Abstract
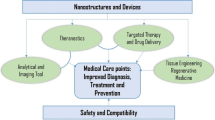
Since current treatment options applicable to cancers are still confined to chemotherapeutics followed by surgical debulking, cancer disease is a second leading cause of death because of chemotherapeutics of non-specific biodistribution. Image-guided drug delivery system (IGDDS) is a real-time noninvasive imaging assessment of therapeutic response that has the strong potential to control or suppress cancer because imaging property offer the quantification of nanomedicine at the intended disease site, thus the potential assurance of adequate treatment and elimination of undesirable delay leading to poor clinical outcomes. Also, combining pH-sensitive advantages of nanoparticle with theranostic property will have high chance to overcome cancer. There have been intensive researches to develop innovative IGDDS by using nanoparticles including organic or inorganic theranostic (therapy + diagnostic) systems including liposomes, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, carbon nanotubes, gold nanoparticles, iron oxide nanoparticles, quantum dots, and silica nanoparticles. In this review, we will introduce various examples of each system and will discuss their theranostic applications.


(Reprinted by permission from (Yang et al. 2010). Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.)

(Reprinted by permission from (Xia et al. 2011). Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd.)

(Reprinted by permission from (He et al. 2011). Copyright 2011 Nature Publishing Group.)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed N, Fessi H, Elaissari A (2012) Theranostic applications of nanoparticles in cancer. Drug Discov Today 17:928–934
Akerman ME, Chan WCW, Laakkonen P et al (2002) Nanocrystal targeting in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99: 12617–12621.
Alqawlaq S, Sivak JM, Huzil JT et al (2014) Preclinical development and ocular biodistribution of gemini-DNA nanoparticles after intravitreal and topical administration: towards non-invasive glaucoma gene therapy. Nanomed Nanotech Biol Med 10: 1637–1647
Benezra M, Penate-Medina O, Zanzonico PB et al (2011) Multimodal silica nanoparticles are effective cancer-targeted probes in a model of human melanoma. J Clin Invest 121:2768–2780
Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S et al (2003) Dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles: influence on fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 24:4551–4557
Bosman AW, Janssen HM, Meijer EW (1999) About dendrimers: structure, physical properties, and applications. Chem Rev 99:1665–1688
Braun GB, Pallaoro A, Wu G et al (2009) Laser-activated gene silencing via gold nanoshell–siRNA conjugates. ACS Nano 3:2007–2015
Cai D, Mataraza JM, Qin Z-H et al (2005) Highly efficient molecular delivery into mammalian cells using carbon nanotube spearing. Nat Meth 2: 449–454
Chakravarty R, Goel S, Hong H et al (2015) Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor vasculature targeting and PET image-guided drug delivery. Nanomedicine 10:1233–1246
Chen F, Hong H, Zhang Y et al (2013) In vivo tumor targeting and image-guided drug delivery with antibody-conjugated, radiolabeled mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Nano 7:9027–9039
Cho H, Kwon GS (2011) Polymeric micelles for neoadjuvant cancer therapy and tumor-primed optical imaging. ACS Nano 5:8721–8729
Cuenca AG, Jiang H, Hochwald SN et al (2006) Emerging implications of nanotechnology on cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Cancer 107:459–466
D’Emanuele A, Attwood D (2005) Dendrimer–drug interactions. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:2147–2162
Derfus AM, Chan WCW, Bhatia SN (2004) Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. Nano Lett 4:11–18
Dreaden EC, Mackey MA, Huang X et al (2011) Beating cancer in multiple ways using nanogold. Chem Soc Rev 40:3391–3404
du Plessis J, Weiner N, Müller DG (1994) The influence of in vivo treatment of skin with liposomes on the topical absorption of a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic drug in vitro. Int J Pharm 103:R1–R5
Dykes GM (2001) Dendrimers: a review of their appeal and applications. J Chem Tech Biotech 76:903–918
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev 35:209–217
Gabizon A, Goren D, Horowitz AT et al (1997) Long-circulating liposomes for drug delivery in cancer therapy: a review of biodistribution studies in tumor-bearing animals. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 24:337–344
Gerweck LE, Seetharaman K (1996) pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res 56:1194–1198
