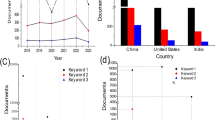
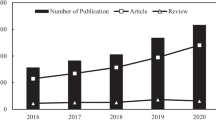
Abstract
Water pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) has lately received considerable attention due to their wide prevalence in the environment and deleterious effects on health. Naphthalene (NP), the simplest and most common PAH, has been extensively utilized for the production of important chemicals such as phthalic anhydride and methyl anthranilate. However, owing to its health-related concerns, NP has been classified as a hazardous pollutant, mandating its removal from water systems. Adsorption has been long the preferred approach for the removal of several pollutants including NP from wastewaters. In this review, we summarize the recent research articles evaluating the removal of NP from aqueous solutions and wastewaters by a series of adsorbents (i.e., activated carbons, graphene derivatives, clay minerals, wastes/by-products, and composites). It is clear from the literature that modified materials have exhibited remarkable performance toward the removal of NP. More importantly, we highlight the potential use of adsorption integrated with other processes for the enhancement of NP removal from wastewaters. Based on the studies published in the last decade (i.e., since 2010), we pinpoint out as well the main existing shortcomings, which need to be considered in future research endeavors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- NP:
-
Naphthalene
- ACs:
-
Activated carbons
- MCM-41:
-
Mobil Composition of Matter-41
- APTES:
-
(3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane
- PABA:
-
P-aminobenzoic acid
- SBA-15:
-
Santa barbara amorphous-15
- MIL-101:
-
Material Institute Lavoisier
- DVB:
-
Polydivinylbenzene
- MMA-DVB:
-
Poly(methyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene)
- TX-100:
-
Triton X-100
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- NR:
-
Not reported
- CNTs:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- MOFs:
-
Metal–organic frameworks
References
Abass A, Omotayo A, Tinuade A, Aderonke O (2012) Adsorption of naphthalene onto activated carbons derived from milk bush kernel shell and flamboyant pod. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 4:124–132. https://doi.org/10.5897/jece11.041
Abo R, Kummer NA, Merkel BJ (2016) Optimized photodegradation of Bisphenol A in water using ZnO, TiO2and SnO2photocatalysts under UV radiation as a decontamination procedure. Drink Water Eng Sci 9:27–35. https://doi.org/10.5194/dwes-9-27-2016
Abu-Elella R, Ossman ME, Abd-Elfatah M, Elgendi A (2013) Kinetic modeling and isotherm study for naphthalene adsorption on boehmite nanopowder. Desalin Water Treat 51:3472–3481. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.749370
Adekunle AS, Oyekunle JAO, Oladele AS et al (2020) Evaluation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and health risk assessment of surface water and sediments of river sasa, ife north local government Area, Nigeria. Chem Africa 3:1109–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-020-00160-5
Agarry SE, Aremu MO (2012) Batch equilibrium and kinetic studies of simultaneous adsorption and biodegradation of naphthalene by orange peels immobilized pseudomonas aeruginosa NCIB 950. J Bioremediation Biodegrad. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000138
Agarry SE, Aremu MO, Ajani AO (2013a) Modelling the simultaneous adsorption and biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons onto non-carbonized biological adsorbent in batch system. Chem Process Eng Res 12:9–19
Agarry SE, Ogunleye OO, Aworanti OA (2013b) Biosorption equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic modelling of naphthalene removal from aqueous solution onto modified spent tea leaves. Environ Technol (united Kingdom) 34:825–839. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2012.720616
Aisien FA, Amenaghawon AN, Adinkwuye AI (2014) Batch study, equilibrium and kinetics of adsorption of naphthalene using waste tyre rubber granules. J Xenobiotics. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2014.2264
Alade AO (2012) Adsorption of naphthalene onto activated carbons derived from milk bush kernel shell and flamboyant pod. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol. https://doi.org/10.5897/jece11.041
Ali I, Basheer AA, Mbianda XY et al (2019) Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ Int 127:160–180
Aliannejadi S, Hassani AH, Panahi HA, Borghei SM (2019) Fabrication and characterization of high-branched recyclable PAMAM dendrimer polymers on the modified magnetic nanoparticles for removing naphthalene from aqueous solutions. Microchem J 145:767–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.11.043
Alshabib M, Oluwadamilare MA, Tanimu A et al (2021) Experimental and DFT investigation of ceria-nanocomposite decorated AC derived from groundnut shell for efficient removal of methylene-blue from wastewater effluent. Appl Surf Sci 536:147749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147749
Araújo DT, de Gomes AM, Silva RS et al (2017) Ternary dimensionally stable anodes composed of RuO2 and IrO2 with CeO2, SnO2, or Sb2O3 for efficient naphthalene and benzene electrochemical removal. J Appl Electrochem 47:547–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-017-1057-2
Arizavi A, Mirbagheri NS, Hosseini Z et al (2020) Efficient removal of naphthalene from aqueous solutions using a nanoporous kaolin/Fe3O4 composite. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1991–2002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02521-1
Arulazhagan P, Vasudevan N (2011) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a halotolerant bacterial strain Ochrobactrum sp. VA1. Mar Pollut Bull 62:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2010.09.020
Awad AM, Shaikh SMR, Jalab R et al (2019) Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: a comprehensive review. Sep Purif Technol 228:115719
