Abstract
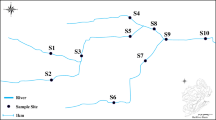
Stormwater runoff from urban areas is a major source of many pollutants to water bodies. Suspended solids are one of the main pollutants because of their association with other pollutants. The objective of this study was to evaluate the relationship between suspended solids and other pollutants in stormwater runoff in the city of Tijuana. Seven sites were sampled during seven rain events during the 2009–2010 season and the different particle size fractions were separated by sieving and filtration. The results have shown that the samples have high concentration of total suspended solids, the values of which ranged from 725 to 4,411.6 mg/L. The samples were analyzed for chemical oxygen demand, total phosphorus, total nitrogen, and turbidity. The results show that most of the particles in suspended solids are in the particle fraction between 10 and 62 μm. A high association between the concentrations of suspended solids was found for chemical oxygen demand, phosphorus, and turbidity but not for total nitrogen.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldy S, Raines TH, Mansfield BL, Sanding JT (1998) Urban stormwater quality, event-mean concentrations and estimates of stormwater pollutant loads, Dallas-Forth Worth area, Texas, 1992–93. USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report, WRIR 98-4158
Bochis-Micus C, Pitt RE (2005) Impervious surfaces in urban watersheds. In: Proceedings of the 78th Annual Water Environment Federation Technical Exposition and Conference, Washington, D.C
Booth DB, Jackson CR (1997) Urbanization of aquatic systems: Degradation thresholds, stormwater detection and the limits of mitigation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 33:1077–1090
Brown JS, Stein ED, Ackerman D, Dorsey JH, Lyon J, Carter PM (2013) Metals and bacteria partitioning to various size particles in Ballona creek storm water runoff. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:320–328
D’Elia CF, Steudler PA, Corwin N (1977) Determination of total nitrogen in aqueous samples using persulfate digestion. Limnol Oceanogr 22:760–764
Domínguez-Chicas A, Kretzschmar T, Núñez-Sánchez F (2004) Sedimentation velocities in pluvial waters of Cd. Juarez, Chihuahua, Mexico. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 21:412–420
García-Flores E, Herrera-Castañon I, Vega-Cruz DA, Lopez-Laureano E, Rodriguez-Ventura G, Espinoza-Gomez H, Wakida FT (2009) Sources of oil and grease in stormwater in Tijuana, Mexico. In: 13th International Conference on Diffuse Pollution and Integrated Watershed Management, 12-15 October 2009. Seoul, Korea, pp 388–390
García-Flores E, Wakida FT, Espinoza-Gomez JH (2013) Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban stormwater runoff in Tijuana, Mexico. Int J Environ Res (In press)
Goonetilleke A, Thomas E, Ginn SP, Gilbert D (2005) Understanding the role of land use in urban stormwater quality management. J Environ Manag 74:31–42
Hansen AM, Van Afferden M, Torres-Bejarano F (2007) Remediation of the Cencali lagoon, Villahermosa, Tabasco. I. Pollution and sediment reuse. Ing Hidraul Mex 22:87–102
Hathaway JM, Tucker RS, Spooner JM, Hunt WF (2012) A traditional analysis of the first flush effect for nutrients in stormwater runoff from two small urban catchments. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:5903–5915
He J, Valeo C, Chu A, Neumman NF (2010) Characterizing physicochemical quality of storm-water runoff from an urban area in Calgary, Alberta. J Environ Eng ASCE 136:1206–1217
Horowitz AJ, Elrick KA, Smith JJ (2008) Monitoring urban impacts on suspended sediment, trace element and nutrient fluxes within the city of Atlanta, Georgia, USA: program design, methodological considerations and initial results. Hydrol Process 22:1473–1496
Hvitved-Jacobsen T, Johansen NB, Yousef YA (1994) Treatment systems for urban and highway runoff in Denmark. Sci Total Environ 146/147:499–506
Implan (2002) Programa de Desarrollo Urbano del Centro de Población Tijuana 2002–2025 (Program of urban development of the City of Tijuana). Periódico Oficial del Estado de Baja California, 13 de diciembre de 2002, No. 54
INE (2000) Instituto Nacional de Ecología. Programa de calidad del aire Tijuana-Rosarito 2001–2005 (Program of air quality Tijuana-Rosarito 2001–2005). INE, Mexico. http://www.epa.gov/Border2012/infrastructure/tijuana-airplans/tijuanarosaritospa.pdf. Accessed 23 October 2009
Mayer B, Boyer EW, Goodale C, Jaworski NA, Van Breemen N, Howarth RW, Seitzinger S, Billen G, Lajtha K, NadelhoffeR K, Van Dam D, Hetling LJ, Nosal M, Paustian K (2002) Sources of nitrate in rivers draining sixteen watersheds in the northeastern US: isotopic constraints. Biogeochemistry 57/58(1):171–197
