Abstract
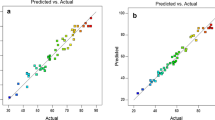
Since 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) is one of the most used explosives for military purposes or different industries such as mining and construction, it is highly probable to cause environmental pollution. Exposure to TNT can cause serious health problems in humans; therefore, its degradation is important. Two advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) were thoroughly investigated for TNT degradation in the presence of 0.04 M Fe(II)-EDTA complex at circumneutral pH (pH 6). In order to produce two different powerful oxidative radicals, namely, •OH and •SO4−, 100 mM H2O2 and K2S2O8 were used, respectively. Interferences of different radical scavengers possibly present in water and soil were also tested in detail. In order to determine TNT concentrations before and after AOP degradation, an existing colorimetric method was modified, depending on the formation of Meisenheimer anion of TNT. The optimal degradation conditions were experimentally determined and analyzed using face-centered composite design (FCCD) program. Both approaches showed that the most important parameters were the concentrations of Fe-EDTA and oxidant for TNT decomposition. The optimal degradation percentages were determined as 84 and 88%, respectively, in the presence of K2S2O8 and H2O2. The persulfate-aided process was much less affected by •OH scavenger solvents such as t-butanol and DMSO. The novel persulfate-driven process was advantageously not affected from catalase (the H2O2 annihilator enzyme) which may exist in soil to eventually obstruct the H2O2 treatment of TNT wastes. This work establishes a comprehensive persulfate process for the first time and improves the existing process with H2O2 in the Fe(II)-EDTA degradation of TNT.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayoub K, van Hullebusch ED, Cassir M, Bermond A (2010) Application of advanced oxidation processes for TNT removal: a review. J Hazard Mater 178(1–3):10–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.042
Ayoub K, Nélieu S, van Hullebusch ED, Maia-Grondard A, Cassir M, Bermond A (2011) TNT oxidation by Fenton reaction: reagent ratio effect on kinetics and early stage degradation pathways. Chem Eng J 173:309– 317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.07.022
Bečanová J, Friedl Z, Šimek Z (2010) Identification and determination of trinitrotoluenes and their degradation products using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 29(3):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2010.01.016
Bokare AD, Choi W (2014) Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J Hazard Mater 275:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.04.054
Busto MD, Perez-Mateos M (1995) Extraction of humic-β-glucosidase fractions from soil. Biol Fertil Soils 20:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307845
Fei T, Jiang K, Zhang T (2014) Highly sensitive TNT photoluminescent sensing by a phosphorescent complex. Sens Actuators B Chem 199:148–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.03.088
Francis KC, Cummins D, Oakes J (1985) Kinetic and structural investigations of [Feııı(EDTA)]—[EDTA = ethylenediaminetetra-acetate(4-)] catalysed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. J Chem Soc Dalton Trans. https://doi.org/10.1039/DT9850000493
Gilbert BC, Hanson P, Jones JR, Whitwood AC, Timms AW (1992) EPR Investigation into the kinetics and mechanism of the one-electron reduction of benzenediazonium ions by FeII-EDTA and other iron(II) complexes. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:629–636. https://doi.org/10.1039/P29920000629
Hou K, Pi Z, Yao F, Wu B, He L, Li X, Wang D, Dong H, Yang Q (2021) A critical review on the mechanisms of persulfate activation by iron-based materials: clarifying some ambiguity and controversies. Chem Eng J 407:127078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127078
Hughes S, Dasary SSR, Begum S, Williams N, Yu H (2015) Meisenheimer complex between 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane and its use for a paper—based sensor. Sens Bio-Sensing Res 5:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2015.06.003
Kalderis D, Hawthorne SB, Clifford AA, Gidarakos E (2008) Interaction of soil, water and TNT during degradation of TNT on contaminated soil using subcritical water. J Hazard Mater 159:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.02.041
Kavitha V, Palanivelu K (2005) Degradation of nitrophenols by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. J Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 170:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2004.08.003
Khan MI, Lee J, Yoo K, Kim S, Park J (2015) Improved TNT detoxification by starch addition in a nitrogen-fixing Methylophilus-dominant aerobic microbial consortium. J Hazard Mater 300:873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.032
Khatebasreh M, Hajhoseini M, Teimouri F (2022) A feasibility study on synergistic effect of radical sulfate activated by ozone on explosive degradation by performance of Taguchi Design method. J Water Chem Technol 44(3):162–168. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X22030067
Lee PA, de Mora SJ, Levasseur M (1999) A review of dimethylsulfoxide in aquatic environments. Atmos Ocean 37(4):439–456. https://doi.org/10.1080/07055900.1999.9649635
Li ZM, Peterson MM, Comfort SD, Horst GL, Shea PJ, Oh BT (1997) Remediating TNT-contaminated soil by soil washing and Fenton oxidation. Sci Total Environ 204:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00158-7
Li Y, Zhang W, Mu K, Li S, Wang J, Zhang S, Wang L (2023) An ultrasound-Fenton process for the degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Int J Environ Res Public Health 20:3102
Liang C, Liang C-P, Chen C-C (2009) pH dependence of persulfate activation by EDTA/Fe(III) for degradation of trichloroethylene. J Contam Hydrol 106:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2009.02.008
Liou M-J, Lu M-C (2007) Catalytic degradation of nitroaromatic explosives with Fenton’s reagent. J Mol Catal A Chem 277:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2007.07.030
