Abstract
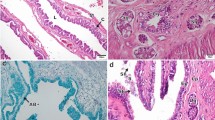
Structure of ovotestis and its parasitic castration were observed histologically in hermaphrodite freshwater snail Melanoides tuberculatus (Mollusca, Gastropoda). In mature healthy snail ovotestis was found to be closely associated with posterior region of digestive gland. It was composed of numerous oval to pear-shaped acini intermingled with loose inter-acinar connective tissue. Each acinus was found to be made up of two unequal zones, the larger testicular zone comprising of male germ cells and the smaller one with the female germ cells. Both of them were lined by germinal epithelium. Oocytes were generally found towards the periphery of ovotestis enclosed by the membrane tunica propria. In infected snails ovotestis was found to be invaded by the larval trematode parasites (sporocysts and xiphidiocercariae) but the larvae were restricted to the connective tissue of ovotestis and did not invade the acini. Except ovotestis no other organ was found to be infected with these larvae. Histopathological changes in the acini of infected ovotestis were associated with the severity of infection. Degenerative changes, hypotrophy and destruction of individual acinus were found in mild infection. In severe infection, autolysis and necrosis of acinar cells were found and ultimately these were completely replaced by parthenitae. In such parasitic castration no sex conversion was detected. In the present communication structure of ovotestis along with parasitic castration and its evolutionary significance are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choubisa SL (2008) Focus on pathogenic trematode cercariae infecting fresh water snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) of tribal region of southern Rajasthan (India). J Parasit Dis 32(1):47–55
Choubisa SL (2010) Snails as bioindicators for dreaded trematodiasis diseases. J Commun Dis 42(3):223–226
Cheng TC (1964) The biology of animal parasites. W. B. Saunders, London, p 727
Choubisa SL, Sharma PN (1986) Incidence of larval trematodes infection and their seasonal variation in the fresh water molluscs of southern Rajasthan. Rec Zool Surv India 83(1&2):69–80
Choubisa SL (1988) Histological and histochemical observations on the digestive gland of Melanoides tuberculatus (Gastropoda) infected with certain larval trematodes and focus on their mode of nutrition. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Anim Sci) 97(3):251–262
Choubisa SL (1990) Histopathological observations on the digestive gland of Lymnaea auricularia infected with the larval trematodes. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Anim Sci) 99(5):363–368
Choubisa SL, Sheikh Z, Jaroli VJ (2012) Histopathological effects of larval trematodes on the digestive gland of freshwater snail species, Vivipara bengalensis and Lymnaea acuminata. J Parasit Dis 36:283–286. doi:10.1007/s12639-012-0116-1
Aurangzeb RP, Siddiqi MN (1984) Histological studies of the genital tract of snails. Pakistan J Agric Res 5(4):264–268
Crews AE, Esch GW (1987) Histopathology of larval trematode infections in the freshwater pulmonate snail, Helisoma anceps. J Invert Pathol 49:76–82
Ngowsiri U, Sertarugsa P, Sobhon P et al (1989) Development of, and seasonal changes in, the reproductive system of Achatina fulica. J Sci Soc Thail 15:237–249
Horn ACM, Achaval A, Zancan DM (2005) The annual reproductive cycle of the snail Megalobulimus abbreviatus (Bequaert, 1948) (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Braz J Biol 65(3):459–467
Cheng TC (1983) Studies on parasitic castration: aminopeptidase activity levels and protein concentrations in Ilyanassa obsoleta (Mollusca) parasitised by larval trematodes. J Invert Pathol 42:42–50
Baudoin M (1975) Host castration as parasitic strategy. Evolution 29:335–352
Cheng TC, Cooperman JS (1964) Studies on host-parasite relationships between larval trematodes and their hosts. V. The invasion of the reproductive system of Helisoma trivolvis by the sporocysts and cercariae of Glypthelmins pennsylvaniensis. Trans Am Microsc Soc 83:12–23
Reader TA (1973) Histological and ultrastructural studies on the testis of Bityhnia tentaculata (Mollusca: Gastropoda), and on the effects of Cercaria helvetica XII (Trematoda: Digenea) on this organ. J Zool 171:541–561
