Abstract
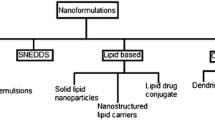
Nanotechnology has been applied to the oral drug delivery for enhancing bioavailability after oral administration. Numerous forms of reported nanomedicines are classified as lipid based nanomedicine (LBNM), polymer based nanomedicine (PBNM), and nanosuspension. LBNM includes self nano-emulsifying drug delivery systems, liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN). PBNM includes polymeric nanoparticles and polymeric micelles. Unlike intravenous administration, oral administration has more complicated barriers that are hard to overcome. The various nanoplatforms described above are used to surmount physical and bio-chemical barriers due to advantageous characteristics of nanoplatforms. The characteristics of nanoplatforms including particle size, stimuli-sensitivity, preventing drug efflux, solubility and permeation of the drug induce the enhanced absorption and high bioavailability. Regardless of passionate researches, some limitations still exist, for instance economic problems, toxicity issue, and development of biopharmaceutic oral nanomedicine. In this review, physiological barriers in oral administration, advantages of nanomedicines, classification of oral nanomedicines, and their challenges are described concisely.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batrakova EV, Kabanov AV (2008) Pluronic block copolymers: evolution of drug delivery concept from inert nanocarriers to biological response modifiers. J Control Release 130:98–106
Bawarski WE, Chidlowsky E, Bharali DJ, Mousa SA (2008) Emerging nanopharmaceuticals. Nanomed Nanotechnol 4:273–282
Bromberg L (2008) Polymeric micelles in oral chemotherapy. J Control Release 128:99–112
Chan HK, Kwok PCL (2011) Production methods for nanodrug particles using the bottom-up approach. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:406–416
Charman WN (1992) Lipid vehicle and formulation effects on intestinal lymphatic drug transport. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Charman WN, Porter CJH, Mithani S, Dressman JB (1997) Physicochemical and physiological mechanisms for the effects of food on drug absorption: the role of lipids and pH. J Pharm Sci 86:269–282
Chavanpatil MD, Khdair A, Gerard B, Bachmeier C, Miller DW, Shekhar MP, Panyam J (2007) Surfactant–polymer nanoparticles overcome P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux. Mol Pharm 4:730–738
Crater JS, Carrier RL (2010) Barrier properties of gastrointestinal mucus to nanoparticle transport. Macromol Biosci 10:1473–1483
Dabholkar RD, Sawant RM, Mongayt DA, Devarajan PV, Torchilin VP (2006) Polyethylene glycol-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate (PEG-PE)-based mixed micelles: some properties, loading with paclitaxel, and modulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux. Int J Pharm 315:148–157
De Jong WH, Borm PJA (2008) Drug delivery and nanoparticles: applications and hazards. Int J Nanomed 3:133–149
des Rieux A, Fievez V, Garinot M, Schneider YJ, Preat V (2006) Nanoparticles as potential oral delivery systems of proteins and vaccines: a mechanistic approach. J Control Release 116:1–27
Desai PP, Date AA, Patravale VB (2012) Overcoming poor oral bioavailability using nanoparticle formulations—opportunities and limitations. Drug Discov Today 9:e87–e95
Dingler A, Weyhers H, zur MuČhlen A, Mehnert W (1997) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) ąein neuartiger Wirkstoff-Carrier fuČr Kosmetika und Pharmazeutika. III. LangzeitstabilitaČt, Gefrierund SpruČhtrocknung, Anwendung in Kosmetika und Pharmazeutika. Pharm. Ind
Dressman J, Vertzoni M, Goumas K, Reppas C (2007) Estimating drug solubility in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:591–602
Drumm B, Neumann AW, Policova Z, Sherman PM (1989) Bacterial cell surface hydrophobicity properties in the mediation of in vitro adhesion by the rabbit enteric pathogen Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1. J Clin Investig 84:1588–1594
Eldem T, Speiser P, Hincal A (1991) Optimization of spray-dried and -congealed lipid micropellets and characterization of their surface morphology by scanning electron microscopy. Pharm Res 8:47–54
Eldridge JH, Hammond CJ, Meulbroek JA, Staas JK, Gilley RM, Tice TR (1990) Controlled vaccine release in the gut-associated lymphoid tissues. I. Orally administered biodegradable microspheres target the peyer’s patches. J Control Release 11:205–214
Ensign LM, Cone R, Hanes J (2012) Oral drug delivery with polymeric nanoparticles: the gastrointestinal mucus barriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 64:557–570
Francis MF, Piredda M, Winnik FM (2003) Solubilization of poorly water soluble drugs in micelles of hydrophobically modified hydroxypropylcellulose copolymers. J Control Release 93:59–68