Matta R, Hanna K, Chiron S (2007) Fenton-like oxidation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene using different iron minerals. Sci Total Environ 385:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.06.030
Matta R, Hanna K, Kone T, Chiron S (2008) Oxidation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in the presence of different iron-bearing minerals at neutral pH. Chem Eng J 144:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.07.013
Niven RK (2005) Ethanol in gasoline: environmental impacts and sustainability review article. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 9:535–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2004.06.003
Pascal I, Tarbell DS (1957) The kinetics of the oxidation of a mercaptan to the corresponding disulfide by aqueous hydrogen peroxide. J Am Chem Soc 79:6015–6020. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01579a045
Perez-Mateos M, Gonzalez-Carcedo S, Busto Nuňez MD (1988) Division S-3-soil microbiology and biochemistry, extraction of catalase from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:408–411. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200020018x
Pignatello JJ, Oliveros E, MacKay A (2006) Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 36:1–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380500326564
Rastogi A, Al-Abed SR, Dionysiou DD (2009) Effect of inorganic, synthetic and naturally occurring chelating agents on Fe(II) mediated advanced oxidation of chlorophenols. Water Res 43:684–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.045
Romera-Castillo C, Jaffé R (2015) Free radical scavenging (antioxidant activity) of natural dissolved organic matter. Marine Chem 177(4):668–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2015.10.008
Serrano-Gonzalez MY, Chandra R, Castillo-Zacarias C, Robledo-Padilla F, Rostro-Alanis MJ, Parra-Saldivar R (2018) Biotransformation and degradation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by microbial metabolism and their interaction. Def Technol 14:151–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dt.2018.01.004
Tachiev G, Roth JA, Bowers AR (2000) Kinetics of hydrogen peroxide decomposition with complexed and “free” iron catalysts. Int J Chem Kinetics 32(1):24–35
United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA, Technical Fact Sheet (2014) https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-03/documents/ffrrofactsheet_contaminant_tnt_january2014_final.pdf
Üzer A, Erçag E, Apak R (2004) Selective spectrophotometric determination of trinitrotoluene, trinitrophenol, dinitrophenol and mononitrophenol. Anal Chim Acta 505:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00674-3
Uzunboy S, Demirci-Çekiç S, Eksin E, Erdem A, Apak R (2017) CUPRAC colorimetric and electroanalytical methods determining antioxidant activity based on prevention of oxidative DNA damage. Anal Biochem 518:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.028
Uzunboy S, Karakaş Ö, Demirci-Çekiç S, Apak R (2021) Sulfate radical formation by Cr(III) activation of peroxydisulfate—Diphenylcarbazide spectrophotometric determination of sulfate radical and its scavenging activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectros 260:119941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119941
Walsh ME (2001) Determination of nitroaromatic, nitramine, and nitrate ester explosives in soil by gas chromatography and an electron capture detector. Talanta 54(3):427–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-9140(00)00541-5
Wang L, Li B, Dionysiou DD, Chen B, Yang J, Li J (2022) Overlooked formation of H2O2 during the hydroxyl radical scavenging process when using alcohols as scavengers. Environ Sci Technol 56:3386–3396. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c03796
Whiteman M, Halliwel B (1997) Thiourea and dimethylthiourea inhibit peroxynitrite-dependent damage: nonspecificity as hydroxyl radical scavenger. Free Radic Biol Med 22(7):1309–1312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00545-X
Yamazaki I, Piette LH (1990) ESR Spin-trapping studies on the reaction of Fe2+ ions with H2O2-reactive species in oxygen toxicity in biology. J Biol Chem 265(23):13589–13594. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)77389-4
Zarzycki PK, Zarzycka MB, Ślączka MM, Clifton VL (2010) Acetonitrile, the polarity chameleon. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:905–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3677-9
Zhang Y, Zhou M (2019) A critical review of the application of chelating agents to enable Fenton and Fenton-like reactions at high pH values. J Hazard Mater 362:436–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.035
Zhang B-T, Zhang Y, Teng Y, Fan M (2015) Sulfate radical and its application in decontamination technologies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1756–1800. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.970681
Zhou D, Zhang H, Chen L (2015) Sulfur-replaced Fenton systems: can sulfate radical substitute hydroxyl radical for advanced oxidation technologies? J Chem Technol Biotechnol 90:775–779. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4525
Zhu Y, Ma J, Chen F, Yu R, Hu G, Zhang S (2020) Remediation of soil polluted with Cd in a postmining area using thiourea-modified biochar. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:7654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207654
Acknowledgements
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seda Uzunboy and Mustafa Bener worked in investigation and methodology. Sema Demirci-Çekiç helped in validation and writing—original draft. Reşat Apak helped in conceptualization and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: S. Rangabhashiyam.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uzunboy, S., Bener, M., Demirci-Çekiç, S. et al. Investigation and modeling of oxidative TNT degradation using Fe(II)-EDTA in conjunction with K2S2O8 and H2O2. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05600-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05600-0