Abstract
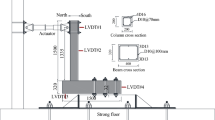
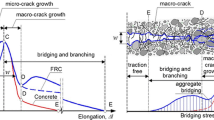
This study aims to investigate the flexural behavior of reinforced concrete (RC) beams strengthened using aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels (AHSPs) with three different thicknesses (6, 10, and 15 mm) and CFRP U-Jackets with different cross-section configurations (i.e. support and middle sections). The experimental performance of RC beams was evaluated utilizing AHSPs and CFRP composites under four-point bending tests. The strengthened RC beams (HCRC-2-HCRC-10) were compared with the control beam (HCRC-1) in terms of flexural load carrying capacity, ductility, failure modes, and cracks patterns. The results revealed that the HCRC-9 beam specimen strengthened using 15 mm thickness AHSP displayed higher flexural performance than its counterparts. The HCRC-9 beam exhibited more ductile behavior, which depends on the failure mode. Strengthening with AHSP decreased visible width shear cracks compared to the un-strengthened beam. It was also detected that increase in the thickness of AHSP improved the flexural behavior of RC beams.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohammed AA, Manalo AC, Maranan GB, Muttashar M, Zhuge Y, Vijay P, Pettigrewg J (2019) Effectiveness of a novel composite jacket in repairing damaged reinforced concrete structures subject to flexural loads. Comp Str 233:111634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111634
Babamohammadi S, Fantuzzi N, Lonardi G (2019) Mechanical assessment of hollow-circular FRP beams. Comp Str 227:111313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111313
Carozzi FG, Bellini A, D’Antino T, Felice G, Focacci F, Hojdys L et al (2017) Experimental investigation of tensile and bond properties of Carbon-FRCM composites for strengthening masonry elements. Comp Part B: Eng 128:100–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.06.018
Li J, Xie J, Liu F, Lu Z (2019) A critical review and assessment for FRP-concrete bond systems with epoxy resin exposed to chloride environments. Comp Str 229:111372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111372
Demers CE (1998) Fatigue strength degradation of E-glass FRP composites and carbon FRP composites. Const Build Mat 12:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(98)00012-9
Hota G, Liang RF, (2011) Advanced fiber reinforced polymer composites for sustainable civil infrastructures, International symposium on innovation & sustainability of structures in civil engineering, Xiamen University, China
Hollaway LC, Head PR (2001) Advanced Polymer Composites and Polymers in the Civil Infrastructure. Elsevier, Oxford
Pham TM, Hao H (2016) Review of concrete structures strengthened with FRP against impact loading. Str 7:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2016.05.003
Maras MM, (2021) Mechanical properties of confined damaged concrete strengthened with fiber reinforced polymer wraps. El-Cez J S Eng 8(2):706–717. https://doi.org/10.31202/ecjse.866687
Frigione M, Lettieri M (2018) Durability issues and challenges for material advancements in FRP employed in the construction industry. Poly 10(3):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030247
Maras MM, Kantarcı F (2021) structural performance of reinforced concrete (RC) moment frame connections strengthened using FRP composite jackets. Arab J Sci Eng 46:10975–10992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06120-6
Nanni A (2003) North American design guidelines for concrete reinforcement and strengthening using FRP: Principles, applications and unresolved issues. Constr Build Mater 17:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-0618(03)00042-4
Turco V, Secondin S, Morbin A, Valluzzi MR, Modena C (2006) Flexural and shear strengthening of un-reinforced masonry with FRP bars. Compos Sci Technol 66(2):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.04.042
Triantafillou TC (1998) Strengthening of masonry structures using epoxy-bonded FRP laminates. J Compos Constr 2(2):96–104. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0268(1998)2:2(96)
Grande E, Imbimbo M, Sacco E (2011) Bond behavior of CFRP laminates glued on clay bricks: experimental and numerical study. Comp Part B 42(2):330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.09.020
Realfonzo R, Napoli A, Pinilla JGR (2014) Cyclic behavior of RC beam–column joints strengthened with FRP systems. Constr Build Mater 54:282–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.12.043
Majumder S, Saha S (2021) Quasi-static cyclic performance of RC exterior beam-column joint assemblages strengthened with geosynthetic materials. Structures 29:1210–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2020.12.010
Majumder S, Saha S (2021) Shear behaviour of RC beams strengthened using geosynthetic materials by external and internal confinement. Structures 32:1665–1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2021.03.107
Majumder S, Saha S (2020) Behaviour of reinforced concrete beam strengthened in shear with geosynthetic. Adv Struct Eng 23(9):1851–1864. https://doi.org/10.1177/1369433220901820