Mijangos-Montiel JL, Wakida FT, Temores-Peña J (2010) Stormwater quality from gas stations in Tijuana, Mexico. Int J Environ Res 4:777–784
Morquecho R (2005) Pollutant associations with particulates in stormwater. Dissertation, The University of Alabama. http://rpitt.eng.ua.edu/Publications/Renee.dissertation.pdf. Accessed 14 October 2012
Morquecho R, Pitt R (2005) Pollutant associations with particulates in stormwater. In: Proceeding of the water environment federation, WEFTEC 2005: Session 51 through Session 60, pp 4973–4999 (27). Water Environment Federation
Morse CC, Huryn AD, Cronan C (2003) Impervious surface area as a predictor of the effects of urbanization on stream insect communities in Maine, USA. Environ Monit Assess 89:95–127
Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) (2002) Cleaning up the Anacostia River. http://www.nrdc.org/water/pollution/fanacost.asp. Accessed 4 August 2010
Pitt R, Clark S, Lantrip J, Day J (1998) Telecommunication manhole water and sediment study. Special report SR-3841. Vol 2: Water and sediment characteristics
Pitt R, Maestre A, Morquecho R (2004) The National Stormwater Quality Database (NSQD, version 1.1). University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa. http://rpitt.eng.ua.edu/Research/ms4/Paper/MS4%20Feb%2016%202004%20paper.pdf. Accessed 20 October 2012
Sansalone JJ, Buchberger GA (1995) Infiltration device as a best management practice for immobilizing heavy metals in urban highway runoff. Water Sci Tech 32:119–125
SE (Secretary of Economy) (2001a) Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-029-SFCI-2001. Determinación de fósforo total en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas (Determination of total phosphorus in natural, wastewaters and wastewaters treated—test method), published in Diario Oficial de la Federación el April 17, 2001
SE (Secretary of Economy) (2001b) Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-030-SCFI-2001. Determinación de la demanda química de oxígeno en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas—método de prueba (Determination for chemical oxygen demand in natural, wastewaters and wastewaters treated—test method). published in Diario Oficial de la Federación el April 17, 2001
SE (Secretary of Economy) (2001c) Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-038-SCFI-2001. Determinación de turbiedad en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas—método de prueba (Determination of turbidity in natural, wastewaters and wastewaters treated -test method), published in Diario Oficial de la Federación el August 1, 2001
SE (Secretary of Economy) (2001d) Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-034-SCFI-2001. Determinación de sólidos y sales disueltas en aguas naturales, residuales y residuales tratadas—método de prueba (Determination of salts and solids dissolved in natural, wastewaters and wastewaters treated—test method), published in Diario Oficial de la Federación el August 1, 2001
Taylor KG, Owens PN (2009) Sediments in urban river basins: a review of sediment–contaminant dynamics in an environmental system conditioned by human activities. J Soils Sediments 9:281–303
Taylor GD, Fletcher TD, Wong TH, Breen PF, Duncan HP (2005) Nitrogen composition in urban runoff—implications for stormwater management. Water Res 39(10):1982–1989
Uusitalo R, Yli-Halla M, Turtola E (2000) Suspended soil as a source of potentially bioavailable phosphorus in surface runoff waters from clay soils. Water Res 34:2477–2482
Vaze J, Chiew FHS (2004) Nutrient loads associated with different sediment sizes in urban stormwater and surface pollutants. J Environ Eng ASCE 130:391–396
Waschbusch RJ, Selbig WR, Bannerman RT (1999) Sources of phosphorus in stormwater and street dirt from two urban residential basins in Madison, Wisconsin, 1994–95, US Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigation Report 99-4021
Zhang J, Chen SZ, Yu ZG, Wang CS, Wu QM (1999) Factors influencing changes in rainwater composition from urban versus remote regions of the Yellow Sea. J Geophys Res Atmospheres 104(1):1631–1644
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Universidad Autónoma de Baja California (UABC) for the financial support through its program of research grants (16ta convocatoria de apoyo a proyectos de investigación de la UABC). The authors are also indebted to Professor Samuel G. Meléndez-Lopez for proofreading an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wakida, F.T., Martinez-Huato, S., Garcia-Flores, E. et al. Pollutant association with suspended solids in stormwater in Tijuana, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 11, 319–326 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0214-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0214-3