Abstract
Background and Objective
MicroRNA (miR)-499 rs3746444 polymorphisms may participate in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, but the results remain conflicting. We further investigated this association using a meta-analysis.
Methods
We conducted a retrieval of studies and obtained the eligible studies if they met inclusion criteria. Two researchers independently extracted the data from original articles. The genotype frequencies were analysed using Stata software.
Results
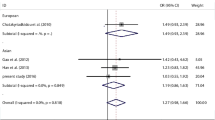
We finally archived six eligible studies that included 1,118 cases and 1,673 controls. After pooling the data, the results indicated that homozygote TT had an overall association with autoimmune diseases (TC + CC vs. TT: odds ratio [OR] 1.31, 95 % CI 1.11–1.55, p = 0.001). The allele C, genotype TC and CC, may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) risks in Mediterranean populations (C vs. T: OR 2. 00, 95 % CI 1.37–2.91, p < 0.001; TC vs. CC + TT: OR 1.76, 95 % CI 1.27–2.44; p = 0.001; CC vs. TC + TT: OR 2.31, 95 % CI 1.24–4.27, p = 0.008; CC vs. TT: OR 2.92, 95 % CI 1.59–5.37, p = 0.001; TC vs. TT: OR 1.98, 95 % CI 1.42–2.77). The genotype TT may decrease the risk of RA in Mediterranean populations (TC + CC vs. TT: OR 2.15, 95 % CI 1.57–2.94, p < 0.001) rather than in East Asians.
Conclusions
This study suggested that miR-499 polymorphisms were associated with a significantly increased risk of RA in Mediterranean populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida MI, Reis RM, Calin GA. MicroRNA history: discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat Res. 2011;717(1–2):1–8.
Davis-Dusenbery BN, Hata A. Mechanisms of control of microRNA biogenesis. J Biochem. 2010;148(4):381–92.
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(4):605–10.
Van Wynsberghe PM, Chan SP, Slack FJ, et al. Analysis of microRNA expression and function. Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:219–52.
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, et al. Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:111–22.
Papoutsidakis N, Deftereos S, Kaoukis A, et al. MicroRNAs and the heart: small things do matter. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13:216–30.
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, et al. Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J Physiol Biochem. 2011;67:129–39.
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107:605–10.
Catalucci D, Gallo P, Condorelli G. MicroRNAs in cardiovascular biology and heart disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009;2:402–8.
Yanaihara N, Harris CC. MicroRNA Involvement in Human Cancers. Clin Chem. Epub 5 March 2013.
Mouradian MM. MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46:279–84.
Ceribelli A, Nahid MA, Satoh M, et al. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:3667–74.
van Eden W. Immunoregulation of autoimmune diseases. Hum Immunol. 2006;67:446–53.
Anaya JM, Gomez L, Castiblanco J. Is there a common genetic basis for autoimmune diseases? Clin Dev Immunol. 2006;13:185–95.
Liang YL, Wu H, Shen X, et al. Association of STAT4 rs7574865 polymorphism with autoimmune diseases: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:8873–82.
Ramirez M, Quintana G, Diaz-Gallo LM, et al. The PTPN22 C1858T variant as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus but not for systemic sclerosis in the Colombian population. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:520–4.
Sonkoly E, Stahle M, Pivarcsi A. MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin inflammation. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008;33:312–5.
Hashemi M, Eskandari-Nasab E, Zakeri Z, et al. Association of pre-miRNA-146a rs2910164 and premiRNA-499 rs3746444 polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7:287–91.
El-Shal AS, Aly NM, Galil SM, et al. Association of microRNAs genes polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Egyptian female patients. Joint Bone Spine. Epub 31 May 2013.
Yang B, Zhang JL, Shi YY, et al. Association study of single nucleotide polymorphisms in pre-miRNA and rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:4913–9.
Zhang H, Pu J, Wang X, et al. IRAK1 rs3027898 C/A polymorphism is associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:369–75.
Zhang J, Yang B, Ying B, et al. Association of pre-microRNAs genetic variants with susceptibility in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:1463–8.
Okubo M, Tahara T, Shibata T, et al. Association study of common genetic variants in pre-microRNAs in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31:69–73.
Thakkinstian A, McElduff P, D’Este C, et al. A method for meta-analysis of molecular association studies. Statist Med. 2005;24(9):1291–306.
van Gaalen FA, van Aken J, Huizinga TW, et al. Association between HLA class II genes and autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCPs) influences the severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2113–21.
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, et al. Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2003;34:395–402.
Harney SM, Meisel C, Sims AM, et al. Genetic and genomic studies of PADI4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005;44:869–72.
Yang B, Chen J, Li Y, et al. Association of polymorphisms in pre-miRNA with inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis in the Chinese Han population. Hum Immunol. 2012;73:101–6.
Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, et al. The case of the misleading funnel plot. BMJ. 2006;333:597–600.
Acknowledgments
Supported by Yunnan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Grant of China (No.2013FB044). The authors are particularly grateful to the editors and reviewers for their help. The authors explicitly state that they have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lechun Lu, Ying Tu and Lingxin Liu contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Tu, Y., Liu, L. et al. MicroRNA-499 rs3746444 Polymorphism and Autoimmune Diseases Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Mol Diagn Ther 18, 237–242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0073-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40291-013-0073-0