Abstract
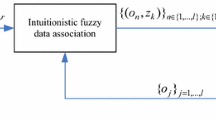
In this paper, a novel intuitionistic fuzzy clustering algorithm based on feature selection (IFC-FS) for multiple object tracking is proposed. In the proposed algorithm, the neighborhood rough set is used to achieve the adaptive selection of the multiple object features of visual objects, which are applied to calculate the distance similarity measure between the objects and the observations. At the same time, in order to incorporate the local information of objects into the intuitionistic fuzzy clustering, the local information distances between objects and observations are estimated by using the optimal subpattern assignment metric based on the reference topology set, and a new intuitionistic fuzzy clustering based on maximum entropy principle is proposed by using the new similarity distance measure. Finally, the association probabilities among the objects and the observations are reconstructed by utilizing the intuitionistic fuzzy membership degrees. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the estimated accuracy and robustness of the association probabilities between the objects and the observations, and have the ability to track accurately multiple objects in the complex background and long-time occlusion environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulbacki, M., Segen, J., Wojciechowski, S., et al.: Intelligent video monitoring system with the functionality of online recognition of people’s behavior and interactions between people. In: Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, 2018, pp. 492–501
Cermeño, E., Pérez, A., Sigüenza, J.A.: Intelligent video surveillance beyond robust background modeling. Expert Syst. Appl. 91(1), 138–149 (2018)
Han, D.T., Suhail, M., Ragan, E.D.: Evaluating remapped physical reach for hand interactions with passive haptics in virtual reality. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 24(4), 1467–1476 (2018)
Chen, C.: A study of the multi-feature gesture recognition tracking algorithm in VR-based human-computer interaction. Softw. Eng. 20(12), 23–25 (2017)
Pop, S., Luculescu, M.C., Cristea, L., et al.: Improving communication between unmanned aerial vehicles and ground control station using antenna tracking systems. In: Auer, M., Zutin, D. (eds.) Online engineering and internet of things, vol. 22, pp. 532–539. Springer, Cham (2018)
Salucci, M., Robol, F., Anselmi, N., et al.: S-band spline-shaped aperture-stacked patch antenna for air traffic control applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66(8), 4292–4297 (2018)
Cano, P., Ruiz-Del-Solar, J.: Robust tracking of soccer robots using random finite sets. IEEE Intell. Syst. 32(6), 22–29 (2018)
Xu, X., Li, W., Ran, Q., et al.: Multisource remote sensing data classification based on convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56, 1–13 (2018)
Han, J., Zhang, D., Cheng, G., et al.: Advanced deep-learning techniques for salient and category-specific object detection: a survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 35(1), 84–100 (2018)
Yang, H., Shao, L., Zheng, F., et al.: Recent advances and trends in visual tracking: a review. Neurocomputing 74(18), 3823–3831 (2011)
Jang, S.I., Choi, K., Toh, K.A., et al.: Object tracking based on an online learning network with total error rate minimization. Pattern Recogn. 48(1), 126–139 (2015)
Ross, D.A., Lim, J., Lin, R.S., et al.: Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 77(1–3), 125–141 (2008)
Azab, M.M., Shedeed, H.A., Hussein, A.S.: New technique for online object tracking-by-detection in video. IET Image Proc. 8(12), 794–803 (2014)
Zhang, S., Yao, H., Zhou, H., et al.: Robust visual tracking based on online learning sparse representation. Neurocomputing 100(1), 31–40 (2013)
Jang, S.I., Choi, K., Toh, K.A., et al.: Object tracking based on an online learning network with total error rate minimization. Pattern Recogn. 48(1), 126–139 (2015)
Mei, X., Ling, H.: Robust visual tracking using ℓ1 minimization. In: International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2009, pp. 1436–1443
Gao, J., Zhang, T., Yang, X., et al.: Deep relative tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(4), 1845–1858 (2017)
Wang, L., Ouyang, W., Wang, X., et al.: Visual tracking with fully convolutional networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE Computer Society, 2015, pp. 3119–3127
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J.F., et al.: Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2016), 2016, pp. 850–865
Atanassov, K.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(1), 87–96 (1986)
Atanassov, K.: Intuitionistic fuzzy logics as tools for evaluation of data mining processes. Knowl. Based Syst. 80, 122–130 (2015)
Chaira, T.: A novel intuitionistic fuzzy C means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images. Appl. Soft Comput. 11, 1711–1717 (2011)
Li, L.Q., Xie, W.X.: Intuitionistic fuzzy joint probabilistic data association filter and its application to multiobject tracking. Signal Process. 96(3), 433–444 (2014)
Li, J., Xie, W.X., Li, L.Q.: Online visual multiple object tracking by intuitionistic fuzzy data association. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(2), 1–12 (2016)
Li, L., Zhan, X., Liu, Z., Xie, W.: Fuzzy logic approach to visual multi-object tracking. Neurocomputing 281(3), 139–151 (2018)
Pawlak, Z.: Rough sets. Int. J. Comput. Inform. Sci. 11(5), 341–356 (1982)
Changzhong, W., Mingwen, S., Qiang, H., Yuhua, Q., Yali, Q.: Feature subset selection based on fuzzy neighborhood rough sets. Knowl. Based Syst. 111(11), 173–179 (2016)
Todorova, L., Vassilev, P.: Algorithm for clustering data set represented by intuitionistic fuzzy estimates. Int. J. Bioautom. 14(1), 61–68 (2010)
Liangqun, L., Hongbing, J., Xinbo, G.: Maximum entropy fuzzy clustering with application to real-time target tracking. Signal Process. 86(11), 3432–3447 (2006)
Tian, W., Wang, Y., Shan, X., Yang, J.: Track-to-track association for biased data based on the reference topology feature. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21(4), 449–453 (2014)
Bae, S., Yoon, K.: Robust online multi-object tracking based on tracklet confidence and online discriminative appearance learning. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2014, pp. 1218–1225
Son, J., Baek, M., Cho, M., Han, B.: Multi-object tracking with quadruplet convolutional neural networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017, pp. 5620–5629
Fischler, M.A., Bolles, R.C.: Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Read. Comput. Vis. 24(6), 726–740 (1987)
Milan, A., Rezatofighi, S., Dick, A., Reid, I. Schindler, K.: Online multi-target tracking using recurrent neural networks. In: AAAI, 2017, pp. 1–9
Dollár, P., Appel, R., Belongie, S.: Fast feature pyramids for object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(8), 1532–1545 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61773267, 61301074), Science and Technology Program of Shenzhen (JCYJ20170302145519524, JCYJ20170818102503604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Lq., Wang, Xl., Liu, Zx. et al. A Novel Intuitionistic Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm Based on Feature Selection for Multiple Object Tracking. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1613–1628 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00645-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00645-7