Guo J, Hong H, Chen G et al (2013) Image-guided and tumor-targeted drug delivery with radiolabeled unimolecular micelles. Biomaterials 34:8323–8332
Gupta AK, Curtis ASG (2004) Surface modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery: interaction studies with human fibroblasts in culture. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:493–496
Guthi JS, Yang S-G, Huang G et al (2010) MRI-visible micellar nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery to lung cancer cells. Mol Pharm 7:32–40
He Q, Shi J, Cui X et al (2011) Synthesis of oxygen-deficient luminescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles for synchronous drug delivery and imaging. Chem Comm 47:7947–7949
Heo DN, Yang DH, Moon H-J et al (2012) Gold nanoparticles surface-functionalized with paclitaxel drug and biotin receptor as theranostic agents for cancer therapy. Biomaterials 33:856–866
Hollis CP, Weiss HL, Leggas M et al (2013) Biodistribution and bioimaging studies of hybrid paclitaxel nanocrystals: lessons learned of the EPR effect and image-guided drug delivery. J Control Rel 172:12–21
Howarth M, Liu W, Puthenveetil S et al (2008) Monovalent, reduced-size quantum dots for imaging receptors on living cells. Nat Methods 5: 397–399
Huang J, Li Y, Orza A et al (2016) Magnetic nanoparticle facilitated drug delivery for cancer therapy with targeted and image-guided approaches. Adv Func Mater 26: 3818–3836
Jackson EF, Esparza-Coss E, Wen X et al (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging of therapy-induced necrosis using gadolinium-chelated polyglutamic acids. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 68:830–838
Jain TK, Morales MA, Sahoo SK et al (2005) Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol Pharm 2:194–205
Jain PK, Qian W, El-Sayed MA (2006) Ultrafast Cooling of photoexcited electrons in gold nanoparticle–thiolated DNA conjugates involves the dissociation of the gold–thiol bond. J Am Chem Soc 128:2426–2433
Jang J-t, Nah H, Lee J-H et al (2009) Critical enhancements of MRI contrast and hyperthermic effects by dopant-controlled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew Chem 121: 1260–1264
Ji S-r, Liu C, Zhang B et al (2010) Carbon nanotubes in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1806: 29–35
Jones M-C, Leroux J-C (1999) Polymeric micelles—a new generation of colloidal drug carriers. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 48:101–111
Josephson L, Kircher MF, Mahmood U et al (2002) Near-infrared fluorescent nanoparticles as combined MR/optical imaging probes. Bioconj Chem 13: 554–560
Jun Y-w, Lee J-H, Cheon J (2008a) Chemical design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:5122–5135
Jun Y-w, Seo J-w, Cheon J (2008b) Nanoscaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicabilities in biomedical sciences. Acc Chem Res 41:179–189
Kam NWS, Liu Z, Dai H (2005) Functionalization of carbon nanotubes via cleavable disulfide bonds for efficient intracellular delivery of siRNA and potent gene silencing. J Am Chem Soc 127:12492–12493
Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y (2001) Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:113–131
Kehoe S, Hook J, Nankivell M et al (2015) Primary chemotherapy versus primary surgery for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (CHORUS): an open-label, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. The Lancet 386:249–257
Kim D, Lee ES, Park K et al (2008) Doxorubicin loaded pH-sensitive micelle: antitumoral efficacy against ovarian A2780/DOXR tumor. Pharm Res 25:2074–2082
Kim J, Piao Y, Hyeon T (2009) Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chem Soc Rev 38:372–390
Kim H, Kim S, Park C et al (2010) Glutathione-induced intracellular release of guests from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers. Adv Mater 22:4280–4283
Krause W (2002). Liver-specific X-ray contrast agents. In: Krause W (ed) Contrast agents II: optical, ultrasound, X-Ray and radiopharmaceutical imaging. Springer, Berlin, pp 173–200
Langereis S, Hijnen N, Strijkers G et al (2013) Research Spotlight: Multifunctional liposomes for MRI and image-guided drug delivery. Ther Deliv 5: 21–24
Lee CC, MacKay JA, Frechet JMJ et al (2005) Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat Biotech 23:1517–1526
Lee ES, Gao Z, Kim D et al (2008a) Super pH-sensitive multifunctional polymeric micelle for tumor pHe specific TAT exposure and multidrug resistance. J Control Rel 129:228–236
Lee S, Cha E-J, Park K et al (2008b) A near-infrared-fluorescence-quenched gold-nanoparticle imaging probe for in vivo drug screening and protease activity determination. Angew Chem 120: 2846–2849