Galindo-Rodriguez SA, Allemann E, Fessi H, Doelker E (2005) Polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of drugs and vaccines: a critical evaluation of in vivo studies. Crit Rev Ther Drug 22:419–463
Gao P, Rush BD, Pfund WP, Huang T, Bauer JM, Morozowich W, Kuo MS, Hageman MJ (2003) Development of a supersaturable SEDDS (S-SEDDS) formulation of paclitaxel with improved oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci 92:2386–2398
Gaucher G, Satturwar P, Jones MC, Furtos A, Leroux JC (2010) Polymeric micelles for oral drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 76:147–158
Goto T, Morishita M, Nishimura K, Nakanishi M, Kato A, Ehara J, Takayama K (2006) Novel mucosal insulin delivery systems based on fusogenic liposomes. Pharm Res 23:384–391
Hillaireau H, Couvreur P (2009) Nanocarriers’ entry into the cell: relevance to drug delivery. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2873–2896
Hillery AM, Lloyd AW, Swarbrick J (2002) Drug delivery and targeting: for pharmacists and pharmaceutical scientists. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hofheinz RD, Gnad-Vogt SU, Beyer U, Hochhaus A (2005) Liposomal encapsulated anti-cancer drugs. Anticancer Drugs 16:691–707
Hu FQ, Ren GF, Yuan H, Du YZ, Zeng S (2006) Shell cross-linked stearic acid grafted chitosan oligosaccharide self-aggregated micelles for controlled release of paclitaxel. Colloid Surf B 50:97–103
Italia JL, Bhatt DK, Bhardwaj V, Tikoo K, Kumar MNVR (2007) PLGA nanoparticles for oral delivery of cyclosporine: nephrotoxicity and pharmacokinetic studies in comparison to Sandimmune Neoral (R). J Control Release 119:197–206
Johnston MJ, Semple SC, Klimuk SK, Ansell S, Maurer N, Cullis PR (2007) Characterization of the drug retention and pharmacokinetic properties of liposomal nanoparticles containing dihydrosphingomyelin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:1121–1127
Junghanns JUAH, Muller RH (2008) Nanocrystal technology, drug delivery and clinical applications. Int J Nanomed 3:295–309
Kararli TT, Needham TE, Griffin M, Schoenhard G, Ferro LJ, Alcorn L (1992) Oral delivery of a renin inhibitor compound using emulsion formulations. Pharm Res 9:888–893
Kawashima Y, Yamamoto H, Takeuchi H, Kuno Y (2000) Mucoadhesive dl-lactide/glycolide copolymer nanospheres coated with chitosan to improve oral delivery of elcatonin. Pharm Dev Technol 5:77–85
Khachane P, Date AA, Nagarsenker MS (2011) Eudragit EPO nanoparticles: application in improving therapeutic efficacy and reducing ulcerogenicity of meloxicam on oral administration. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:590–597
Kreuter J (2001) Nanoparticulate systems for brain delivery of drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47:65–81
Kumari A, Yadav SK, Yadav SC (2010) Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloid Surf B 75:1–18
Kwon SH, Kim SY, Ha KW, Kang MJ, Huh JS, Im TJ, Kim YM, Park YM, Kang KH, Lee S, Chang JY, Lee J, Choi YW (2007) Pharmaceutical evaluation of genistein-loaded pluronic micelles for oral delivery. Arch Pharm Res 30:1138–1143
Lee SC, Huh KM, Lee J, Cho YW, Galinsky RE, Park K (2007) Hydrotropic polymeric micelles for enhanced paclitaxel solubility: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Biomacromolecules 8:202–208
Li XM, Gu L, Xu YL, Wang YL (2009) Preparation of fenofibrate nanosuspension and study of its pharmacokinetic behavior in rats. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 35:827–833
Li D, Tang J, Wei C, Guo J, Wang SL, Chaudhary D, Wang CC (2012) Doxorubicin-conjugated mesoporous magnetic colloidal nanocrystal clusters stabilized by polysaccharide as a smart anticancer drug vehicle. Small 8:2690–2697
Liu ZH, Jiao YP, Wang YF, Zhou CR, Zhang ZY (2008) Polysaccharides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1650–1662
Lo YK, Chen CJ, Tsai TR, Cham TM (2007) Comparison of the solubility and dissolution rate between gliclazide solid complex and its nanospheres. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 33:301–309
Lucks S, Müller R (1996) Arzneistoffträger aus festen lipidteilchen (feste lipidnanosphären (sln)) (EP 0605497B1)
Malcolmson C, Lawrence MJ (1993) A comparison of the incorporation of model steroids into non-ionic micellar and microemulsion systems. J Pharm Pharmacol 45:141–143
Mantle M, Basaraba L, Peacock SC, Gall DG (1989) Binding of Yersinia enterocolitica to rabbit intestinal brush border membranes, mucus, and mucin. Infect Immun 57:3292–3299
Maya S, Indulekha S, Sukhithasri V, Smitha KT, Nair SV, Jayakumar R, Biswas R (2012) Efficacy of tetracycline encapsulated O-carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles against intracellular infections of Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Biol Macromol 51:392–399
Morishita M, Peppas NA (2006) Is the oral route possible for peptide and protein drug delivery? Drug Discov Today 11:905–910