Bacelo H, Pintor AMA, Santos SCR et al (2020) Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem Eng J 381:122566
Balati A, Shahbazi A, Amini MM et al (2014) Comparison of the efficiency of mesoporous silicas as absorbents for removing naphthalene from contaminated water. Eur J Environ Sci 4:69–76. https://doi.org/10.14712/23361964.2015.7
Balati A, Shahbazi A, Amini MM, Hashemi SH (2015) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater by using silica-based organic–inorganic nanohybrid material. J Water Reuse Desalin 5:50–63. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2014.013
Balati A, Ghanbari M, Behzad SK, Amini MM (2017) Functionalization of graphene oxide with 9-aminoanthracene for the adsorptive removal of persistent aromatic pollutants from aqueous solution. Acta Chim Slov 64:479–490. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2017.3372
Barman SR, Banerjee P, Das P, Mukhopadhayay A (2018) Urban wood waste as precursor of activated carbon and its subsequent application for adsorption of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Int J Energy Water Resour 2:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-018-0001-4
Bayazit ŞS, Yildiz M, Aşçi YS et al (2017) Rapid adsorptive removal of naphthalene from water using graphene nanoplatelet/MIL-101 (Cr) nanocomposite. J Alloys Compd 701:740–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.111
Beg S, Rizwan M, Sheikh AM et al (2011) Advancement in carbon nanotubes: Basics, biomedical applications and toxicity. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:141–163
Benincá C, Charao Boni E, Gonçalves FF et al (2019) Photo-fenton and UV photo degradation of naphthalene with zero- and two-valent iron in the presence of persulfate. Chem Eng Commun 206:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1469015
Bhadra BN, Song JY, Lee SK et al (2018) Adsorptive removal of aromatic hydrocarbons from water over metal azolate framework-6-derived carbons. J Hazard Mater 344:1069–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.057
Bhatnagar A, Anastopoulos I (2017) Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 168:885–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.121
Bibi S, Yasin T, Hassan S et al (2015) Chitosan/CNTs green nanocomposite membrane: Synthesis, swelling and polyaromatic hydrocarbons removal. Mater Sci Eng C 46:359–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.10.057
Boateng LK, Heo J, Flora JRV et al (2013) Molecular level simulation of the adsorption of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol onto carbon nanomaterials. Sep Purif Technol 116:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.06.028
Bouiahya K, Oulguidoum A, Laghzizil A et al (2020) Hydrophobic chemical surface functionalization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for naphthalene removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 595:124706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124706
Bruno P, Campo R, Giustra MG et al (2020) Bench scale continuous coagulation-flocculation of saline industrial wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons. J Water Process Eng 34:101156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101156
Chai WS, Cheun JY, Kumar PS et al (2021) A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J Clean Prod 296:126589
Chatterjee S, Lee DS, Lee MW, Woo SH (2010) Enhanced molar sorption ratio for naphthalene through the impregnation of surfactant into chitosan hydrogel beads. Bioresour Technol 101:4315–4321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.062
Chatterjee S, Lim SR, Lee MW, Woo SH (2017) Highly efficient capture of naphthalene by nonionic surfactants in hydrogel capsules. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 78:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.06.007
Chen B, Yuan M, Liu H (2011) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution using plant residue materials as a biosorbent. J Hazard Mater 188:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.114
Chen Z, Chen B, Chiou CT (2012) Fast and slow rates of naphthalene sorption to biochars produced at different temperatures. Environ Sci Technol 46:11104–11111. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302345e
Chen F, Zhao J, An W et al (2017a) Inserting AgCl@rGO into graphene hydrogel 3D structure: Synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis for efficient removal of bisphenol A. RSC Adv 7:39814–39823. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06126a
Chen M, Qin X, Zeng G (2017b) Biodegradation of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives. Trends Biotechnol 35:836–846
Chowdhury S, Balasubramanian R (2014) Recent advances in the use of graphene-family nanoadsorbents for removal of toxic pollutants from wastewater. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 204:35–56
Chuang YH, Liu CH, Tzou YM et al (2010) Comparison and characterization of chemical surfactants and bio-surfactants intercalated with layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for removing naphthalene from contaminated aqueous solutions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 366:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2010.06.009
Costa JAS, Sarmento VHV, Romão LPC, Paranhos CM (2019a) Synthesis of functionalized mesoporous material from rice husk ash and its application in the removal of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25476–25490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05852-1
Costa JAS, Sarmento VHV, Romão LPC, Paranhos CM (2019b) Adsorption of organic compounds on mesoporous material from rice husk ash (RHA). Biomass Convers Biorefinery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00476-4
Costa JAS, Sarmento VHV, Romão LPC, Paranhos CM (2020) Performance of the MCM-41-NH2 Functionalized Mesoporous Material Synthetized from the Rice Husk Ash on the Removal of the Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. SILICON 12:1913–1923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00289-0
