Abstract
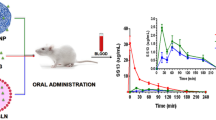
The oral bioavailability of several clinically relevant drugs is compromised because of their limited absorption across the gastrointestinal tract. Active efflux of the drug by transporters such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp) present on the luminal side of the intestinal epithelial cells limits drug absorption. Encapsulation of drugs in nanoparticles can reduce transporter-mediated efflux and increase drug absorption. The purpose of this manuscript is to determine if the bioavailability of doxorubicin, a P-gp substrate, could be increased by encapsulation in nanoparticles. We synthesized polymer-surfactant nanoparticles comprised of a sodium alginate core complexed with doxorubicin and stabilized by the surfactant Aerosol OT (AOT). Encapsulation of doxorubicin in nanoparticles improved its transport across cell monolayers as evidenced by Transwell® studies. Drug uptake studies were carried out in cells overexpressing P-gp and those with basal levels of P-gp. These studies revealed that AOT inhibited P-gp activity and improved drug uptake in P-gp expressing cells by ~5-6-fold. Increase in drug uptake was found only in cells expressing P-gp and was limited to P-gp substrates. We also determined the in vivo oral bioavailability of the nanoparticle formulation of doxorubicin in mice. Doxorubicin delivered in the form of nanoparticles had a higher bioavailability relative to that with the free drug. This study shows that the oral bioavailability of P-gp substrates such as doxorubicin can be enhanced by delivering them in AOT-alginate nanoparticles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Jain R, Pal D, Mitra AK (2007) “Functional characterization of peptide transporters in MDCKII-MDR1 cell line as a model for oral absorption studies”. Int J Pharm 332(1–2):147–152
Aller SG, Yu J, Ward A, Weng Y, Chittaboina S, Zhuo R, Harrell PM, Trinh YT, Zhang Q, Urbatsch IL, Chang G (2009) “Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding”. Science 323(5922):1718–1722
Amidon GL, Lennernas H, Shah VP, Crison JR (1995) “A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability”. Pharm Res 12(3):413–420
Aubel-Sadron G, Londos-Gagliardi D (1984) “Daunorubicin and doxorubicin, anthracycline antibiotics, a physicochemical and biological review”. Biochimie 66(5):333–352
Aungst BJ (1993) “Novel formulation strategies for improving oral bioavailability of drugs with poor membrane permeation or presystemic metabolism”. J Pharm Sci 82(10):979–987
Bardelmeijer HA, Ouwehand M, Buckle T, Huisman MT, Schellens JH, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (2002) “Low systemic exposure of oral docetaxel in mice resulting from extensive first-pass metabolism is boosted by ritonavir”. Cancer Res 62(21):6158–6164
Bogman K, Erne-Brand F, Alsenz J, Drewe J (2003) “The role of surfactants in the reversal of active transport mediated by multidrug resistance proteins”. J Pharm Sci 92(6):1250–1261
Borner MM, Schoffski P, de Wit R, Caponigro F, Comella G, Sulkes A, Greim G, Peters GJ, van der Born K, Wanders J, de Boer RF, Martin C, Fumoleau P (2002) “Patient preference and pharmacokinetics of oral modulated UFT versus intravenous fluorouracil and leucovorin: a randomised crossover trial in advanced colorectal cancer”. Eur J Cancer 38(3):349–358
Chavanpatil MD, Khdair A, Gerard B, Bachmeier C, Miller DW, Shekhar MP, Panyam J (2007a) “Surfactant-polymer nanoparticles overcome P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux”. Mol Pharm 4(5):730–738
Chavanpatil MD, Khdair A, Panyam J (2007b) “Surfactant-polymer nanoparticles: a novel platform for sustained and enhanced cellular delivery of water-soluble molecules”. Pharm Res 24(4):803–810