Morrow KJ Jr, Bawa R, Wei C (2007) Recent advances in basic and clinical nanomedicine. Med Clin North Am 91:805–843
Muller RH, Mader K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:161–177
Muller RH, Runge S, Ravelli V, Mehnert W, Thunemann AF, Souto EB (2006) Oral bioavailability of cyclosporine: solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus drug nanocrystals. Int J Pharm 317:82–89
Muller RH, Runge SA, Ravelli V, Thunemann AF, Mehnert W, Souto EB (2008) Cyclosporine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): drug-lipid physicochemical interactions and characterization of drug incorporation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68:535–544
Müllertz A, Ogbonna A, Ren S, Rades T (2010) New perspectives on lipid and surfactant based drug delivery systems for oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:1622–1636
Norris DA, Sinko PJ (1997) Effect of size, surface-charge, and hydrophobicity on the translocation of polystyrene microspheres through gastrointestinal mucin. J Appl Polym Sci 63:1481–1492
Norris DA, Puri N, Sinko PJ (1998) The effect of physical barriers and properties on the oral absorption of particulates. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 34:135–154
Ojer P, Neutsch L, Gabor F, Irache JM, López De Cerain A (2013) Cytotoxicity and cell interaction studies of bioadhesive poly(anhydride) nanoparticles for oral antigen/drug delivery. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:1891–1903
Ojer P, Iglesias T, Azqueta A, Irache JM, López de Cerain A (2015) Toxicity evaluation of nanocarriers for the oral delivery of macromolecular drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm Part A 97:206–217
Olmsted SS, Padgett JL, Yudin AI, Whaley KJ, Moench TR, Cone RA (2001) Diffusion of macromolecules and virus-like particles in human cervical mucus. Biophys J 81:1930–1937
Omri A, Suntres ZE, Shek PN (2002) Enhanced activity of liposomal polymyxin B against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a rat model of lung infection. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1407–1413
Ould-Ouali L, Noppe M, Langlois X, Willems B, Riele PT, Timmerman P, Brewster ME, Arien A, Preat V (2005) Self-assembling PEG-p(CL-co-TMC) copolymers for oral delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs: a case study with risperidone. J Controlled Release 102:657–668
Pierri E, Avgoustakis K (2005) Poly(lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol) micelles as a carrier for griseofulvin. J Biomed Mater Res A 75a:639–647
Pouton CW (2000) Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci 11:S93–S98
Preetham AC, Satish CS (2011) Formulation of a poorly water-soluble drug sirolimus in solid dispersions to improve dissolution. J Dispers Sci Technol 32:778–783
Prietl B, Meindl C, Roblegg E, Pieber TR, Lanzer G, Frohlich E (2014) Nano-sized and micro-sized polystyrene particles affect phagocyte function. Cell Biol Toxicol 30:1–16
Ramesan RM, Sharma CP (2009) Challenges and advances in nanoparticle-based oral insulin delivery. Expert Rev Med Devices 6:665–676
Rouxhet L, Dinguizli M, Dwan’Isa JPL, Ould-Ouali L, Twaddle P, Nathan A, Brewster ME, Rosenblatt J, Arien A, Preat V (2009) Monoglyceride-based self-assembling copolymers as carriers for poorly water-soluble drugs. Int J Pharm 382:244–253
Sajjan U, Reisman J, Doig P, Irvin RT, Forstner G, Forstner J (1992) Binding of nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to normal human intestinal mucin and respiratory mucin from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Investig 89:657–665
Sarmento B, Martins S, Ferreira D, Souto EB (2007) Oral insulin delivery by means of solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 2:743–749
Saupe A, Gordon KC, Rades T (2006) Structural investigations on nanoemulsions, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers by cryo-field emission scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy. Int J Pharm 314:56–62
Schiffelers RM, Storm G, Bakker-Woudenberg IA (2001) Host factors influencing the preferential localization of sterically stabilized liposomes in Klebsiella pneumoniae-infected rat lung tissue. Pharm Res 18:780–787
Shah NH, Carvajal MT, Patel CI, Infeld MH, Malick AW (1994) Self-emulsifying drug-delivery systems (Sedds) with polyglycolyzed glycerides for improving in-vitro dissolution and oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Int J Pharm 106:15–23
Shahidi F, Kamil YVAJ (2001) Enzymes from fish and aquatic invertebrates and their application in the food industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 12:435–464
Shegokar R, Muller RH (2010) Nanocrystals: industrially feasible multifunctional formulation technology for poorly soluble actives. Int J Pharm 399:129–139
