Abstract
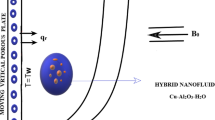
A mathematical model is constructed to examine the impact of magnetic field and thermal radiation on flow and heat transfer analysis of carbon nanotubes-based nanofluids by taking base fluid as the water between two revolving stretchable disks with convective boundary conditions in the present investigation. The most extensively validated finite element technique is employed to solve the reduced nonlinear ordinary differential equations together with boundary conditions. Velocity and temperature distributions are calculated and are displayed through graphs for various values of pertinent parameters entered into the problem. Furthermore, the values of rates of change of velocity and temperature are examined in detail and are portrayed in tabular form. The values of skin friction coefficient at both upper and lower disks elevates in the boundary layer regime with rising values of Deborah number in both nanofluids, and this augmentation is higher in MWCNTs–water- than SWCNTs–water-based Maxwell nanofluid. Temperature of the fluid in both nanofluids deteriorates as the values of nanoparticle volume fraction parameter upsurge, and this deterioration in temperature distributions is higher in SWCNTs–water- than the MWCNTs–water-based Maxwell nanofluid.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B 0 :
-
Magnetic field strength
- B 5 :
-
Upper disk thermal Biot number
- B 2 :
-
Stretching parameter at upper disk
- T ∞ :
-
Ambient temperature attained
- T :
-
Fluid temperature
- C f :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- ρ f :
-
Density of the base fluid
- f(η):
-
Dimensionless stream function
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- μ :
-
Fluid viscosity
- \(K^{*}\) :
-
Mean absorption coefficient
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity
- k s :
-
Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle
- M :
-
Magnetic parameter
- Nr :
-
Buoyancy ratio parameter
- Nu x :
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- q r :
-
Radiative heat flux
- R :
-
Radiation parameter
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- B 4 :
-
Lower disk thermal Biot number
- B 3 :
-
Rotation parameter
- B 1 :
-
Stretching parameter at lower disk
- T w :
-
Temperature at the cone surface
- ρ p :
-
Nanoparticle mass density
- \(\left( {\rho c_{\text{p}} } \right)_{\text{nf}}\) :
-
Heat capacitance of the nanofluid
- \(\left( {\rho c_{\text{p}} } \right)_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Heat capacitance of the nanofluid
- ρ nf :
-
Density of the nanofluid
- ψ :
-
Stream function
- \((\rho c_{\text{p}} )_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Heat capacitance of the base fluid
- a :
-
Constant
- \(\sigma^{*}\) :
-
Stephan–Boltzmann constant
- ε :
-
Pressure parameter
- τ w :
-
Shear stress
- θ(η):
-
Dimensionless temperature
- (x, y):
-
Cartesian coordinates
- (u, v):
-
Velocity components in x- and y-axis
- q w :
-
Wall heat flux
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity of base fluid
- η :
-
Similarity variable
- (μ)nf :
-
Viscosity of the nanofluid
- φ :
-
Volume fraction of nanoparticles
- λ :
-
Maxwell parameter
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- k nf :
-
Thermal conductivity of nanofluid
- ν f :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the base fluid
- β :
-
Deborah number
- f:
-
Base fluid
- w:
-
Condition at cone surface
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- ∞:
-
Condition far away from cone surface
References
Choi SUS, Zhang ZG, Yu W, Lockwood FE, Grulke EA (2001) Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nano-tube suspensions. Appl Phys 79:2252–2254
Sheremet MA, Pop I (2015) Natural convection in a horizontal cylindrical annulus filled with a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. Eur Phys J Plus 130:107
Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA (2016) Magnetic field effect on mixed convection in lid-driven trapezoidal cavities filled with a Cu–water nanofluid with an aiding or opposing side wall. ASME J Therm Sci Eng Appl 8:031009–031009-12
Sheremet MA, Revnic C, Pop I (2017) Natural convective heat transfer through two entrapped triangular cavities filled with a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Int J Mech Sci 133:484–494