Costa JAS, De Jesus RA, Santos DO et al (2021) Synthesis, functionalization, and environmental application of silica-based mesoporous materials of the M41S and SBA-n families: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105259
da Lima AC, Heleno FF, de Afonso RJCF, Coutrim MX (2015) Determination of PAHs in surface waters from the doce and piracicaba rivers in Brazil. J Water Resour Prot 07:422–429. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.75034
da Silva CMF, da Rocha QC, Rocha PCS et al (2015) Removal of naphthalene from aqueous systems by poly(divinylbenzene) and poly(methyl methacrylate-divinylbenzene) resins. J Environ Manage 157:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.04.025
Das P, Goswami S, Maiti S (2016) Removal of naphthalene present in synthetic waste water using novel Graphene /Graphene Oxide nano sheet synthesized from rice straw: comparative analysis, isotherm and kinetics. Front Nanosci Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.15761/fnn.1000107
Demirkan MM, Aydilek AH, Seagren EA, Hower JC (2011) Naphthalene and o-xylene adsorption onto high carbon fly ash. J Environ Eng 137:377–387. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000335
Derikvand E, Borghei SM, Hassani AH et al (2013) Comparison of ozonation and aeration methods in removal of naphthalene from aqueous solution. Asian J Chem 25:9135–9137. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2013.15053
Duc PA, Dharanipriya P, Velmurugan BK, Shanmugavadivu M (2019) Groundnut shell -a beneficial bio-waste. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 20:101206
Eeshwarasinghe D, Loganathan P, Kalaruban M et al (2018) Removing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water using granular activated carbon: kinetic and equilibrium adsorption studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13511–13524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1518-0
Eslami A, Borghei SM, Rashidi A, Takdastan A (2018) Preparation of activated carbon dots from sugarcane bagasse for naphthalene removal from aqueous solutions. Sep Sci Technol 53:2536–2549. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1462832
Fatemch S, Allahbakhsh R, Masumcli K (2011) Photo degradation and removal of naphthalene and its derivatives from the petroleum refinery wastewater by nanoparticles of Ti0 2. Res J Chem Environ 15:387–392
Fernandes A, Rose M, Falandysz J (2017) Polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) in food and humans. Environ Int 104:1–13
Frescura LM, de Menezes BB, Duarte R, da Rosa MB (2020) Application of multivariate analysis on naphthalene adsorption in aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:3329–3337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07278-1
Fu S, Fan J, Hashi Y, Chen Z (2012) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples using online microextraction by packed sorbent coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 94:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.03.010
Ge X, Ma X, Wu Z et al (2015a) Modification of coal-based activated carbon with nitric acid using microwave radiation for adsorption of phenanthrene and naphthalene. Res Chem Intermed 41:7327–7347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1815-2
Ge X, Tian F, Wu Z et al (2015b) Adsorption of naphthalene from aqueous solution on coal-based activated carbon modified by microwave induction: Microwave power effects. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 91:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2015.03.019
Ge X, Wu Z, Wu Z et al (2016) Enhanced PAHs adsorption using iron-modified coal-based activated carbon via microwave radiation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 64:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.050
Ghaedi M, Daneshyar A, Asfaram A, Purkait MK (2016) Adsorption of naphthalene onto high-surface-area nanoparticle loaded activated carbon by high performance liquid chromatography: Response surface methodology, isotherm and kinetic study. RSC Adv 6:54322–54330. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra09500c
Ghasemi S, Nematollahzadeh A (2018) Molecularly imprinted polymer membrane for the removal of naphthalene from petrochemical wastewater streams. Adv Polym Technol 37:2288–2293. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21904
Gładysz-Płaska A, Lipke A, Tarasiuk B et al (2017) Naphthalene sorption on red clay and halloysite modified by quaternary ammonium salts. Adsorpt Sci Technol 35:464–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617417696090
Gupta H, Gupta B (2016) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on banana peel activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 57:9498–9509. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1029007
Gupta H, Gupta B (2018) Vehicular Tire as Potential Adsorbent for the Removal of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Polycycl Aromat Compd 38:354–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2016.1217890
Güzel B, Canlı O (2020) Applicability of purge and trap gas chromatography- mass spectrometry method for sensitive analytical detection of naphthalene and its derivatives in waters. J Mass Spectrom 55:e4672. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.4672
Hanrahan G (2012) Water treatment and related technologies. Key concepts in environmental chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 155–176
He X, Wu Z, Sun Z et al (2018) A novel hybrid of β-cyclodextrin grafted onto activated carbon for rapid adsorption of naphthalene from aqueous solution. J Mol Liq 255:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.153
Hedayati MS, Li LY (2020) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous media using modified clinoptilolite. J Environ Manage 273:111113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111113