Khan HA, Nanda RP (2020) Out-of-plane bending of masonry wallette strengthened with geosynthetic. Constr Build Mater 231:117198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117198
Maras MM, Kose MM (2021) Structural behavior of masonry panels strengthened using geopolymer composites in compression tests. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45:767–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00433-6
Heimbs S (2009) Virtual testing of sandwich core structures using dynamic finite element simulations. Comput Mater Sci 45:205–216
He M, Hu W (2008) A study on composite honeycomb sandwich panel structure. Mater Des 29(3):709–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2008.09.017
Bai Y, Yu K, Zhao J, Zhao R (2018) Experimental and simulation investigation of temperature effects on modal characteristics of composite honeycomb structure. Compos Struct 201:816–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.06.106
Davalos JF, Qiao P, Xu XF, Robinson J, Barth KE (2001) Modeling and characterization of fiber-reinforced plastic honeycomb sandwich panels for highway bridge applications. Compos Struct 52:441–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(01)00034-4
Renji K, Nair PS, Narayanan S (1996) Modal density of composite honeycomb sandwich panels. J Sound Vib 195(5):687–699. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.1996.0456
Paik JK, Thayamballi AK, Kim GS (1999) The strength characteristics of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels. Thin-Walled Struct 35(3):205–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8231(99)00026-9
Dharmasena KP et al (2008) Mechanical response of metallic honeycomb sandwich panel structures to high-intensity dynamic loading. Int J Impact Eng 35(9):1063–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.06.008
Huang WC, Ng CF (1998) Sound insulation improvement using honeycomb sandwich panels. Appl Acoust 53(1):163–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-682X(97)00033-9
Zhao Y, Sun Y, Li R, Sun Q, Feng J (2017) Response of aramid honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to Intense impulse loading by Mylar Flyer. Int J Impact Eng 104:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.008
Zhou G, Hill MD (2009) Impact damage and energy absorbing characteristics and residual in-plane compressive strength of Honeycomb sandwich panels. J Sandwich Struct Mater 11:329–356. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636209105704
Beukers A (1999) Lightness, the inevitable renaissance of minimum energy structures. In: Van Hinte (ed). Rotterdam: 010 Publishers
Zhong J, Zhou Y, Bao Q, Wang E, Li Q (2017) Strengthening mechanism of channel steel plate for notched concrete beams against fracture: test and numerical study. Eng Fracture Mech 180:132–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.05.027
Yang C, Xu P, Yao S et al (2018) Optimization of honeycomb strength assignment for a composite energy-absorbing structure. Thin Wall Struct 127:741–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2018.03.014
Farooq U, Ahmad MS, Rakha SA et al (2017) Interfacial mechanical performance of composite honeycomb sandwich panels for aerospace applications. Arab J Sci Eng 42:1775–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2307-z
Zaki MA, Rasheed HA, Alkhrdaji T (2019) Performance of CFRP-strengthened concrete beams fastened with distributed CFRP dowel and fiber anchors. Compos B Eng 176:107117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107117
Kim Y, Ghannoum WM, Jirsa JO (2015) Shear behavior of full-scale reinforced concrete T-beams strengthened with CFRP strips and anchors. Constr Build Mater 94:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.06.005
Lestari W, Qiao PZ (2005) Damage detection of fiber-reinforced polymer honeycomb sandwich beams. Compos Struc 67(3):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.01.023
Gartner A, Douglas E, Dolan C, Hamilton H (2011) Small beam bond test method for CFRP composites applied to concrete. J Compos Constr 10(6):52–61. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CC.1943-5614.0000151
Tatar J, Hamilton HR (2015) Bond durability factor for externally bonded CFRP systems in concrete structures. J Compos Constr. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CC.1943-5614.0000587
Bezazi A et al (2007) Fatigue life prediction of sandwich composite materials under flexural tests using Bayesian trained artificial, neural network. Int J Fat 29:738–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.06.013
Giglio M, Manes A, Gilioli A (2012) Investigations on sandwich core properties through an experimental–numerical approach. Compos Part B-Eng 43:361–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.08.016
Toradmal K, Waghmare P, Sollapur S (2017) Three-point bending analysis of honeycomb sandwich panels experimental approach. Int J Eng Tech 3(5):189–193
Belingardi G et al (2007) Fatigue analysis of honeycomb-composite sandwich beams. Comp Part A 38:1183–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2006.06.007
Wahl L, Maas S, Waldmann D, Zürbes A, Frères P (2012) Shear stresses in honeycomb sandwich plates: analytical solution, finite element method and experimental verification. J Sandwich Struct Mater 14(4):449–468. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636212444655
