Abstract
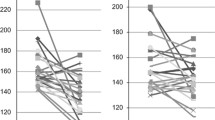
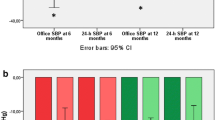
Renal denervation (RD) is an intriguing treatment strategy for resistant hypertension. However, limited data are available about its long time efficacy as well as its effects on intermediate phenotypes like arterial stiffness and carotid IMT. 12 patients (9 males, mean 69 years) with resistant hypertension underwent bilateral RDN (Medtronic System) since April 2012 in Niguarda Ca’ Granda Hospital (Milan). Patients were studied before intervention, and at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months after RD. Carotid intima media thickness (Esaote Mylab) and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (Complior, Alam medical) were assessed at each step. Compared to baseline, patients showed a marked reduction of office systolic blood pressure at each follow-up step (p < 0.05 versus baseline for all steps) as well as pulse wave velocity (p < 0.01 at 1 year versus baseline). Moreover, reduction in pulse wave velocity was higher than the expected value obtained only considering blood pressure drop. Conversely, no significant effect was observed on diastolic blood pressure as well as carotid intima-media thickness. In our study, renal denervation was a safe and effective procedure. The BP lowering effect was maintained during follow-up and a beneficial effect on arterial stiffness was observed, which implies that this effect can’t passively originate from the BP fall but rather from an improvement of arterial mechanical properties, possibly related to a reduced sympathetic arterial drive.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–23.
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010;121:e46–215.
Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Kramer H, Banegas JR, Giampaoli S, Joffres MR, et al. Hypertension treatment and control in five European countries, Canada, and the United States. Hypertension. 2004;43:10–7.
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K, et al. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for resistant hypertension: a multicentre safety and proof-of-principle cohort study. Lancet. 2009;373:1275–81.
Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators, Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP, Schmieder RE, Böhm M. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376(9756):1903–9.
Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D’Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT, SYMPLICITY HTN-3 Investigators, et al. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(15):1393–401.
Kandzari DE, Bhatt DL, Brar S, Devireddy CM, Esler M, Fahy M, et al. Predictors of blood pressure response in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(4):219–27.
Ram CV, Kumar AS. Renal denervation therapy for resistant hypertension: a clinical update. J Hum Hypertens. 2014;28(12):699–704.
Brandt MC, Reda S, Mahfoud F, Lenski M, Böhm M, Hoppe UC. Effects of renal sympathetic denervation on arterial stiffness and central hemodynamics in patients with resistant hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(19):1956–65.
Mortensen K, Franzen K, Himmel F, Bode F, Schunkert H, Weil J, Reppel M. Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation improves central hemodynamics and arterial stiffness: a pilot study. J Clin Hypertens. 2012;14(12):861–70.
Verloop WL, Vink EE, Spiering W, Blankestijn PJ, Doevendans PA, Bots ML, et al. Effects of renal denervation on end organ damage in hypertensive patients. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015;22(5):558–67.
Weber T, Ammer M, Rammer M, Adji A, O’Rourke MF, Wassertheurer S, et al. Noninvasive determination of carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity depends critically on assessment of travel distance: a comparison with invasive measurement. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1624–30.
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, European Network for Non-invasive Investigation of Large Arteries, et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:2588–605.
Reference Values for Arterial Stiffness’ Collaboration. Determinants of pulse wave velocity in healthy people and in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors: ‘establishing normal and reference values’. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(19):2338–50.
Baldassarre D, Hamsten A, Veglia F, de Faire U, Humphries SE, Smit AJ, IMPROVE Study Group, et al. Measurements of carotid intima-media thickness and of interadventitia common carotid diameter improve prediction of cardiovascular events: results of the IMPROVE (Carotid Intima Media Thickness [IMT] and IMT-Progression as Predictors of Vascular Events in a High Risk European Population) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(16):1489–99.
Giannattasio C, Failla M, Lucchina S, Zazzeron C, Scotti V, Capra A, et al. Arterial stiffening influence of sympathetic nerve activity: evidence from hand transplantation in humans. Hypertension. 2005;45(4):608–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baroni, M., Nava, S., Giupponi, L. et al. Effects of Renal Sympathetic Denervation on Arterial Stiffness and Blood Pressure Control in Resistant Hypertensive Patients: A Single Centre Prospective Study. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 22, 411–416 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0121-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0121-4