Hossain MA, Salehuddin SM, Kabir MJ, Ali M (2009) Identification and quantification of naphthalene in water samples of Buriganga River in Bangladesh by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. As J Energy Env 10:230–240
Hu E, Shang S, Wang N et al (2019) Influence of the pyrolytic temperature and feedstock on the characteristics and naphthalene adsorption of crop straw-derived biochars. BioResources 14:2885–2902. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.14.2.2885-2902
Ishizaki A, Saito K, Hanioka N et al (2010) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food samples by automated on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1217:5555–5563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.06.068
Jafari M, Aghamiri SF (2011) Evaluation of carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction sorbent for the removal of cephalexin from aqueous solution. Desalin Water Treat 28:55–58. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2011.2200
Jahangiri M, Kiani F, Tahermansouri H, Rajabalinezhad A (2015) The removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions by modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes with 1-isatin-3-thiosemicarbazone. J Mol Liq 212:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.09.010
Jia C, Batterman S (2010) A critical review of naphthalene sources and exposures relevant to indoor and outdoor air. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7:2903–2939
Jiang Y-F, Hu X-F, Yves U (2014) Effectiveness and mechanisms of naphthalene adsorption by biochar pyrolyzed from wheat straw. Adv Civ Environ Mater Res Busan Korea
Jing Q, Yi Z, Lin D et al (2013) Enhanced sorption of naphthalene and p-nitrophenol by Nano-SiO2 modified with a cationic surfactant. Water Res 47:4006–4012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.057
Kamaraj M, Srinivasan NR, Assefa G et al (2020) Facile development of sunlit ZnO nanoparticles-activated carbon hybrid from pernicious weed as an operative nano-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue and chromium from aqueous solution: Extended application in tannery industrial wastewater. Environ Technol Innov 17:100540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100540
Kaya EMÖ, Özcan AS, Gök Ö, Özcan A (2013) Adsorption kinetics and isotherm parameters of naphthalene onto natural- and chemically modified bentonite from aqueous solutions. In: Adsorption. pp 879–888
Kirankumar VS, Sumathi S (2020) A review on photodegradation of organic pollutants using spinel oxide. Mater Today Chem 18:100355
Kong H, He J, Gao Y et al (2011) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution on soybean stalk-based carbon. J Environ Qual 40:1737–1744. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2010.0343
Kumar A, Gupta H (2020) Activated carbon from sawdust for naphthalene removal from contaminated water. Environ Technol Innov 20:101080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101080
Kumar JA, Amarnath DJ, Narendrakumar G, Anand KV (2018a) Optimization of process parameters for naphthalene removal onto nano-iron oxide/carbon composite by response surface methodology, isotherm and kinetic studies. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 3:17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-018-0046-y
Kumar JA, Amarnath DJ, Senthil Kumar P et al (2018b) Mass transfer and thermodynamic analysis on the removal of naphthalene from aqueous solution using oleic acid modified palm shell activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 106:238–250. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22066
Kushwaha S, Soni H, Ageetha V, Padmaja P (2013) An insight into the production, characterization, and mechanisms of action of low-cost adsorbents for removal of organics from aqueous solution. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:443–549. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2011.604263
Lamichhane S, Bal Krishna KC, Sarukkalige R (2016) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) removal by sorption: a review. Chemosphere 148:336–353
Larsen TA, Hoffmann S, Lüthi C et al (2016) Emerging solutions to the water challenges of an urbanizing world. Science (80-) 352:928–933. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad8641
Li X, Zhao H, Quan X et al (2011) Adsorption of ionizable organic contaminants on multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different oxygen contents. J Hazard Mater 186:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.012
Li X, Li F, Fang L (2015) Effect of Microbes on the Adsorption of Naphthalene by Graphene Oxide. J Nanoparticles 2015:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/816982
Li N, Cheng W-Y, Pan Y-Z (2017) Adsorption of Naphthalene on Modified Zeolite from Aqueous Solution. J Environ Prot (irvine, Calif) 08:416–425. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2017.84030
Li J, Li J, Liu X et al (2018) Effect of silicon content on preparation and coagulation performance of poly-silicic-metal coagulants derived from coal gangue for coking wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 202:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.055
Lin Y-H (2017) Adsorption and biodegradation of 2-chlorophenol by mixed culture using activated carbon as a supporting medium-reactor performance and model verification. Appl Water Sci 7:3741–3757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0522-0
Liu FF, Zhao J, Wang S et al (2014) Effects of solution chemistry on adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) by graphenes and carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 48:13197–13206. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5034684
Liu D, Wu Z, Ge X et al (2016) Comparative study of naphthalene adsorption on activated carbon prepared by microwave-assisted synthesis from different typical coals in Xinjiang. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 59:563–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.09.001