Al-Tersawy SH (2013) Effect of fiber parameters and concrete strength on shear behavior of strengthened RC beams. Constr Build Mater 44:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.007
Li W, Leung CKY (2017) Effect of shear span-depth ratio on mechanical performance of RC beams strengthened in shear with U-wrapping FRP strips. Compos Struct 177:141–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.06.059
Fu B, Teng JG, Chen JF, Chen GM, Guo YC (2017) Concrete cover separation in FRP plated RC beams: mitigation using FRP U-Jackets. J Compos Constr 21:204016077. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CC.1943-5614.0000721
Juliyana M, Krishnan RS (2018) Experimental and simulation of split semi-torus key in PVC foam core to improve the debonding resistance of composite sandwich panel. Mater Res Expr 5:025307
Mosallam AS (2016) Structural evaluation and design procedure for wood beams repaired and retrofitted with FRP laminates and honeycomb sandwich panels. Compos Part B Eng 87:196e213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.09.053
Sun Z, Shi S, Guo X, Hu X, Chen H (2016) On compressive properties of composite sandwich structures with grid reinforced honeycomb core. Comp Part B: Eng 94:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.03.054
Wang D (2009) Impact behavior and energy absorption of paper honeycomb sandwich panels. Int J Impact Eng 36:110–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.03.002
Sun G, Chen D, Huo X, Zheng G, Li Q (2018) Experimental and numerical studies on indentation and perforation characteristics of honeycomb sandwich panels. Compos Struct 184:110–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.09.025
Yi-Ming J et al (2017) Two-stage cumulative bending fatigue behavior for the adhesively bonded aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels. Mater Desig 54:805–813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.010
Abbadi A et al (2015) Experimental study on the fatigue behaviour of honeycomb sandwich panels with artificial defects. Compos Struct 120:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.10.020
Arbaoui J, Schmitt Y, Pierrot JL, Royer FX (2014) Effect of core thickness and intermediate layers on mechanical properties of polypropylene honeycomb multi-layer sandwich structures. Arch Metal Mater 59:11–16. https://doi.org/10.2478/amm-2014-0002
Arbaoui J, Moustabchir H, Pruncu CI, Schmitt Y (2016) Modeling and experimental analysis of polypropylene honeycomb multi-layer sandwich composites under four-point bending. J Sand Struct Mater 00:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636216659779
Li D, Zhao C, Jiang L, Jiang N (2014) Experimental study on the bending properties and failure mechanism of 3D integrated woven spacer composites at room and cryogenic temperature. Compos Struct 111:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.12.026
Nirupama G, Reddy VD, Krishnaiah G (2014) Design and fabrication of spot welded corrugated panel under three point bending by FEM. Proc Eng 97:1282–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.408
Crupi V, Epasto G, Guglielmino E (2012) Collapse modes in aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels under bending and impact loading. Int J Imp Eng 43:6–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.12.002
Murthy O, Munirudrappa N, Srikanth L, Rao RMVGK (2006) Strength and Stiffness Optimization Studies on Honeycomb Core Sandwich Panels. J Reinf Plast Comp 25(6):663. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684406058288
Daniel IM, Gdoutos EE, Rajapakse YDS (2009) Major accomplishments in composite materials and sandwich structures. Springer, Netherlands, p 818
Jeyakrishnan PR, Chockalingam KKSK, Narayanasamy R (2013) Studies on buckling behavior of honeycomb sandwich panel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65:803–815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-012-4218-9
Shahverdi H, Barati MR, Hakimelahi B (2019) Post-buckling analysis of honeycomb core sandwich panels with geometrical imperfection and graphene reinforced nano-composite face sheets. Mater Res Express 6(9):095017
Gutierrez AJ, Webber JPH (1980) Flexural wrinkling of honeycomb sandwich beams with laminated faces. Int J Solids Struct 16(7):645–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7683(80)90023-2
Amran YHM, Rashid RSM, Hejazi F, Safiee NA, Ali AAA (2016) Response of precast foamed concrete sandwich panels to flexural loading. J Build Eng 7:143–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2016.06.006
Farkas J, Jármai K (1982) Structural synthesis of sandwich beams with outer layers of box-section. J Sound Vib 84(1):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(82)90431-X
Potzta G, Kollár LP (2003) Analysis of building structures by replacement sandwich beams. Int J Solids Struct 40(3):535–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7683(02)00622-4
Sayyad AS, Ghugal YM (2017) Bending, buckling and free vibration of laminated composite and sandwich beams: a critical review of literature. Compos Struc 171:486–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.03.053