Sullivan J, Cheng TC, Howland K (1985) Studies on parasitic castration: castration of Ilyanassa obsoleta (Mollusca: Gastropoda) by several marine trematodes. Trans Am Microsc Soc 104:154–171
Oliva M (1992) Parasitic castration in Fissurella crassa (Archaeogastropoda) due to an adult digenea, Proctoeces lintoni (Fellostomidae). Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 87:37–42
Lafferty KD (1993) Effects of parasitic castration on growth, reproduction and population dynamics of the marine snail Cerithidea californica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 96:229–237
Oliva M, Olivares A, Diaz C, Pasten M (1999) Parasitic castration in Concholepas conholepas (Gastropoda: Muricidae) due to a larval digenean in northern Chile. Dis Aquat Org 36:61–65
Tetreault F, Himmelman JH, Measures L (2000) Impact of a castrating trematode, Neophasis sp., on the common whelk, Buccinum undatum, in the northern gulf of St. Lawrence. Biol Bull 198:261–271
Feng SL (1988) Host response to Proctoeces maculatus infection in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. J Shellfish Res 7:118
Costeau C, Combes C, Maillard C et al (1990) Prosorhynchus squamatus (Trematoda) parasitosis in the Mytilus edulis–Mytilus galloprovincialis complex: specificity and host- parasite relationships. In: Perkins FO, Cheng TC (eds) Pathology in marine science. Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 291–298
Jonsson R, Andre C (1992) Mass mortality of the bivalve Cerastoderma edule on the Swedish west coast caused by the infestation with the digenean trematode Cercaria cerastoderma I. Ophelia 36:151–157
Lasiak T (1991) Bucephalid trematode infections in mytilid bivalves from the rocky intertidal of southern Chile. J Molluscan Stud 58:29–36
Santos AMT, Coimbra J (1995) Growth and production of raft cultured Mytilus edulis L., in Ria de Aveiro: gonad symbiotic infestation. Aquaculture 132:195–211
Calvo-Ugarteburu G, McQuaid CD (1998) Parasitism and invasive species: effects of digenetic trematodes on mussels. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 169:149–163
Rantanen JT, Valtonen ET, Holopianen IJ (1998) Digenean parasites of the bivalve mollusc Pisidium amnicum in a small river in eastern Finland. Dis Aquat Org 33:201–208
Silva PM, Magalhaes ARM, Barraccco MA (2002) Effects of Bucephalus sp. (Trematoda: Bucephalidae) on Perna perna mussels from a culture station in Ratones Grande Island. Braz J Invert Pathol 79:154–162
Valderrama K, Oliva M, Campos B, Brown DI (2004) Parasitic castration of Eurhomalea lenticularis (Bivalvia: Veneridae) by a digenetic trematode: quantitative histological analysis. Dis Aquat Org 59:151–158
Rothschild M (1941) Observations on the growth and trematode infections of Peringia ulvae (Pennant 1777) in a pool in the Tamar saltings, Plymouth. Parasitology 33:406–415
Mouritsen KN, Jensen KT (1994) The enigma of gigantism: effect of larval trematodes on growth, fecundity, egestion and locomotion in Hydrobia ulvae (Pennant) (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 181:53–66
Gorbushin ANM (1997) Field evidence of trematode-induced gigantism in Hydrobia spp. (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia). J Mar Biol Assoc 77:785–800
Duncan CJ (1975) Reproduction. Pulmonates I functional anatomy and physiology. Academic Press, London, pp 309–365
Lafferty KD, Kuris AM (2009) Parasitic castration: the evolution and ecology of body snatchers. Trends Parasitol 25(12):564–572
Choubisa SL (2008) Mode of nutrition in pathogenic trematode larvae (redia and cercaria) which infect hepatopancreas of fresh water snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda). J Parasit Dis 32(1):68–73
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, for financial assistance (39-658/2010, SR) and to V. J. Jaroli for his technical assistance. Authors sincerely thank Late Prof.P.N.Sharma, eminent parasitologist for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choubisa, S.L., Sheikh, Z. Parasitic Castration in Freshwater Snail Melanoides tuberculatus (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 83, 193–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0133-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0133-y