Liu P, Wu Z, Sun Z, Ye J (2018) Comparison study of naphthalene adsorption on activated carbons prepared from different raws. Korean J Chem Eng 35:2086–2096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0124-7
Liu P, Wu Z, Ge X, Yang X (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis and microwave-assisted activation of starch-derived carbons as an effective adsorbent for naphthalene removal. RSC Adv 9:11696–11706. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra01386e
Liu Y, Bai J, Yao H et al (2020) Embryotoxicity assessment and efficient removal of naphthalene from water by irradiated graphene aerogels. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:110051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110051
Ma L, Li K, Wang C et al (2020) Enhanced adsorption of hydrophobic organic contaminants by high surface area porous graphene. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:7309–7317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07439-2
Machado CFC, Gomes MA, Silva RS et al (2018) Time and calcination temperature influence on the electrocatalytic efficiency of Ti/SnO2:Sb(5%), Gd(2%) electrodes towards the electrochemical oxidation of naphthalene. J Electroanal Chem 816:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.03.053
Malekzadeh M, Nejaei A, Baneshi MM et al (2018) The use of starch-modified magnetic Fe0 nanoparticles for naphthalene adsorption from water samples: adsorption isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4434
Mashkoor F, Nasar A (2020) Magsorbents: Potential candidates in wastewater treatment technology - A review on the removal of methylene blue dye. J Magn Magn Mater 500:166408
Mateos R, Vera-López S, Saz M et al (2019) Graphene/sepiolite mixtures as dispersive solid-phase extraction sorbents for the anaysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in wastewater using surfactant aqueous solutions for desorption. J Chromatogr A 1596:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.03.004
McQuillan RV, Stevens GW, Mumford KA (2020) Electrochemical removal of naphthalene from contaminated waters using carbon electrodes, and viability for environmental deployment. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121244
Mohammadi S, Kargari A, Sanaeepur H et al (2015) Phenol removal from industrial wastewaters: a short review. Desalin Water Treat 53:2215–2234. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.883327
Mohan D, Pittman CU (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents-A critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53
Mojiri A, Zhou JL, Ohashi A et al (2019) Comprehensive review of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water sources, their effects and treatments. Sci Total Environ 696:133971
Molinari R, Lavorato C, Argurio P (2017) Recent progress of photocatalytic membrane reactors in water treatment and in synthesis of organic compounds. A Rev Catal Today 281:144–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.06.047
Moradi SE (2013) Naphthalene Removal From Water by Novel Mesoporous Carbon Nitride Adsorbent. Chem Biochem Eng Q 27(37):365–372
Moradi O, Yari M, Moaveni P, Norouzi M (2012) Removal of p-nitrophenol and naphthalene from petrochemical wastewater using SWCNTs and SWCNT-COOH surfaces. Fullerenes Nanotub Carbon Nanostruct 20:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2010.533309
More MGUS (2013) Biological degradation of naphthalene: a new era. J Bioremediation Biodegrad 04:7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000203
Mukwevho N, Gusain R, Fosso-Kankeu E et al (2020) Removal of naphthalene from simulated wastewater through adsorption-photodegradation by ZnO/Ag/GO nanocomposite. J Ind Eng Chem 81:393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.09.030
Nacheva P, Sotelo A (2016) Removal of naphthalene and phenanthrene using aerobic membrane bioreactor. Biodegradation 27:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-016-9757-6
Nas B, Argun ME, Dolu T et al (2020) Occurrence, loadings and removal of EU-priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in wastewater and sludge by advanced biological treatment, stabilization pond and constructed wetland. J Environ Manage 268:110580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110580
Nesterenko-Malkovskaya A, Kirzhner F, Zimmels Y, Armon R (2012) Eichhornia crassipes capability to remove naphthalene from wastewater in the absence of bacteria. Chemosphere 87:1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.01.060
Okoro HK, Tella AC, Ajibola OA et al (2019) Adsorptive removal of naphthalene and anthracene from aqueous solution with zinc and copper-terephthalate metal-organic frameworks. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 33:229–241. https://doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v33i2.4
Osagie EI, Owabor CN (2015) Adsorption of naphthalene on clay and sandy soil from aqueous solution. Adv Chem Eng Sci 05:345–351. https://doi.org/10.4236/aces.2015.53036
Ou L, Song B, Liang H et al (2016) Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: a general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part Fibre Toxicol 13:1–24
Owabor C, Audu J (2010) Studies on the adsorption of naphthalene and pyrene from aqueous medium using ripe orange peels as adsorbent. Glob J Pure Appl Sci 16:131–139. https://doi.org/10.4314/gjpas.v16i1.62822
Owabor NC, Ono MU, Isuekevbo A (2012) Enhanced sorption of naphthalene onto a modified clay adsorbent: effect of acid, base and salt modifications of clay on sorption kinetics. Adv Chem Eng Sci 02:330–335. https://doi.org/10.4236/aces.2012.23038
Owabora CN, Agarry SE, Jato D (2012) Removal of naphthalene from aqueous system using unripe orange peel as adsorbent: Effects of operating variables. Desalin Water Treat 48:315–319. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.698834