Lee H-Y, Li Z, Chen K et al (2008c) PET/MRI dual-modality tumor imaging using arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD)–conjugated radiolabeled iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nucl Med 49:1371–1379
Lee JE, Lee N, Kim H et al (2010) Uniform mesoporous dye-doped silica nanoparticles decorated with multiple magnetite nanocrystals for simultaneous enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, fluorescence imaging, and drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 132:552–557
Lim E-K, Huh Y-M, Yang J et al (2011) pH-triggered drug-releasing magnetic nanoparticles for cancer therapy guided by molecular imaging by mri. Adv Mater 23:2436–2442
Liu Z, Cai W, He L et al (2007) In vivo biodistribution and highly efficient tumour targeting of carbon nanotubes in mice. Nat Nano 2: 47–52
Lorenzato C, Cernicanu A, Meyre M-E et al (2013) MRI contrast variation of thermosensitive magnetoliposomes triggered by focused ultrasound: a tool for image-guided local drug delivery. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 8:185–192
Lovell JF, Jin CS, Huynh E et al (2011) Porphysome nanovesicles generated by porphyrin bilayers for use as multimodal biophotonic contrast agents. Nat Mater 10:324–332
Lu W, Singh AK, Khan SA et al (2010) Gold nano-popcorn-based targeted diagnosis, nanotherapy treatment, and in situ monitoring of photothermal therapy response of prostate cancer cells using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132:18103–18114
Lu P-L, Chen Y-C, Ou T-W et al (2011) Multifunctional hollow nanoparticles based on graft-diblock copolymers for doxorubicin delivery. Biomaterials 32:2213–2221
Marchesan S, Melchionna M, Prato M (2014) Carbon Nanostructures for Nanomedicine: Opportunities and Challenges. Fuller Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct 22: 190–195
Martina M-S, Fortin J-P, Ménager C et al (2005) Generation of superparamagnetic liposomes revealed as highly efficient MRI contrast agents for in vivo imaging. J Am Chem Soc 127:10676–10685
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER et al (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat Mater 4:435–446
Meng H, Liong M, Xia T et al (2010) engineered design of mesoporous silica nanoparticles to deliver doxorubicin and P-glycoprotein siRNA to overcome drug resistance in a cancer cell line. ACS Nano 4:4539–4550
Menjoge AR, Kannan RM, Tomalia DA (2010) Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov Today 15:171–185
Min KH, Kim J-H, Bae SM et al (2010) Tumoral acidic pH-responsive MPEG-poly(β-amino ester) polymeric micelles for cancer targeting therapy. J Control Rel 144:259–266
Moon HK, Lee SH, Choi HC (2009) In vivo near-infrared mediated tumor destruction by photothermal effect of carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 3:3707–3713
Moon GD, Choi S-W, Cai X et al (2011) A new theranostic system based on gold nanocages and phase-change materials with unique features for photoacoustic imaging and controlled release. J Am Chem Soc 133:4762–4765
Moore A, Medarova Z, Potthast A et al (2004) In vivo targeting of underglycosylated MUC-1 tumor antigen using a multimodal imaging probe. Cancer Res 64:1821–1827
Na HB, Lee IS, Seo H et al (2007) Versatile PEG-derivatized phosphine oxide ligands for water-dispersible metal oxide nanocrystals. Chem Comm: 5167–5169
Nasongkla N, Bey E, Ren J et al (2006) Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett 6:2427–2430
Nurunnabi M, Cho KJ, Choi JS et al (2010) Targeted near-IR QDs-loaded micelles for cancer therapy and imaging. Biomaterials 31:5436–5444
Oerlemans C, Bult W, Bos M et al (2010) Polymeric micelles in anticancer therapy: targeting, imaging and triggered release. Pharm Res 27:2569–2589
Olson ES, Jiang T, Aguilera TA et al (2010) Activatable cell penetrating peptides linked to nanoparticles as dual probes for in vivo fluorescence and MR imaging of proteases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107: 4311–4316
Panowski S, Bhakta S, Raab H et al (2014) Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. mAbs 6: 34–45
Pantarotto D, Singh R, McCarthy D et al (2004) Functionalized carbon nanotubes for plasmid DNA gene delivery. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:5242–5246
Park J-H, von Maltzahn G, Ong LL et al (2010) Cooperative nanoparticles for tumor detection and photothermally triggered drug delivery. Adv Mater 22:880–885
Parungo CP, Ohnishi S, De Grand AM et al (2004) In vivo optical imaging of pleural space drainage to lymph nodes of prognostic significance. Ann Surg Oncol 11:1085–1092
Perche F and Torchilin VP (2013) Recent trends in multifunctional liposomal nanocarriers for enhanced tumor targeting. J Drug Deliv 2013: 705265