Mullen SJ (1986) I-Beam Honeycomb Material, U.S. Patent No. 4,632,862
Imbalzano G, Linforth S, Ngo TD, Lee PVS, Tran P (2018) Blast resistance of auxetic and honeycomb sandwich panels: Comparisons and parametric designs. Compos Struct 183:242–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.03.018
Mousanezhad D, Ghosh R, Ajdari A, Hamouda A, Nayeb-Hashemi H, Vaziri A (2014) Impact resistance and energy absorption of regular and functionally graded hexagonal honeycombs with cell wall material strain hardening. Int J Mech Sci 89:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.10.012
Silva MJ, Gibson LJ (1997) The effects of non-periodic microstructure and defects on the compressive strength of two-dimensional cellular solids. Int J Mech Sci 39:549–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7403(96)00065-3
Li JR, Cheng HF, Yu JL, Han FS (2003) Effect of dual-size cell mix on the stiffness and strength of open-cell aluminum foams. Mater Sci Eng A 362:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00570-7
Spadoni A, Ruzzene M, Scarpa F (2005) Global and local linear buckling behaviour of chiral cellular structure. Phys Status Solid B 242(3):695–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200460387
Scarpa F, Burriesci G, Smith FC, Chambers B (2003) Mechanical and electromagnetic behaviour of auxetic honeycomb structures. Aeronaut J 2774:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0001924000013269
. Carruthers J, Kettle A, Robinson A (1998) Energy absorption capability and crash worthiness of composite material structures: a review. Appl Mech Rev 51635-51649.https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3100758
Bates SRG, Farrow IR, Trask RS (2016) 3D printed polyurethane honeycombs for repeated tailored energy absorption. Mater Des 112:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.08.062
Al Antali A, Umer R, Zhou J, Cantwell WJ (2017) The energy-absorbing properties of composite tube-reinforced aluminum honeycomb. Compos Struct 176:630–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.05.063
Liu Y, Zhou Q, Wei X, Xia Y (2020) Testing and modeling tearing and air effect of aluminum honeycomb under out-of-plane impact loading. Int J Impact Eng 135:103402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103402
Xie S, Zhou H (2015) Analysis and optimisation of parameters influencing the out-of-plane energy absorption of an aluminium honeycomb. Thin-Walled Struct 89:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2014.12.024
Gao P, Gu X, Mosallam AS (2016) Flexural behavior of preloaded reinforced concrete beams strengthened by prestressed CFRP laminates. Compos Struct 157:33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.08.013
Ismail MK, Hassan AAA (2017) Ductility and cracking behavior of reinforced self consolidating rubberized concrete beams. J Mater Civil Eng 29:1. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001699
Meng D, Lee CK, Zhang YX (2017) Flexural and shear behaviours of plain and reinforced polyvinyl alcohol-engineered cementitious composite beams. Eng Struct 151:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.08.036
Xu S, Hou L, Zhang X (2012) Flexural and shear behaviors of reinforced ultra high toughness cementitious composite beams without web reinforcement under concentrated load. Eng Struct 39:176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.01.011
Hou L, Xu S, Zhang X et al (2013) Shear behaviors of reinforced ultra high toughness cementitious composite slender beams with stirrups. J Mater Civ Eng 26(3):466–475. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000833
Yuan F, Pan J, Wu Y (2014) Numerical study on flexural behaviors of steel reinforced engineered cementitious composite (ECC) and ECC/concrete composite beams. Sci China Technol Sci 57:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5478-4
Thomsen H, Spacone E, Limkatanyu S, Camata G (2004) Failure mode analyses of reinforced concrete beams strengthened in flexure with externally bonded fiber-reinforced polymers. J Compos Const 8(2):123–131. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0268(2004)8:2(123)
Buyle-Bodin F, David E, Ragneau E (2002) Finite element modeling of flexural behaviour of externally bonded CFRP reinforced concrete structures. Eng Struct 24:1423–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(02)00085-8
Lu C, Zhao M, Jie L, Wang J, Gao Y, Cui X, Chen P (2015) Stress Distribution on Composite Honeycomb Sandwich Structure Suffered from Bending Load. Proce Eng 99:405–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.554
Othman A, Barton D (2008) Failure initiation and propagation characteristics of honeycomb sandwich composites. Compos Struct 85(2):126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.10.034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conficts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kantarci, M., Maras, M. & Ayaz, Y. Experimental Performance of RC Beams Strengthened with Aluminum Honeycomb Sandwich Composites and CFRP U-Jackets. Exp Tech 47, 767–786 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-022-00589-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40799-022-00589-y