Özcan AS, Gök Ö (2012) Structural characterization of dodecyltrimethylammonium (DTMA) bromide modified sepiolite and its adsorption isotherm studies. J Mol Struct 1007:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.09.044
Pei Z, Li L, Sun L et al (2013) Adsorption characteristics of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene, 2,4,6- trichlorophenol, 2-naphthol and naphthalene on graphene and graphene oxide. Carbon N Y 51:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.08.024
Puszkarewicz A, Kaleta J (2020) The efficiency of the removal of naphthalene from aqueous solutions by different adsorbents. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165969
Qu J, Wang Y, Tian X et al (2021) KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) and naphthalene from water: affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J Hazard Mater 401:123292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123292
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80
Ramteke LP, Gogate PR (2015a) Synthesis and characterization of modified activated sludge for biological oxidation with isolation studies and performance evaluation. Sep Purif Technol 141:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.11.044
Ramteke LP, Gogate PR (2015b) Treatment of toluene, benzene, naphthalene and xylene (BTNXs) containing wastewater using improved biological oxidation with pretreatment using Fenton/ultrasound based processes. J Ind Eng Chem 28:247–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.02.022
Rani CN, Karthikeyan S (2019) Investigation of naphthalene removal from aqueous solutions in an integrated slurry photocatalytic membrane reactor: effect of operating parameters, identification of intermediates, and response surface approach. Polycycl Aromat Compd. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2019.1622135
Ranjithkumar V, Sangeetha S, Vairam S (2014) Synthesis of magnetic activated carbon/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite and its application in the removal of acid yellow 17 dye from water. J Hazard Mater 273:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.034
Rattier M, Reungoat J, Gernjak W et al (2012) Investigating the role of adsorption and biodegradation in the removal of organic micropollutants during biological activated carbon filtration of treated wastewater. J Water Reuse Desalin 2:127–139. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2012.012
Rennane S, Bendjaballah-Lalaoui N, Trari M (2019) Comparative removal of naphthalene by adsorption on different sand/bentonite mixtures. Bulg Chem Commun 51:315–325. https://doi.org/10.34049/bcc.51.3.4897
Sakkos JK, Mutlu BR, Wackett LP, Aksan A (2017) Adsorption and biodegradation of aromatic chemicals by bacteria encapsulated in a hydrophobic silica gel. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:26848–26858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b06791
Samiee L, Yadegari A, Tasharrofi S et al (2016) Adsorption of naphthalene by carbon mesoporous (Cmk-3) from aqueous solutions. J Appl Chem Sci Int 7:168–180
Sci C, Osagie EI, Cn O (2016) Investigation of mixture effects on the adsorption rates of aromatics from aqueous solution on clay and sandy soil. Chem Sci J 6:112. https://doi.org/10.4172/2150-3494.1000112
Segneanu AE, Orbeci C, Lazau C et al (2013) Waste water treatment. Methods. https://doi.org/10.5772/53755
Şener S, Özyilmaz A (2010) Adsorption of naphthalene onto sonicated talc from aqueous solutions. Ultrason Sonochem 17:932–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.12.014
Shabeer TPA, Saha A, Gajbhiye VT et al (2014) Removal of poly aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from water: effect of nano and modified nano-clays as a flocculation aid and adsorbent in coagulation-flocculation process. Polycycl Aromat Compd 34:452–467. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2014.895949
Sharma A, Lee BK (2015) Adsorptive/photo-catalytic process for naphthalene removal from aqueous media using in-situ nickel doped titanium nanocomposite. J Environ Manage 155:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.008
Shen L, Liu Y, Lou XuH (2010) Treatment of ampicillin-loaded wastewater by combined adsorption and biodegradation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:814–820. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2369
Shi Q, Li A, Zhu Z, Liu B (2013) Adsorption of naphthalene onto a high-surface-area carbon from waste ion exchange resin. J Environ Sci (china) 25:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60017-5
Sule MN, Templeton MR, Bond T (2016) Rejection of organic micro-pollutants from water by a tubular, hydrophilic pervaporative membrane designed for irrigation applications. Environ Technol U K 37:1382–1389. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1116610
Sun Y, Yang S, Zhao G et al (2013) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on graphene oxides and reduced graphene oxides. Chem - an Asian J 8:2755–2761. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201300496
Sun H, Jiang J, Xiao Y, Du J (2018a) Efficient removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dyes, and heavy metal ions by a homopolymer vesicle. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:713–722. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b15242
Sun Z, Wu Z, Liu D, He X (2018b) Microwave-assisted modification of activated carbon with cationic surfactants for enhancement of naphthalene adsorption. Korean J Chem Eng 35:557–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0290-z
Tang X, Zhou Y, Xu Y et al (2010) Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution by hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide modified fibric peat. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1084–1091. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2403
Tikilili PV, Nkhalambayausi-Chirwa EM (2011) Characterization and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in radioactive wastewater. J Hazard Mater 192:1589–1596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.079
