Abstract
Background:
Prosthetic joint infections (PJIs) caused by methicillin-resistant gram-positive bacteria are primarily treated by intravenous vancomycin. Linezolid, active against methicillin-resistant strains and available in oral and intravenous dosage forms, is a potential alternative to vancomycin for the treatment of PJIs.
Objective:
To analyze the cost of linezolid therapy (outpatient setting) and vancomycin therapy (inpatient and outpatient settings) for PJIs caused by methicillin-resistant gram-positive bacteria.
Methods:
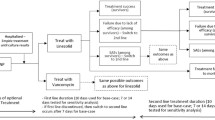
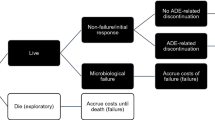
A decision tree was designed to simulate the clinical outcome and healthcare resource utilization of linezolid, vancomycin by outpatient and home parenteral antimicrobial therapies (OHPAT) and vancomycin administered in inpatient setting (rehabilitation facility) for patients with PJIs caused by methicillin-resistant strains. Clinical inputs were estimated from literature and the cost analysis was conducted from the perspective of the public healthcare provider in Hong Kong.
Results:
The base-case analysis showed that the vancomycin (OHPAT) group (USD14,470 per patient) was the least costly alternative, followed by the linezolid group (USD17,877 per patient) and the vancomycin (rehabilitation) group (USD19,980 per patient) (1USD = 7.8HKD). The clinical treatment success rates of vancomycin and linezolid were influential factors. Monte Carlo 10,000 simulations showed that the vancomycin (OHPAT) group was less costly than the arms of linezolid and vancomycin (rehabilitation) 64% and 100% of the time, respectively. The linezolid group was less costly than the vancomycin (rehabilitation) group in 65%of the times.
Conclusion:
Home-infusion of vancomycin therapy appears to be the least costly treatment approach for PJIs caused by methicillin-resistant gram-positive bacteria from the perspective of a Hong Kong public health organization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, J.H.S., Lee, G.C.H., So, R.K.H. et al. Linezolid versus Vancomycin for Prosthetic Joint Infections: a Cost Analysis. Infection 35, 265–270 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6304-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-007-6304-8