Choi JS, Piao YJ, Kang KW (2011a) “Effects of quercetin on the bioavailability of doxorubicin in rats: role of CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibition by quercetin.” Arch Pharm Res 34(4):607–13
Choi SJ, Shin SC, Choi JS (2011b) “Effects of myricetin on the bioavailability of doxorubicin for oral drug delivery in rats: possible role of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein inhibition by myricetin.” Arch Pharm Res 34(2):309–15
Das S, Chaudhury A (2011) “Recent advances in lipid nanoparticle formulations with solid matrix for oral drug delivery”. AAPS Pharmscitech 12(1):62–76
DeMario MD, Ratain MJ (1998) “Oral chemotherapy: rationale and future directions”. J Clin Oncol 16(7):2557–2567
Derakhshandeh K, Hochhaus G, Dadashzadeh S (2011) “In-vitro cellular uptake and transport study of 9-nitrocamptothecin PLGA nanoparticles across Caco-2 cell monolayer model”. Iran J Pharm Res 10(3):425–434
Desai MP, Labhasetwar V, Amidon GL, Levy RJ (1996) “Gastrointestinal uptake of biodegradable microparticles: effect of particle size”. Pharm Res 13(12):1838–1845
Dong Y, Feng SS (2005) “Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)/montmorillonite nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs”. Biomaterials 26(30):6068–6076
Findlay M, von Minckwitz G, Wardley A (2008) “Effective oral chemotherapy for breast cancer: pillars of strength”. Ann Oncol 19(2):212–222
Hall SD, Thummel KE, Watkins PB, Lown KS, Benet LZ, Paine MF, Mayo RR, Turgeon DK, Bailey DG, Fontana RJ, Wrighton SA (1999) “Molecular and physical mechanisms of first-pass extraction”. Drug Metab Dispos 27(2):161–166
Hanani M (2012) “Lucifer yellow—an angel rather than the devil”. J Cell Mol Med 16(1):22–31
He C, Yin L, Tang C, Yin C (2012) “Size-dependent absorption mechanism of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of protein drugs”. Biomaterials 33(33):8569–8578
Huang RY, Yu YL, Cheng WC, OuYang CN, Fu E, Chu CL “Immunosuppressive effect of quercetin on dendritic cell activation and function.” (2010) J Immunol 184(12):6815–21
Jabr-Milane LS, van Vlerken LE, Yadav S, Amiji MM (2008) “Multi-functional nanocarriers to overcome tumor drug resistance”. Cancer Treat Rev 34(7):592–602
Jain AK, Swarnakar NK, Godugu C, Singh RP, Jain S (2011) “The effect of the oral administration of polymeric nanoparticles on the efficacy and toxicity of tamoxifen”. Biomaterials 32(2):503–515
Jain S, Patil SR, Swarnakar NK, Agrawal AK (2012) “Oral delivery of doxorubicin using novel polyelectrolyte-stabilized liposomes (layersomes)”. Mol Pharm 9(9):2626–2635
Kalaria DR, Sharma G, Beniwal V, Ravi Kumar MN (2009) “Design of biodegradable nanoparticles for oral delivery of doxorubicin: in vivo pharmacokinetics and toxicity studies in rats”. Pharm Res 26(3):492–501
Karande P, Jain A, Mitragotri S (2004) “Discovery of transdermal penetration enhancers by high-throughput screening”. Nat Biotechnol 22(2):192–197
Ke W, Zhao Y, Huang R, Jiang C, Pei Y (2008) “Enhanced oral bioavailability of doxorubicin in a dendrimer drug delivery system”. J Pharm Sci 97(6):2208–2216
Khdair A, Chen D, Patil Y, Ma L, Dou QP, Shekhar MP, Panyam J (2010) “Nanoparticle-mediated combination chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy overcomes tumor drug resistance”. J Control Release 141(2):137–144
Kirtane AR, Kalscheuer SM, Panyam J (2013) “Exploiting nanotechnology to overcome tumor drug resistance: challenges and opportunities”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(13–14):1731–1747
Lo YL (2003) “Relationships between the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values of pharmaceutical excipients and their multidrug resistance modulating effect in Caco-2 cells and rat intestines”. J Control Release 90(1):37–48