Tsyntsarski B, Petrova B, Budinova T et al (2011) Characterization and application of activated carbon from biomass and coal wastes for naphthalene removal. Bulg Chem Commun 43:552–557
Vidal CB, Barros AL, Moura CP et al (2011) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solutions by modified periodic mesoporous organosilica. J Colloid Interface Sci 357:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.02.013
Walcarius A, Mercier L (2010) Mesoporous organosilica adsorbents: Nanoengineered materials for removal of organic and inorganic pollutants. J Mater Chem 20:4478–4511. https://doi.org/10.1039/b924316j
Wan Ngah WS, Teong LC, Hanafiah MAKM (2011) Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: A review. Carbohydr Polym 83:1446–1456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.004
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156:11–24
Wang S, Ng CW, Wang W et al (2012) Synergistic and competitive adsorption of organic dyes on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 197:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.008
Wang F, Haftka JJH, Sinnige TL et al (2014a) Adsorption of polar, nonpolar, and substituted aromatics to colloidal graphene oxide nanoparticles. Environ Pollut 186:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.12.010
Wang J, Chen Z, Chen B (2014b) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets. Environ Sci Technol 48:4817–4825. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405227u
Wang J, Chen B, Xing B (2016) Wrinkles and Folds of Activated Graphene Nanosheets as Fast and Efficient Adsorptive Sites for Hydrophobic Organic Contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 50:3798–3808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04865
Wang C, Leng S, Xu Y et al (2018) Preparation of amino functionalized hydrophobic zeolite and its adsorption properties for chromate and naphthalene. Minerals. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8040145
Wei Z, Van Le Q, Peng W et al (2021) A review on phytoremediation of contaminants in air, water and soil. J Hazard Mater 403:123658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123658
Weng YH, Wu HC, Li KC (2013) Comparative study on electro-microfiltration (EMF) of water containing different carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Water Sci Technol 67:1247–1253. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2013.682
Wołowiec M, Muir B, Zieba K et al (2017) Experimental Study on the Removal of VOCs and PAHs by Zeolites and Surfactant-Modified Zeolites. Energy Fuels 31:8803–8812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b01124
Wu W, Chen W, Lin D, Yang K (2012) Influence of surface oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes on the adsorption affinity and capacity of polar and nonpolar organic compounds in aqueous phase. Environ Sci Technol 46:5446–5454. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3004848
Wu Z, Sun Z, Liu P et al (2020) Competitive adsorption of naphthalene and phenanthrene on walnut shell based activated carbon and the verification: Via theoretical calculation. RSC Adv 10:10703–10714. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra09447d
Xi Z, Chen B (2014) Removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous solution by raw and modified plant residue materials as biosorbents. J Environ Sci (china) 26:737–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(13)60501-X
Xiao X, Liu D, Yan Y et al (2015) Preparation of activated carbon from Xinjiang region coal by microwave activation and its application in naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene adsorption. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 53:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.031
Xie J, Meng W, Wu D et al (2012) Removal of organic pollutants by surfactant modified zeolite: Comparison between ionizable phenolic compounds and non-ionizable organic compounds. J Hazard Mater 231–232:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.035
Xie Q, Xie J, Wang Z et al (2013) Adsorption of organic pollutants by surfactant modified zeolite as controlled by surfactant chain length. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 179:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.05.027
Xin W, Song Y (2015) Mesoporous carbons: recent advances in synthesis and typical applications. RSC Adv 5:83239–83285
Xu L, Zhang M, Zhu L (2014) Adsorption-desorption behavior of naphthalene onto CDMBA modified bentonite: Contribution of the π-π interaction. Appl Clay Sci 100:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.03.001
Xue SW, Tang MQ, Xu L, Guo SZ (2015) Magnetic nanoparticles with hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity for solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1411:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.07.104
Yakout SM, Daifullah AAM, El-Reefy SA (2013a) Equilibrium and kinetic studies of sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water using rice husk activated carbon. Asian J Chem 25:10037–10042. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2013.14783
Yakout SM, Daifullah AAM, El-Reefy SA (2013b) Adsorption of naphthalene, phenanthrene and pyrene from aqueous solution using low-cost activated carbon derived from agricultural wastes. Adsorpt Sci Technol 31:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.31.4.293
Yang K, Jing Q, Wu W et al (2010a) Adsorption and conformation of a cationic surfactant on single-walled carbon nanotubes and their influence on naphthalene sorption. Environ Sci Technol 44:681–687. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902173v
Yang K, Wu W, Jing Q et al (2010b) Competitive adsorption of naphthalene with 2,4-dichlorophenol and 4-chloroaniline on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 44:3021–3027. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100018a