Shen H, Zhong M (2006) Preparation and evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) containing atorvastatin. J Pharm Pharmacol 58:1183–1191
Shidhaye SS, Vaidya R, Sutar S, Patwardhan A, Kadam VJ (2008) Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers–innovative generations of solid lipid carriers. Curr Drug Deliv 5:324–331
Shono Y, Jantratid E, Kesisoglou F, Reppas C, Dressman JB (2010) Forecasting in vivo oral absorption and food effect of micronized and nanosized aprepitant formulations in humans. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 76:95–104
Singh R, Lillard JW (2009) Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp Mol Pathol 86:215–223
Solans C, Izquierdo P, Nolla J, Azemar N, Garcia-Celma M (2005) Nano-emulsions. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 10:102–110
Sosnik A, das Neves J, Sarmento B (2014) Mucoadhesive polymers in the design of nano-drug delivery systems for administration by non-parenteral routes: a review. Prog Polym Sci 39:2030–2075
Speiser PPD (1990). Lipidnanopellets als Trägersystem für Arzneimittel zur peroralen Anwendung. Google Patents
Stano P, Bufali S, Pisano C, Bucci F, Barbarino M, Santaniello M, Carminati P, Luisi PL (2004) Novel camptothecin analogue (gimatecan)-containing liposomes prepared by the ethanol injection method. J Liposome Res 14:87–109
Suresh G, Manjunath K, Venkateswarlu V, Satyanarayana V (2007) Preparation, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of lovastatin solid lipid nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 8:24
Swarbrick J (2007) Encyclopedia of pharmaceutical technology. Informa Healthcare, New York
Tang BC, Dawson M, Lai SK, Wang YY, Suk JS, Yang M, Zeitlin P, Boyle MP, Fu J, Hanes J (2009) Biodegradable polymer nanoparticles that rapidly penetrate the human mucus barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19268–19273
Thomas N, Holm R, Mullertz A, Rades T (2012) In vitro and in vivo performance of novel supersaturated self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (super-SNEDDS). J Control Release 160:25–32
Trull AK, Tan KK, Tan L, Alexander GJ, Jamieson NV (1995) Absorption of cyclosporin from conventional and new microemulsion oral formulations in liver transplant recipients with external biliary diversion. Br J Clin Pharmacol 39:627–631
Van Eerdenbrugh B, Van den Mooter G, Augustijns P (2008) Top-down production of drug nanocrystals: nanosuspension stabilization, miniaturization and transformation into solid products. Int J Pharm 364:64–75
Vila A, Sanchez A, Tobio M, Calvo P, Alonso MJ (2002) Design of biodegradable particles for protein delivery. J Control Release 78:15–24
Werle M, Takeuchi H (2009) Chitosan-aprotinin coated liposomes for oral peptide delivery: development, characterisation and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm 370:26–32
Yamanaka YJ, Leong KW (2008) Engineering strategies to enhance nanoparticle-mediated oral delivery. J Biomat Sci Polym Ed 19:1549–1570
Yeni P (2003) Tipranavir: a protease inhibitor from a new class with distinct antiviral activity. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 34(Suppl 1):S91–94
Yi Y, Yoon HJ, Kim BO, Shim M, Kim SO, Hwang SJ, Seo MH (2007) A mixed polymeric micellar formulation of itraconazole: characteristics, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. J Control Release 117:59–67
Yun Y, Cho YW, Park K (2013) Nanoparticles for oral delivery: targeted nanoparticles with peptidic ligands for oral protein delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:822–832
Zaki NM, Hafez MM (2012) Enhanced antibacterial effect of ceftriaxone sodium-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against intracellular Salmonella typhimurium. AAPS PharmSciTech 13:411–421
Zhang L, Katapodi K, Davis TP, Barner-Kowollik C, Stenzel MH (2006) Using the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process to synthesize core-crosslinked micelles. J Polym Sci Pol Chem 44:2177–2194
Acknowledgments
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. And All authors (T Sim, C Lim, NH Hoang, H Joo, JW Lee, D Kim, ES Lee, YS Youn, JO Kim, KT Oh) declare that they have no conflict of interest. This research was supported by a Grant (15182MFDS486) from Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2016. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2014R1A2A1A11050094), a grant from the Medical Cluster R&D Support Project of Daegu Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation, Republic of Korea (2013) (No. HT13C0011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, T., Lim, C., Hoang, N.H. et al. Nanomedicines for oral administration based on diverse nanoplatform. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 46, 351–362 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0255-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0255-y