Murakami M, Cabral H, Matsumoto Y, Wu S, Kano MR, Yamori T, Nishiyama N, Kataoka K (2011) “Improving drug potency and efficacy by nanocarrier-mediated subcellular targeting”. Sci Transl Med 3(64):64ra2
Panyam J, Zhou WZ, Prabha S, Sahoo SK, Labhasetwar V (2002) “Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: implications for drug and gene delivery”. FASEB J 16(10):1217–1226
Patel NR, Pattni BS, Abouzeid AH, Torchilin VP (2013) “Nanopreparations to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(13–14):1748–1762
Putnam WS, Ramanathan S, Pan L, Takahashi LH, Benet LZ (2002) “Functional characterization of monocarboxylic acid, large neutral amino acid, bile acid and peptide transporters, and P-glycoprotein in MDCK and Caco-2 cells”. J Pharm Sci 91(12):2622–2635
Reineke JJ, Cho DY, Dingle YT, Morello AP 3rd, Jacob J, Thanos CG, Mathiowitz E (2013) “Unique insights into the intestinal absorption, transit, and subsequent biodistribution of polymer-derived microspheres”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(34):13803–8
Roger E, Kalscheuer S, Kirtane A, Guru BR, Grill AE, Whittum-Hudson J, Panyam J (2012) “Folic acid functionalized nanoparticles for enhanced oral drug delivery”. Mol Pharm 9(7):2103–2110
Sarthy PV, Johnson SM, Detwiler PB (1982) “Selective uptake of lucifer yellow by retinal cells”. J Comp Neurol 206(4):371–378
Sastry SV, Nyshadham JR, Fix JA (2000) “Recent technological advances in oral drug delivery—a review”. Pharm Sci Technol Today 3(4):138–145
Schleh C, Semmler-Behnke M, Lipka J, Wenk A, Hirn S, Schaffler M, Schmid G, Simon U, Kreyling WG (2012) “Size and surface charge of gold nanoparticles determine absorption across intestinal barriers and accumulation in secondary target organs after oral administration”. Nanotoxicology 6(1):36–46
Sharom FJ (1997) “The P-glycoprotein efflux pump: how does it transport drugs?” J Membr Biol 160(3):161–175
Smith AJ, Kavuru P, Wojtas L, Zaworotko MJ, Shytle RD (2011) “Cocrystals of quercetin with improved solubility and oral bioavailability”. Mol Pharm 8(5):1867–1876
Sosnik A (2013) “Reversal of multidrug resistance by the inhibition of ATP-binding cassette pumps employing “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) nanopharmaceuticals: a review”. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65(13–14):1828–1851
Sparreboom A, van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Smit JW, Meijer DK, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (1997) “Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (Taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(5):2031–2035
Stegemann S, Leveiller F, Franchi D, de Jong H, Linden H (2007) “When poor solubility becomes an issue: from early stage to proof of concept”. Eur J Pharm Sci 31(5):249–261
Usacheva M, Swaminathan SK, Kirtane AR, Panyam J (2014) “Enhanced photodynamic therapy and effective elimination of cancer stem cells using surfactant-polymer nanoparticles”. Mol Pharm 11(9):3186–3195
Zhang H, Yao M, Morrison RA, Chong S (2003) “Commonly used surfactant, Tween 80, improves absorption of P-glycoprotein substrate, digoxin, in rats”. Arch Pharm Res 26(9):768–772
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ameya R. Kirtane and Priyanka Narayan have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirtane, A.R., Narayan, P., Liu, G. et al. Polymer-surfactant nanoparticles for improving oral bioavailability of doxorubicin. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 47, 65–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0293-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0293-5