Abstract
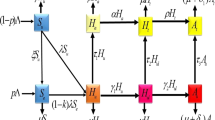
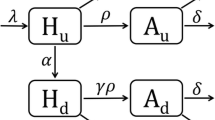
In response to the severe HIV/AIDS epidemic in Botswana, the Botswana government recently adopted the test and treat strategy which provides immediate treatment to people who test positive to HIV. In this paper, a deterministic HIV/AIDS model incorporating the test and treat strategy, individuals dropping out and re-enrolling to treatment is formulated and analysed. The model has two steady states, the disease free and the endemic equilibrium points. The global stabilities of the disease-free and the endemic equilibria using Lyapunov functions are established. The model is fitted to Botswana HIV/AIDS data to estimate model parameters. The numerical results and projections show that a combination of increasing enrolment and retainment to treatment reduce the disease spread but is not enough to end the disease. The results suggest the need to reduce new infections in order to end the epidemic.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNAIDS Ending AIDS:Progress towards 90-90-90 targets, (2017). http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/20170720_Global_AIDS_update_2017
UNAIDS ‘The Gap Report’, (2014). http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/campaigns/2014/2014gapreport/gapreport
UNAIDS Prevention Gap Report, (2016). http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2016/prevention-gap
Nah, K., Nishiura, H., Tsuschiya, N., Sun, X., Imamura, A.: Test-and-treat approach to HIV/AIDS: a primer for mathematical modeling. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 14, 16 (2017)
Granich, R.M., Gilks, C.F., Dye, C., De Cock, K.M., Williams, B.G.: Universal voluntary HIV testing with immediate antiretroviral therapy as a strategy for elimination of HIV transmission: a mathematical model. Lancet 373, 48–57 (2009)
Quinn, T.C., Wawer, M.J., Sewankambo, N., Serwadda, D., Li, C., Wabwire-Mangen, F., et al.: Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. For Rakai Project Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 342, 921–929 (2000)
World Health Organisation: Guideline on when to start antiretroviral therapy and on pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV. In; (2015). http://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/earlyrelease-arv/en/
Eaton, J.W., Johnson, L.F., Salomon, J.A., Bärnighausen, T., Bendavid, E., Bershteyn, A., et al.: HIV treatment as prevention: systematic comparison of mathematical models of the potential impact of antiretroviral therapy on HIV incidence in South Africa. PLoS Med. 9(7), e1001245 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001245
Dodd, P.J., Garnett, G.P., Hallett, T.B.: Examining the promise of HIV elimination by ’test and treat’ in hyperendemic settings. AIDS 24(5), 729–735 (2010)
HIV Modelling Consortium Treatment as Prevention Editorial Writing Group. HIV treatment as prevention: Models, data, and questions-towards evidence-based decision-making. PloS Med 9(7), e1001259, (2012)
Baggaley, R.F., Garnett, G.P., Ferguson, N.M.: Modelling the impact of antiretroviral use in resource-poor settings. PLoS Med. 3, e124 (2006)
Shah, M., Risher, K., Berry, S.A., Dowdy, D.W.: The epidemologic and economic impact of improving HIV testing, linkage and retention in care in the United States. Clin. Infet. Dis. 62, 220–229 (2016)
Sorensen, S.W., Sansom, S.L., Brooks, J.T., Marks, G., Begier, E.M., Buchacz, K., et al.: A mathematical model of comprehensive test-and-treat services and HIV incidence among men who have sex with men in the United States. PLoS ONE 7(2), e29098 (2012)
Luo, S., Han, L., Lu, H., Tao, Q., et al.: Evaluating the impact of test-and-treat on the HIV epidemic among MSM in China Using a mathematical model. PLOS ONE 10(6), e0126893 (2015)
McCreesh, N., Andrianakis, I., Nsubuga, R.N., Strong, M., Vernon, I., McKinley, T.J., Oakley, J.E., Goldstein, M., Hayes, R., White, R.G.: Universal test, treat, and keep: improving ART retention is key in cost-effective HIV control in Uganda. BMC Infect. Dis. 17, 322 (2017)
Omondi, E.O., Mbogo, R.W., Luboobi, L.S.: Modelling the trend of HIV transmission and treatment in Kenya. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 4(5), 123 (2018)
