Abstract
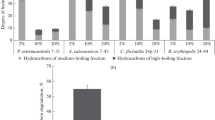
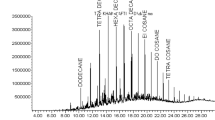
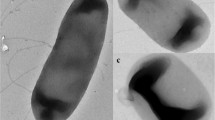
Bioremediation of oil spillage in soils using consortia of microbes beckons much exploration. The present study involves bioremediation of oil-contaminated soils from north Chennai, India, using indigenous microbial consortia. Totally, 32 positive oil degrading isolates were obtained from 3 different locations, i.e., petrol filling stations, automobile workshops and oil refineries. Substrate utilization patterns of individual isolates and the consortial sets were observed. Mixture of three common hydrocarbons (petrol, diesel and engine oil) was used for studies. The substrate oil utilized by consortia was taken for thin-layer and column chromatography which perfectly resulted in varied fractions of oil compared to the unused oil as control. The best consortia were used directly for bioremediation experiment. Three different oil-contaminated soils were used and bioremediation patterns were observed. The rate of bioremediation differed within soils, nevertheless all soils were almost 100 % reclaimed within 30 days. Bioremediation kinetics showed that the process corresponds to first-order kinetics and kinetic constants for the different soils ranged from 0.051 to 0.077/day. Assessment of detoxification of acute phytotoxicity owing to the pollutant oil was done, and results observed were significant. An increase of 25, 300 and 212 % in germination index, average growth index and sustenance index, respectively, of Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn. in treated soils was observed, compared to untreated soils. Thus, this study confirmed that microbes in ‘Consortial Union’ serve as better treating agents in bioremediation of oil-contaminated soils than individual microorganisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulsalam S, Bugaje IM, Adefila SS, Ibrahim S (2011) Comparison of biostimulation and bioaugmentation for remediation of soil contaminated with spent motor oil. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8(1):187–194
Alexander M (1999) Biodegradation and Bioremediation, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, p 350
Antizar-Ladislao B, Lopez-Real J, Beck AJ (2005) Laboratory studies of the remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil by in-vessel composting. Waste Manage 25(3):281–289
Atlas RM, Bartha R (1998) Fundamentals and Applications. Microbial Ecol, 4th edn. Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc, California, pp 523–530
Banks MK, Schultz KE (2005) Comparison of plants for germination toxicity test in petroleum contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Poll 167(1-4):211–219
Bock M, Kampfer K, Dott W (1994) Isolation and characterization of heterotrophic aerobic bacteria from oil storage caverns in northern Germany. Appl Microbial Biotechnol 42(1):463–468
Boehm PD, Douglas GS, Brown JS (1995) Advanced chemical fingerprinting for oil spill identifications and natural resource damage assessments. In: Proceedings of the 1995 International oil spill conference, American Petroleum Institute, Long Beach, California, pp 967–969
Bonaventura C, Johnson FJVI (1996) Healthy environment for healthy people: bioremediation now and tomorrow. Environ Health Persp 105(1):5–21
Boonchan S, Britz ML, Stanley GA (2000) Degradation and mineralization of high-molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by defined fungal-bacterial co cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(3):1007–1019
Brito EMS, Guyoneaud R, Goñi-Urriza M, Ranchou-Peyruse A, Verbaere A, Crapez MA, Wasserman JCA, Duran R (2006) Characterization of hydrocarbonoblastic bacterial communities from mangrove sediments in Guanabara Bay Brazil. Res Microbiol 157(8):752–762
Chaillana F, Flècheb A, Burya E, Phantavonga Y, Saliot A, Oudot J (2004) Identification and biodegradation potential of tropical aerobic hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms. Res Microb 155(7):587–595
Chang R (1998) Chemistry, 6th edn. McGraw–Hill Companies, Inc, New York, pp 962–963
Fletcher J (1991) A brief overview of plant toxicity testing. In: Plants for toxicity Assessment, vol 2, ASTMSTP, Philadelphia, PA
Ghazali MF, Zaliha NR, Salleh B, Basri M (2004) Biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial consortium. Inter Biodeter Biodegrad 54(1):61–67
Greene EA, Kay JG, Jaber K, Stehmeier G, Voordouw G (2000) Composition of soil microbial communities enriched on a mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(12):5282–5289
Holliger C, Gaspard S, Glod G, Heijman C, Schumacher W, Schwarzenbach RP, Vazquez F, Gaspard S (1997) Contaminated environments in the subsurface and bioremediation: organic contaminants. FEMS Microbiol Rev 20(3–4):517–523
Hutchins SR, Sewell GW, Kovacs DA, Smith GA (1991) Biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by aquifer microorganisms under denitrifying conditions. Environ Sci Technol 25(1):68–76
Hwang E, Namkoong W, Park J (2001) Recycling of remediated soil for effective composting of diesel-contaminated soil. Compost Sci Util 9(2):143–149
Lliros M, Munill X, Sole A, Martinez-Alonso, Diestra E, Esteve I (2003) Analysis of cyanobacteria biodiversity in pristine and polluted microbia mats in microcosmos by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Science, Technology and Education of Microscopy: An Overview, vol 1. Formatex Research Center, Badajoz, Spain, pp 483–489
Mandri T, Lin J (2007) Isolation and characterization of engine oil degrading indigenous microorganisms in Kwazulu-Natal South Africa. Afr J Biotechnol 6(1):23–27
Marquez-Rocha FJ, Hernandez-Rodriguez V, Lamela MT (2001) Biodegradation of engine and diesel oil in soil by a microbial consortium. Water Air Soil Poll 128(1):313–320
Millioli VS, Servulo E-LC, Sobral LGS, de Carvalho DD (2009) Bioremediation of crude oil-bearing soil: evaluating the effect of rhamnolipid addition to soil toxicity and to crude oil biodegradation efficiency. Glob NEST J 11(2):181–188
Mittal A, Singh P (2009) Isolation of hydrocarbon degrading bacteria from soils contaminated with crude oil spills. Indian J Exp Biol 47(9):760–765
Nester EW, Anderson DG, Evans Roberts C Jr, Pearsall NN, Nester MT (2001) Microbiology: a human perspective, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 120
Radwan SS, Sorkhoh NA (1993) Lipids of n-alkanes utilizing microorganisms and their application potential. Adv Appl Microbiol 39(1):29–90
Reardon KF, Mosteller DC, Rogers JB, DuTeau NM, Kee-Hong K (2002) Biodegradation kinetic of aromatic hydrocarbon mixtures by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Environ Health Perspec 110(1):1005–1012
Tang Y, Qi JL, Krieger-Brockett B (2005) Evaluating factors that influence microbial phenanthrene biodegradation rates by regression with categorical variables. Chemosphere 59(5):729–741
Thouand G, Bauda P, Oudot J, Kirsch G, Sutton C, Vidalie JF (1999) Laboratory evaluation of crude oil biodegradation with commercial or natural microbial inocula. Can J Microb 45(2):106–115
Tugrul T, Cansunar E (2005) Detecting surfactant-producing microorganisms by the drop-collapse test. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21(1):45–49
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation. An overview. Pure Appl Chem 73(7):1163–1172
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere thanks to Dr. I. Seethalakshmi, Director, Life Teck Research Centre, Chennai for proving facilities and support for successful completion of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, S., Kansrajh, C., Dinesh, M.G. et al. Application of indigenous microbial consortia in bioremediation of oil-contaminated soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 367–376 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0366-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0366-1