Qian XM, Nie SM (2008) Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: from fundamental mechanisms to biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 37:912–920
Ranjan A, Jacobs GC, Woods DL et al (2012) Image-guided drug delivery with magnetic resonance guided high intensity focused ultrasound and temperature sensitive liposomes in a rabbit Vx2 tumor model. J Control Rel 158:487–494
Rizzo LY, Theek B, Storm G et al (2013) Recent progress in nanomedicine: therapeutic, diagnostic and theranostic applications. Curr Opin. Biotech 24:1159–1166
Santra S, Perez JM (2011) Selective N-alkylation of β-alanine facilitates the synthesis of a poly(amino acid)-based theranostic nanoagent. Biomacromolecules 12:3917–3927
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65:5–29
Sun I-C, Eun D-K, Koo H et al (2011) Tumor-targeting gold particles for dual computed tomography/optical cancer imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:9348–9351
Tan WB, Jiang S, Zhang Y (2007) Quantum-dot based nanoparticles for targeted silencing of HER2/neu gene via RNA interference. Biomaterials 28:1565–1571
Tanaka K, Kitamura N and Chujo Y (2011) Bimodal quantitative monitoring for enzymatic activity with simultaneous signal increases in 19F NMR and fluorescence using silica nanoparticle-based molecular probes. Bioconj Chem 22: 1484–1490
Taratula O, Schumann C, Naleway MA et al (2013) A multifunctional theranostic platform based on phthalocyanine-loaded dendrimer for image-guided drug delivery and photodynamic therapy. Mol Pharm 10:3946–3958
Thomas R, Park I-K, Jeong Y (2013) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and therapy of cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14:15910
Tomalia DA, Reyna LA, Svenson S (2007) Dendrimers as multi-purpose nanodevices for oncology drug delivery and diagnostic imaging. Biochem Soc Transac 35: 61–67
Vemuri S, Rhodes CT (1995) Preparation and characterization of liposomes as therapeutic delivery systems: a review. Pharm Acta Helv 70:95–111
von Maltzahn G, Park J-H, Agrawal A et al (2009) Computationally guided photothermal tumor therapy using long-circulating gold nanorod antennas. Cancer Res 69:3892–3900
Voura EB, Jaiswal JK, Mattoussi H et al (2004) Tracking metastatic tumor cell extravasation with quantum dot nanocrystals and fluorescence emission-scanning microscopy. Nat Med 10:993–998
Wang T, Zhang L, Su Z et al (2011) Multifunctional hollow mesoporous silica nanocages for cancer cell detection and the combined chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3: 2479–2486
Wen X, Jackson EF, Price RE et al (2004) Synthesis and characterization of poly(l-glutamic acid) gadolinium chelate: a new biodegradable mri contrast agent. Bioconj Chem 15: 1408–1415
Wiener E, Brechbiel MW, Brothers H et al (1994) Dendrimer-based metal chelates: a new class of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Magn Reson Med 31: 1–8
Willmann JK, van Bruggen N, Dinkelborg LM et al (2008) Molecular imaging in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:591–607
Xia Y, Li W, Cobley CM et al (2011) Gold nanocages: from synthesis to theranostic applications. Acc of Chem Res 44: 914–924
Xie J, Chen K, Huang J et al (2010) PET/NIRF/MRI triple functional iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31:3016–3022
Yang K, Zhang S, Zhang G et al (2010) Graphene in mice: ultrahigh in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett 10:3318–3323
Yang H-M, Oh BC, Kim JH et al (2011) Multifunctional poly(aspartic acid) nanoparticles containing iron oxide nanocrystals and doxorubicin for simultaneous cancer diagnosis and therapy. Coll Surf A 391:208–215
Ye F, Barrefelt Å, Asem H et al (2014) Biodegradable polymeric vesicles containing magnetic nanoparticles, quantum dots and anticancer drugs for drug delivery and imaging. Biomaterials 35:3885–3894
Yu MK, Jeong YY, Park J et al (2008) Drug-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:5362–5365
Zhang Z, Jia J, Lai Y et al (2010) Conjugating folic acid to gold nanoparticles through glutathione for targeting and detecting cancer cells. Bioorgan. Med Chem 18:5528–5534
Zhu Z-J, Yeh Y-C, Tang R et al (2011) Stability of quantum dots in live cells. Nat Chem 3:963–968
Zhu A, Qu Q, Shao X et al (2012) Carbon-dot-based dual-emission nanohybrid produces a ratiometric fluorescent sensor for in vivo imaging of cellular copper ions. Angew Chem 124: 7297–7301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, J.H., Lee, Y.J. & Kim, D. Image-guided nanomedicine for cancer. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 47, 51–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0297-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0297-1