Rahman, S.M.A., Vaidya, N.K., Zou, X.: Impact of early treatment programs on HIV epidemics: an immunity-based mathematical model. Math. Biosci. 280, 38–49 (2016)
Hove-Musekwa, S.D., Nyabadza, F.: The dynamics of an HIV/AIDS model and screened disease carriers. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 10(4), 289–305 (2009)
van den Driessche, P., Watmought, J.: Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibrium for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180, 29–48 (2002)
Marks, G., Crepaz, N., Janssen, R.S.: Estimating sexual transmission of HIV from persons aware and unaware that they are infected with the virus in the USA. AIDS 20, 1447–1450 (2006)
Kretzschmara, M.E., van der Loeffc, M.F.S., Birrelle, P.J., De Angelise, D., Coutinho, R.A.: Prospects of elimination of HIV with test-and-treat strategy. PNAS 110(39), 15538–15543 (2013). www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2014/90-90-90
UNAIDS. 90-90-90: An ambitious treatment target to help end AIDS epidemic. UNAIDS, (2014). http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/90-90-90_en.pdf
Farahani, M., Vable, A., Lebelonyane, R., Seipone, K., Anderson, M., et al.: Outcomes of the Botswana national HIV/AIDS treatment programme from 2002 to 2010: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2, e44–50 (2014)
Gaolathe, T., Wirth, K.E., Holme, M.P., et al.: Botswana’s progress toward achieving the 2020 UNAIDS 90–90-90 antiretroviral therapy and virological suppression goals: a population-based survey. Lancet HIV 3(5), e221–230 (2016). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/23523018
Williams, B.G., Gupta, S., Wollmers, M., Granich, R.: The impact and cost of ending AIDS in Botswana. Lancet HIV 3(9), e409 (2016)
Population Division of the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations Secretariat, World Population Prospects: The 2010 Revision https://population.un.org
Saltelli, A., Ratto, M., Andres, T., Campolongo, F., Cariboni, J., Gatelli, D., Saisana, M., Tarantola, S.: Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, UK (2008)
Chitnis, N., Hyman, J.M.: Determining important parameters in the spread of malaria through the sensitivity analysis of a mathematical model. Bull. Math. Biol. 70, 1272–1296 (2008)
Mushanyu, J., Nyabadza, F., Muchatibaya, G., Stewart, A.G.R.: On the role of imitation on adolescences mathemphetamine abuse dynamics. Acta Boitheor. 65, 37–61 (2017)
Farahani, M., Vable, A., Lebelonyane, R., et al.: Outcomes of the Botswana national HIV/AIDS treatment programme from 2002 to 2010: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2, e44–50 (2014)
Blower, S.M., Dowlatabadi, H.: Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of complex models of disease transmission: an HIV model, as example. Int. Stat. Rev. 2, 229–243 (1994)
Nyabadza, F., Njagarah, J.B.H., Smith, R.J.: Modelling the dynamics of crystal meth (’Tik’) abuse in the pesence of drug-supply chains in South Africa. Bull. Math. Biol. 75, 24–48 (2013)
Ehlers, V.J., Tshisuyi, E.T.: Adherence to antiretroviral treatment by adults in a rural area of Botswana. Curationis 38(1), 1255 (2015)
Kgatlwane, J., Ogenyi, R., Ekezie, C., et al.: Factors that facilitate or constrain adherence to antiretroviral therapy among adults at four public health facilities in Botswana: A pre-intervention study, in World Health Organization, From access to adherence: The challenges of antiretroviral treatment – studies from Botswana, Tanzania and Uganda. WHO, Geneva, pp. 75–164 (2006). http://archives.who.int/prduc2004/Book/MULTICOUNTRY.pdf
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the University of Johannesburg during the production of the manuscript. TK would like to acknowledge the support of the Botswana International University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaisara, T., Nyabadza, F. On the Future of HIV/AIDS in Botswana in the Presence of Drop-Outs: Insights from a Simple Mathematical Model. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math 6, 116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-020-00843-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40819-020-00843-0