Sheremet MA, Pop I (2015) Free convection in a triangular cavity filled with a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 25:1138–1161
Ghalambaz M, Sheremet MA, Pop I (2015) Free convection in a parallelogrammic porous cavity filled with a nanofluid using Tiwari and Das’ nanofluid model. PLoS ONE 10:e0126486
Ghalambaz M, Doostani A, Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA (2017) Melting of nanoparticles-enhanced phase-change materials in an enclosure: effect of hybrid nanoparticles. Int J Mech Sci 134:85–97
Ghalambaz M, Doostanidezfuli A, Izadpanahi E, Chamkha AJ (2017) Phase-change heat transfer in a cavity heated from below: the effect of utilizing single or hybrid nanoparticles as additives. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 7:52–53
Ghalambaz M, Doostanidezfuli A, Zargartalebi H, Chamkha AJ (2017) MHD phase change heat transfer in an inclined enclosure: effect of a magnetic field and cavity inclination. Numer Heat Transf A Appl 71:91–109
Sheremet MA, Pop I (2018) Natural convection combined with thermal radiation in a square cavity filled with a viscoelastic fluid. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow 28:624–640
Alsabery AI, Sheremet MA, Chamkha AJ, Hashim I (2018) Conjugate natural convection of Al2O3–water nanofluid in a square cavity with a concentric solid insert using Buongiorno’s two-phase model. Int J Mech Sci 136:200–219
Halelfadl S, Estelle P, Mare T (2014) Heat transfer properties of aqueous carbon nanotubes nanofluids in coaxial heat exchanger under laminar regime. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 55:174–180
Khan WA, Khan ZH, Rahi M (2014) Fluid flow and heat transfer of carbon nanotubes along a flat plate with Navier slip boundary. Appl Nanosci 4:633–641
Sadri R, Ahmadi G, Togun H et al (2014) An experimental study on thermal conductivity and viscosity of nanofluids containing carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:151–166
Hayat T, Liaz Khan M, Farooq M, Yasmeen T, Alsaedi A (2016) Water-carbon nanofluid flow with variable heat flux by a thin needle. J Mol Liq 224:786–791
Kandasamy R, Muhaimin I, Mohammad R (2016) Single walled carbon nanotubes on MHD unsteady flow over a porous wedge with thermal radiation with variable stream conditions. Alex Eng J 55:275–285
Binesh AR, Kamali R (2017) Effects of chirality on single-file water permeability and diffusivity through single wall carbon nanotubes. IET Micro Nano Lett 12:109–112
Hussien A, Abdullah MZ, Yusop NMd et al (2017) Experiment on forced convective heat transfer enhancement using MWCNTs/GNPs hybrid nanofluid and mini-tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf 115:1121–1131
Palanisamy K, Nithyanandam T (2018) Experimental investigation on convective heat transfer and pressure drop in vertical and horizontal helically coiled tube heat exchanger using MWCNT/water nanofluid. Int J Mech Prod Eng Res Dev 8:649–658
Sreedevi P, Sudarsana Reddy P, Chamkha AJ (2018) Magneto-hydrodynamics heat and mass transfer analysis of single and multi-wall carbon nanotubes over vertical cone with convective boundary condition. Int J Mech Sci 135:646–655
Jyothi K, Sudarsana Reddy P, Suryanarayana Reddy M (2018) Influence of magnetic field and thermal radiation on convective flow of SWCNTs-water and MWCNTs-water nanofluid between rotating stretchable disks with convective boundary conditions. Powder Technol 331:326–337
Ramesh G, Gireesha B (2014) Influence of heat source/sink on a Maxwell fluid over a stretching surface with convective boundary condition in the presence of nanoparticles. Ain Shams Eng J 5:991–998
Nandy SK (2015) Unsteady flow of Maxwell fluid in the presence of nanoparticles toward a permeable shrinking surface with Navier slip. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 52:22–30
Shafique Z, Mustafa M, Mushtaq A (2016) Boundary layer flow of Maxwell fluid in rotating frame with binary chemical reaction and activation energy. Results Phys 6:627–633
Ahmad M, Ahmad I, Sajid M (2016) Magneto-hydrodynamic time-dependent three dimensional flow of Maxwell fluid over a stretching surface through porous space with variable thermal conditions. J Braz Soc Mech Sci 38(6):1767–1778
Bilal M, Sagheer M, Hussain S (2018) On MHD 3D upper convected Maxwell fluid flow with thermophoretic effect using non-linear radiative heat flux. Can J Phys 96:1–10
