Abstract
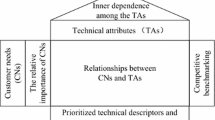
Collaborative product development (CPD) is a technology intensive process and effective planning in information technologies (IT) can improve the performance of CPD activities. Considering that quality function deployment (QFD) can be utilized as a planning tool for products and systems, the use of the QFD can enable IT systems to align their structure for CPD. In the QFD approach, the house of quality matrix is used for converting customer requirements into engineering characteristics. The challenge in this process is the profile of the inputs that are collected from the participants who provide feedback on customer requirements. Individual judgments of these participants can be in various formats, or can indicate preferences that are incomplete. This study aims to tackle with this issue by making use of an extended QFD methodology in CPD for IT planning. For this purpose, two group decision making (GDM) approaches are used to address both challenges of multiple preference formats and incomplete information. The validity of the developed IT planning model for CPD is tested with a case study at a Turkish software company using the two GDM approaches, and the obtained results are discussed. As customer requirements are important at every phase of CPD, the proposed model can help implementers to improve their decision processes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsai, K.H.: Collaborative networks and product innovation performance: toward a contingency perspective. Res. Policy 38(5), 765–778 (2009)
Shen, W., Hao, Q., Li, W.: Computer supported collaborative design: retrospective and perspective. Comput. Ind. 59(9), 855–862 (2008)
Büyüközkan, G., Çifçi, G.: A new incomplete preference relations based approach to quality function deployment. Inf. Sci. 206(5), 30–34 (2012)
Büyüközkan, G., Çifçi, G.: An integrated QFD framework with multiple formatted and incomplete preferences: a sustainable supply chain application. Appl. Soft Comput. 13(9), 3931–3941 (2013)
Nahm, Y.-E., Ishikawa, H., Inoue, M.: New rating methods to prioritize customer requirements in QFD with incomplete customer preferences. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 65, 1587–1604 (2013)
Büyüközkan, G., Feyzioğlu, O.: Group decision making to better respond customer needs in software development. Comput. Ind. 48(2), 427–441 (2005)
Yeh, C.-H., Deng, H., Wibowo, S., Xu, Y.: Fuzzy multicriteria decision support for information systems project selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12(2), 170–179 (2010)
Urena, R., Chiclana, F., Alonsc, S., Morente-Molineraa, J.A., Herrera-Viedmaa, E.: On incomplete fuzzy and multiplicative preference relations in multi-person decision making. Proc. Comput. Sci. 31, 793–801 (2014)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Chiclana, F.: Multiperson decision-making based on multiplicative preference relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 129(2), 372–385 (2001)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Yu, S.: Linguistic multi-person decision making based on the use of multiple preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 160(5), 603–623 (2009)
Zhang, Z., Chu, X.: Fuzzy group decision-making for multi-format and multi-granularity linguistic judgments in quality function deployment. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(5), 9150–9158 (2009)
Rodriguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: A group decision making model dealing with comparative linguistic expressions based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Inf. Sci. 241, 28–42 (2013)
Chen, S.-M., Lin, T.-E., Lee, L.-W.: Group decision making using incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on the additive consistency and the order consistency. Inf. Sci. 259, 1–15 (2014)
Büyüközkan, G., Feyzioğlu, O., Ruan, D.: Fuzzy group decision making to multiple preference formats in quality function deployment. Comput. Ind. 58(5), 392–402 (2007)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Alonso, S.: A consensus model for group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15(5), 863–877 (2007)
Xu, Z.: Incomplete linguistic preference relations and their fusion. Information Fusion 7(3), 7331–7337 (2006)
Xu, Z.: A practical procedure for group decision making under incomplete multiplicative linguistic preference relations. Group Decis. Negot. 15(6), 581–591 (2006)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Alonso, S.: Group decision-making model with incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on additive consistency. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 37(1), 176–189 (2007)
Liu, F., Zhang, W.-G.: TOPSIS-based consensus model for group decision-making with incomplete interval fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(8), 1283–1294 (2014)
Akao, Y.: Quality Function Deployment: Integrating Customer Requirements into Product Design. Productivity Press, Cambridge MA (1990)
Wang, X.T., Xiong, W.: An integrated linguistic based group decision making approach for quality function deployment. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(1), 14428–14438 (2011)
Ayağ, Z., Samanlıogluand, F., Büyüközkan, G.: A fuzzy QFD approach to determine supply chain management strategies in the dairy industry. J. Intell. Manuf. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0639-4
Shin, J.-S., Kim, K.-J.: Complexity reduction of a design problem in QFD using decomposition. J. Intell. Manuf. 11, 339–354 (2000)
Ding, J.F.: Applying fuzzy quality function deployment (QFD) to identify solutions of service delivery system for port of Kaohsiung. Qual. Quant. 43(4), 553–570 (2009)
Kutschenreiter-Praszkiewicz, I.: Application of neural network in QFD matrix. J. Intell. Manuf. (2013). doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0604-7
Chan, K., Wu, M.L.: Quality function deployment: a literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 143(3), 463–497 (2002)
Zandi, F., Tavana, M.: A fuzzy group quality function deployment model for e-CRM framework assessment in agile manufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 61(1), 1–19 (2011)
Zaim, S., Sevkli, M., Camgöz-Akdag, H., Demirel, O.F., Yayla, A.Y., Delen, Dursun: Use of ANP weighted crisp and fuzzy QFD for product development. Expert Syst. Appl. 41, 4464–4474 (2014)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F., F.Chiclana, : A consensus model for multiperson decision making with different preference structures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A 32(3), 394–402 (2002)