Yang X, Li J, Wen T et al (2013) Adsorption of naphthalene and its derivatives on magnetic graphene composites and the mechanism investigation. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem Eng Asp 422:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.11.063
Yang K, Wang J, Chen B (2014) Facile fabrication of stable monolayer and few-layer graphene nanosheets as superior sorbents for persistent aromatic pollutant management in water. J Mater Chem A 2:18219–18224. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta04300f
Yang Q, Liu YS, Li ZY et al (2015) Study on the adsorption behaviours of naphthalene on MCM-41 and SBA-15 mesoporous molecular sieves. Ranliao Huaxue Xuebao/journal Fuel Chem Technol 43:1482–1488
Yang K, Zhu L, Yang J, Lin D (2018a) Adsorption and correlations of selected aromatic compounds on a KOH-activated carbon with large surface area. Sci Total Environ 618:1677–1684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.018
Yang L, Qian X, Wang Z et al (2018b) Steel slag as low-cost adsorbent for the removal of phenanthrene and naphthalene. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36:1160–1177. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617418756407
Yang X, Zhang C, Jiang L et al (2019) Molecular simulation of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and pyrene adsorption on MCM-41. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030665
Yaqub A, Isa MH, Ajab H, Junaid M (2017) Electrochemical degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons (PAHS) from synthetic aqueous solutions. Pet Chem 57:457–465. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544117050140
Yaqubzadeh AR, Ahmadpour A, Bastami TR, Hataminia MR (2016) Low-cost preparation of silica aerogel for optimized adsorptive removal of naphthalene from aqueous solution with central composite design (CCD). J Non Cryst Solids 447:307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.06.022
Yazdanpanah M, Nojavan S (2019) Micro-solid phase extraction of some polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples using magnetic β-cyclodextrin-carbon nano-tube composite as a sorbent. J Chromatogr A 1585:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.11.066
Ye H, Zhao B, Zhou Y et al (2021) Recent advances in adsorbents for the removal of phthalate esters from water: Material, modification, and application. Chem Eng J 409:128127
Younis SA, El-Gendy NS, El-Azab WI, Moustafa YM (2015) Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons biosorption from petroleum refinery wastewater using spent waste biomass. Desalin Water Treat 56:3013–3023. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.964331
Younker JM, Walsh ME (2016) Effect of adsorbent addition on floc formation and clarification. Water Res 98:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.044
Yu JG, Zhao XH, Yang H et al (2014) Aqueous adsorption and removal of organic contaminants by carbon nanotubes. Sci Total Environ 482–483:241–251
Yu B, Jin X, Kuang Y et al (2015) An integrated biodegradation and nano-oxidation used for the remediation of naphthalene from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 141:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.050
Yu D, Wang L, Wu M (2018) Simultaneous removal of dye and heavy metal by banana peels derived hierarchically porous carbons. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 93:543–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.038
Yuan M, Tong S, Zhao S, Jia CQ (2010) Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water using petroleum coke-derived porous carbon. J Hazard Mater 181:1115–1120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.130
Yuan J, Feng L, Wang JX (2020) Rapid adsorption of naphthalene from aqueous solution by naphthylmethyl derived porous carbon materials. J Mol Liq 304:112768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.112768
Zhang H, Low WP, Lee HK (2012) Evaluation of sulfonated graphene sheets as sorbent for micro-solid-phase extraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1233:16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.02.020
Zhang C, Lu J, Wu J (2019) Adsorptive removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by detritus of green tide algae deposited in coastal sediment. Sci Total Environ 670:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.296
Zhao G, Jiang L, He Y et al (2011) Sulfonated graphene for persistent aromatic pollutant management. Adv Mater 23:3959–3963. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201101007
Zhou J, Yang B, Li Z et al (2015) Selective adsorption of naphthalene in aqueous solution on mesoporous carbon functionalized by task-specific ionic liquid. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:2329–2338. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5040144
Zhou Y, Lu J, Zhou Y, Liu Y (2019) Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: a review. Environ Pollut 252:352–365
Zhu M, Yao J, Dong L, Sun J (2016) Adsorption of naphthalene from aqueous solution onto fatty acid modified walnut shells. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.050
Zhu M, Tian W, Chai H, Yao J (2017) Acid-hydrolyzed agricultural residue: A potential adsorbent for the decontamination of naphthalene from water bodies. Korean J Chem Eng 34:1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0348-3
Zhu Z, Ouyang S, Li P et al (2020) Persistent organic pollutants removal via hierarchical flower-like layered double hydroxide: Adsorption behaviors and mechanism investigation. Appl Clay Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105500
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Maryam Shabani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshabib, M. Removal of naphthalene from wastewaters by adsorption: a review of recent studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 4555–4586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03428-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03428-6