacon OC, Bocourt YP, Ochoa RR (2009) First report of binucleate Rhizoctonia causing damping-off in tobacco seedlings in Cuba. Fitosanidad 13:221
Godoy-Lutz G, Steadman JR, Higgins B, Powers K (2003) Genetic variation among isolates of the web blight pathogen of common bean based on PCR–RFLP of the ITS-rDNA region. Plant Dis 87:766–771
Godoy-Lutz G, Kuninaga S, Steadman JR, Powers K (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani subgroups associated with web blight symptoms on common bean based on ITS-5.8S rDNA. J Gen Plant Pathol 74:32–40
González García M (2008) Aspectos de sistemática y biología del complejo Rhizoctonia. Fitosanidad 12:147–159
González M, Pujol M, Metraux J, González-García V, Bolton M, Borrás-Hidalgo O (2011) Tobacco leaf spot and root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani Künh. Mol Plant Pathol 12(3):209–216
Gurkanli CT, Ozkoc I (2011) First report of B.N. Rhizoctonia from Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) in Samsum, Turkey. Pak J Bot 43:51–57
Gurkanli CT, Ozkoc I, Gunduz I (2009) Molecular and conventional identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) in Samsun, Turkey. J Phytopathol 157:686–696
Gutierrez WA, Shew HD, Melton TA (1997) Sources of inoculum and management for Rhizoctonia solani damping-off on tobacco transplants under greenhouse conditions. Plant Dis 81:604–606
Hall T (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series 41:95–98. Available at: http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html. Accessed 6 Oct 2014
Johnk JS, Jones RK (1993) Differentiation of population of AG-2-2 of Rhizoctonia solani by analysis of fatty acids. Phytopathology 83:278–283
Jones RK, Belmar SB (1989) Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. isolated from rice, soybean, and other crops grown in rotation with rice in Texas. Plant Dis 73:1004–1010
Laroche JP, Jabaji-Hare S, Charest PM (1992) Differentiation of two anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani by isozyme analysis. Phytopathology 82:1387–1393
Li H, Wu B, Yan S (1998) Aetiology of Rhizoctonia in sheath blight of maize in Sichuan. Plant Pathol 47:16–21
Liu ZL, Sinclair JB (1993) Differentiation of intraspecific groups within anastomosis group I of Rhizoctonia solani using ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer and isozyme analysis. Can J Plant Pathol 12:376–382
Liu ZL, Domier LL, Sinclair JB (1993) ISG-specific ribosomal DNA polymorphism of the Rhizoctonia solani species complex. Mycologia 85:795–800
Lucas G (1975) Diseases of Tobacco. 3rd ed. Biological Consulting Associates, Box 5726. Raleigh, North Carolina. Parker and Sons Printers
Masuka AJ (1998) Binucleate Rhizoctonia on tobacco in Zimbawe. Plant Dis 82:263
Mercado Cárdenas G, Galván M, Barrera V, Carmona M (2012) First report of target spot of tobacco caused by Rhizoctonia solani (AG-2.1). Plant Dis 96:456
Nicoletti R, Lahoz E (1995) Recovery of Rhizoctonia solani AG-5 from tobacco in Italy. Plant Dis 79:540
Nicoletti R, Lahoz E, Kanematsu S, Naito S, Contillo R (1999) Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from tobacco fields related to anastomosis groups 2-1 and BI (AG 2-1 and AG BI). J Phytopathol 147:71–77
Page RD (1996) TREEVIEW: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Pascual CB, Toda T, Raymondo AD, Hyakumachi M (2000) Characterization by conventional techniques and PCR of Rhizoctonia solani isolates causing banded leaf sheath blight in maize. Plant Pathol 49:108–118
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA, Chen W, Fungal Barcoding Consortium (2012) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for fungi. Proc Nat Acad Sci 109:6241–6246
Sharon M, Kuninaga S, Hyakumachi M, Sneh B (2006) The advancing identification and classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using molecular and biotechnological methods compared with the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 47:299–316
Sharon M, Kuninaga S, Hyakumachi M, Naito S, Sneh B (2008) Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 49:93–114
Sherwood RT (1969) Morphology and physiology in four anastomosis groups of Thanatephorus cucumeris. Phytopathology 59:1924–1929
Shew HD, Lucas GB (1991) Compendium of tobacco diseases. The American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul
Shew HD, Melton TA (1995) Target spot of tobacco. Plant Dis 79:6–11
Sneh B, Burpee L, Ogoshi A (1991) Identification of Rhizoctonia species. The American Phytopathological Society, APS Press, EE.UU
Stenglein SA, Balatti PA (2006) Genetic diversity of Phaeoisariopsis griseola in Argentina as revealed by virulence and molecular markers. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 68:158–167
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods), Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA
Tarantino P, Caiazzo R, Carella A, Lahoz E (2007) Control of Rhizoctonia solani in a tobacco-float system using low rates of iprodione and iprodione-resistant strains of Gliocladium roseum. Crop Prot 26:1298–1302
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thorn RG, Reddy CA, Harris D, Paul EA (1996) Isolation of saprophytic Basidiomycetes from soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4288–4292
Tu C, Hsieh T, Chang Y (1996) Vegetable diseases incited by Rhizoctonia sp. In: Sneh B, Jabaji-Hare S, Neate S, Dijst G (eds) Rhizoctonia Species: taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 369–377
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press Inc, New York, pp 315–322
Zhao Y, Wu Y, Fu Y, An M, Chen J, Zhao X (2013) Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 isolates causing Target Spot of Flue-cured Tobacco in China. Adv Mater Res 17:4321–4325
Acknowledgments
We thank C. Sanchez for statistical advice. Thanks are also given to Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria for providing a doctorate fellowship for the first author and support by means of research grants (PNIN082511 and PRSalJu09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Adalberto Café-Filho
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercado Cárdenas, G.E., Galván, M.Z., Barrera, V.A. et al. Molecular identification and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. from tobacco growing areas in northwestern Argentina. Trop. plant pathol. 40, 160–168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-015-0035-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-015-0035-7