Liu, C.-H.: A group decision-making method with fuzzy set theory and genetic algorithms in quality function deployment. Qual. Quant. 44(6), 1175–1189 (2010)
Li, Y.-I., Tang, J.-F., Chin, K.-S., Luo, X.-G., Pu, Y., Jiang, Y.-S.: On integrating multiple type preferences into competitive analyses of customer requirements in product planning. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 139(1), 168–179 (2012)
Büyüközkan, G., Çifçi, G.: A novel fuzzy multi-criteria decision framework for sustainable supplier selection with incomplete information. Comput. Ind. 62(2), 164–174 (2011)
Han, C.H., Kim, J.K., Choi, S.H.: Prioritizing engineering characteristics in quality function deployment with incomplete information: a linear partial ordering approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 91(3), 235–249 (2004)
Chen, S.-M., Lin, T.-E., Lee, L.-W.: Group decision making using incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on the additive consistency and the order consistency. Inf. Sci. 259, 1–15 (2014)
Wang, T.C., Peng, S.C., Hsu, S.C., Chang, J.: The evaluation of the incomplete linguistic preference relations on the performance of web shops. Ninth Int. Conf. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 2, 363–368 (2009)
Palacio, R.R., Vizcaino, A., Moran, A.L., Gonzalez, V.M.: Tool to facilitate appropriate interaction in global software development. IET Softw. 5(2), 157–171 (2011)
Fraser, P., Farrukh, C., Gregory, M.: Managing product development collaborations a process maturity approach. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B 217(11), 1499–1519 (2003)
Krishnan, V., Bhattacharya, S.: Technology selection and commitment in new product development: the role of uncertanity and design flexibility. Manuf. Sci. 48(3), 313–327 (2002)
Büyüközkan, G., Dereli, T., Baykasoğlu, A.: A survey on the methods and tools of concurrent new product development and agile manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 15, 731–751 (2004)
Lai, L.F.: A knowledge engineering approach to knowledge management. Inf. Sci. 177(19), 4072–4094 (2007)
Rodriguez, K., Al-Ashaab, A.: Knowledge web-based system architecture for collaborative product development. Comput. Ind. 56(1), 125–140 (2005)
Lee, E.S., McDonald, D.W., Anderson, N., Tarczy-Hornoch, P.: Incorporating collaboratory concepts into informatics in support of translational interdisciplinary biomedical research. Int. J. Med. Inform. 78(1), 10–21 (2009)
Hammers, C., Schmitt, R.: Governing the process chain of product development with an enhanced quality gate approach, CIRP. J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 1(3), 206–211 (2009)
Arsenyan, J. Designing and implementing collaboration structure for product development. Ph.D. Thesis, Galatasaray University, (2009)
Alonso, S., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Alcala, J., Porcel, C.: A consistency based procedure to estimate missing pair-wise preference values. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 23(2), 155–175 (2008)
Wang, Y.-M.: A fuzzy-normalisation-based group decision-making approach for prioritising engineering design requirements in QFD under uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Res. 15, 6963–6977 (2011)
Fedrizzi, M., Giove, S.: Incomplete pair wise comparison and consistency optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 183(1), 303–313 (2007)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Alonso, S.: A consensus model for group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 15(5), 863–877 (2007)
Gong, Z.W.: Least square method to priority of the fuzzy preference relations with incomplete information. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 47(2), 258–264 (2008)
Xu, Z.S., Chen, J.: Group decision-making procedure based on incomplete reciprocal relations. Soft. Comput. 12(6), 515–521 (2008)
Chiclana, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Alonso, S.: A note on two methods for estimating missing pair wise preference values. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 39(6), 1628–1633 (2009)
Alonso, S., Herrera-Viedma, E., Chiclana, F., Herrera, F.: A web based consensus support system for group decision making problems and incomplete preferences. Inf. Sci. 180(23), 4477–4495 (2010)
Porcel, C., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Dealing with incomplete information in a fuzzy linguistic recommender system to disseminate information in university digital libraries. Knowl.-Based Syst. 23(1), 32–39 (2010)
Wang, T.C., Chen, Y.H.: Incomplete fuzzy linguistic preference relations under uncertain environments. Inf. Fusion 11(2), 201–207 (2010)
Hsu, S.C., Wang, T.C.: Solving multi-criteria decision making with incomplete linguistic preference relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(9), 10882–10888 (2011)
Xu, Y.: On group decision making with four formats of incomplete preference relations. Comput. Ind. Eng. 61(1), 48–54 (2011)
Liu, F., Zhang, W.G., Wang, Z.X.: A goal programming model for incomplete interval multiplicative preference relations and its application in group decision-making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 218(3), 747–754 (2012)
Zhang, G., Dong, Y., Xu, Y.: Linear optimization modeling of consistency issues in group decision making based on fuzzy preference relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(3), 2415–2420 (2012)
Lee, L.-W.: Group decision making with incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on the additive consistency and the order consistency. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(14), 11666–11676 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This paper is prepared with the support of The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK), within the scope of the research project number 109M147. The authors kindly thank for the financial support provided by TUBITAK and for the contributions of the experts committee members. Gülçin Büyüközkan acknowledges the financial support of the Galatasaray University Research Fund (Project number: 15.402.003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Büyüközkan, G., Güleryüz, S. Extending Fuzzy QFD Methodology with GDM Approaches: An Application for IT Planning in Collaborative Product Development. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 17, 544–558 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0065-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0065-9