Khan N, Mehmood T, Sajid M, Hashmi MS (2016) Heat and mass transfer of MHD mixed convection axisymmetric chemically reactive flow of Maxwell fluid driven by exothermal and isothermal stretching disks. Int J Heat Mass Transf 92:1090–1105
Volkan Ersoy H (2014) Flow of a Maxwell fluid between two porous disks rotating about non coincident axes. Adv Mech Eng Article ID 347196
Khan NA, Khan S, Riaz F (2016) 3D stagnation point flow of Maxwell fluid towards an off-centered rotating disk. Multidiscip Model Mater Struct 12:345–361
Awais M, Hayat T, Irum S, Alsaedi A (2015) Heat generation/absorption effects in a boundary layer stretched flow of Maxwell nanofluid; analytic and numeric solutions. PLoS ONE 10:e0129814
Cao Z, Zhao J, Wang Z, Cheng L (2016) MHD flow and heat transfer of fractional Maxwell viscoelastic nanofluid over a moving plate. J Mol Liq 222:1121–1127
Prabhavathi B, Sudarsana Reddy P, Bhuvana Vijaya R (2018) Heat and mass transfer enhancement of SWCNTs and MWCNTs based Maxwell nanofluid flow over a vertical cone with slip effects. Powder Technol 340:253–263
Ramzan M, Bilal M, Chung JD, Farooq U (2016) Mixed convective flow of Maxwell nanofluid past a porous vertical stretched surface—an optimal solution. Results Phys 6:1072–1079
Jusoh R, Nazar R, Pop I (2017) Flow and heat transfer of magneto hydrodynamic three-dimensional Maxwell nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking surface with convective boundary conditions. Int J Mech Sci 124–125:166–173
Anki Reddy PB, Suneetha S, Bhaskar Reddy N (2017) Numerical study of magneto-hydrodynamics (MHD) boundary layer slip flow of a Maxwell nanofluid over an exponentially stretching surface with convective boundary condition, Propulsion and Power. Research 6:259–268
Madhu M, Kishan N, Chamkha AJ (2017) Unsteady flow of a Maxwell nanofluid over a stretching surface in the presence of magneto-hydrodynamic and thermal radiation effects. Propuls Power Res 6:31–40
Bilal M, Sagheer M, Hussain S (2017) Three dimensional MHD upper-convected Maxwell nanofluid flow with nonlinear radiative heat flux. Alex Eng J 57(3):1917–1925
Aman S, Khan I, Ismail Z, Salleh MZ, Al-Mdallal QM (2017) Heat transfer enhancement in free convection flow of CNTs Maxwell nanofluids with four different types of molecular liquids. Sci Rep 7:2445
Tahir F, Gul T, Islam S, Shah Z, Khan A, Khan W, Ali L, Muradullah (2017) Flow of a nano-liquid film of Maxwell fluid with thermal radiation and magneto hydrodynamic properties on an unstable stretching sheet. J Nano Fluids 6:1021–1030
Sajid T, Sagheer M, Hussain S, Bilal M (2018) Darcy–Forchheimer flow of Maxwell nanofluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and activation energy. AIP Adv 8:035102
Khan M, Irfan M, Khan WA (2018) Impact of heat source/sink on radiative heat transfer to Maxwell nanofluid subject to revised mass flux condition. Results Phys 9:851–857
Sudarsana Reddy P, Chamkha AJ (2016) Soret and Dufour effects on unsteady MHD heat and mass transfer over a stretching sheet with thermophoresis and non-uniform heat generation/absorption. J Appl Fluid Mech 9(5):2443–2455
Sreedevi P, Sudarsana Reddy P, Chamkha AJ (2017) Heat and mass transfer analysis of nanofluid over linear and non- linear stretching surface with thermal radiation and chemical reaction. Powder Technol 315:194–204
Sudarsana Reddy P, Chamkha AliJ, Al-mudhaf AliF (2017) MHD heat and mass transfer flow of a nanofluid over an inclined vertical porous plate with radiation and heat generation/absorption. Adv Powder Technol 28(3):1008–1017
Imtiaz M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Ahmad B (2016) Convective flow of carbon nanotubes between rotating stretchable disks with thermal radiation effects. Int J Heat Mass Transf 101:948–957
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Technical Editor: Cezar Negrao, PhD.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudarsana Reddy, P., Jyothi, K. & Suryanarayana Reddy, M. Flow and heat transfer analysis of carbon nanotubes-based Maxwell nanofluid flow driven by rotating stretchable disks with thermal radiation. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40, 576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1494-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1494-9