Abstract
Background
Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) has different neurological outcomes.
Aim
We wanted to see if there was any developmental delay in neonates with hypoxia ischemic encephalopathy who were given therapeutic hypothermia.
Study design
Retrospective cohort study.
Methods
The Denver developmental screening test II (DDST-II) was performed to newborns who had been applied to therapeutic hypothermia.
Results
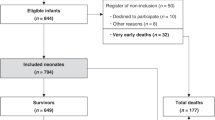
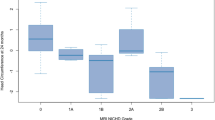
There were 69 male and 36 female newborns. The mean 1-min and 5-min Apgar scores were 4.72 ± 2.51 and 7.03 ± 2.017, respectively. The mean pH and mean base excess were 6.92 ± 0.1 and −18.05 ± 5.72, respectively. The most common risk factors were meconium staining (17.1%). There were 67 patients with Stage I, 20 with Stage II, and 18 with Stage III. Diffusion restriction was seen in 13 patients. 28 patients had seizures. In aEEG, 12 patients had burst suppression. Three (2.9%) infants died during hospitalization. 19 patients missed follow-up appointments. Thirteen patients had abnormal development according to DDST-II. Seven patients had gross motor function delays and were diagnosed with cerebral palsy. Three had language skill delays, but two of them had speech disorders after two years of age. Two had delayed milestones. Two had delays in fine motor skills but did not have any sequels after two years of age.
A significant difference was found between seizures and the severity of Sarnat stage, intubation in the delivery room with developmental delay. Apgar scores were significantly lower in patients with CP.
Conclusion
We should closely follow-up neonates who had low Apgar scores, seizures, a high Sarnat stage, were intubated in the delivery room.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
We deposit our datasets in publicly available repositories prior to peer review, or include them as supplementary information files with our manuscript. We deposit our data in an appropriate repository, and we agree to make the data publicly available without restriction, unless reasonable controls on data access are needed to protect human privacy or biosafety (Research data policy type 4).
References
Perlman JM (1997) Intrapartum hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury and subsequent cerebral palsy: medicolegal issues. Pediatrics 99:851–859
Volpe JJ (2012) Neonatal encephalopathy: an inadequate term for hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy. Ann Neurol 72:156–166
Millar LJ, Shi L, Hoerder-Suabedissen A, Molnár Z (2017) Neonatal hypoxia ischaemia mechanisms models and therapeutic challenges. Front Cell Neurosci 11:78
Levene M, Grindulis H, Sands C, Moore J (1986) Comparison of two methods of predicting outcome in perinatal asphyxia. Lancet 327:67–69
Robertson NJ, Iwata O (2007) Bench to bedside strategies for optimizing neuroprotection following perinatal hypoxia–ischaemia in high and low resource settings. Early Hum Dev 83:801–811
Gancia P, Pomero G (2012) Therapeutic hypothermia in the prevention of hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy: new categories to be enrolled. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 25(4):94–96
Tagin MA, Woolcott CG, Vincer MJ, Whyte RK, Stinson DA (2012) Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 166:558–566
Rodriguez PJM, Golombek S, Augusto S (2021) Clinical hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy score of the Iberoamerican Society of Neonatology (Siben): a new proposal for diagnosis and management. Rev Assoc Med Bras 63:64–69
Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS (1976) Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress. A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol 33:696–705
Jacobs SE, Berg M, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi WO, Inder TE (2013) Davis PG (2013) Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013(1):CD003311
Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD et al (2009) TOBY Study Group Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 361(14):1349–58
Toet MC, van der Meij W, de Vries LS, Uiterwaal CS, van Huffelen KC (2002) Comparison between simultaneously recorded amplitude integrated electroencephalogram (cerebral function monitor) and standard electroencephalogram in neonates. Pediatrics 109(5):772–779
Weeke LC, Groenendaal F, Mudigonda K et al (2018) A novel magnetic resonance imaging score predicts neurodevelopmental outcome after perinatal asphyxia and therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr 192:33-40.e2
Anlar B, Yalaz K. Denver II Development Screening Test: Adaptation and standardization for Turkish children (1996) Hacettepe unıversity publications, Ankara
Rossi AC, Prefumo F (2019) Antepartum and intrapartum risk factors for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 31(6):410–417
Simon LV, Hashmi MF, Bragg BN.(2022) APGAR Score. Treasure Island (FL):StatPearls Publishing . https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470569/ .Accessed 23 May
Perez JM, Golombek SG, Fajardo C, Sola A (2013) A laminar flow unit for the care of critically ill newborn infants. Med Devices 6:163–167
Shetty J (2015) Neonatal seizures in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy-risks and benefits of anticonvulsant therapy. Dev Med Child Neurol 57(3):40–43
van Laerhoven H, de Haan TR, Offringa M, Post B, van der Lee JH (2013) Prognostic tests in term neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a systematic review. Pediatrics 131(1):88–98
Biagioni E, Mercuri E, Rutherford M et al (2001) Combined use of electroencephalogram and magnetic resonance imaging in full-term neonates with acute encephalopathy. Pediatrics 107(3):461–468
Vasiljević B, Maglajlić-Djukić S, Gojnić M (2012) The prognostic value of amplitude-integrated electroencephalography in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Vojnosanit Pregl 69(6):492–499
Krishnan P, Shroff M (2016) Neuroimaging in Neonatal Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy. Indian J Pediatr 83(9):995–1002
Rutherford MA, Malamateniou C, McGuiness A, Allsop J, Biarge MM, Counsell SJ (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging in hypoxicischemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev 86:351–360
Barkovich AJ, Hajnal BL, Vigneron D et al (1998) Prediction of neuromotor outcome in perinatal asphyxia: evaluation of MR scoring systems. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:143–149
Katyucia R, Grant E (2011) Diffusion-weighted imaging in neonates. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 21:127–151
Huang BY, Castillo M (2008) Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: imaging findings from birth to adulthood. Radiographics 28:417–439
Procianoy RS, Corso AL, Longo MG, Vedolin L, Silveira RC (2019) Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: magnetic resonance imaging findings and neurological outcomes in a Brazilian cohort. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 32(16):2727–2734
Robertson CM, Finer NN, Grace MG (1989) School performance of survivors of neonatal encephalopathy associated with birth asphyxia at term. J Pediatr 114(5):753–760
Jacobs S, Hunt R, Tarnow-Mordi W, Inder T, Davis P (2007) Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 17 (4): CD003311
Shah PS, Beyene J, To T, Ohlsson A, Perlman M (2006) Postasphyxial hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates: outcome prediction rule within 4 hours of birth. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 160(7):729–736
Martinez C, Carneiro L, Vernier L, Cesa C, Guardiola A, Vidor D (2014) Language in children with neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 18(3):255–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SY, EY made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; SY, TBK, YB, AE made the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; or the creation of new software used in the work; SY, SA, AE drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; SY, TBK, SA, EY, YB, AE approved the version to be published; and all authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yimenicioglu, S., Kaya, T.B., Yıldırım, E. et al. The factors affecting neurodevelopmental outcomes in HIE. Acta Neurol Belg 123, 1903–1909 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-022-02126-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-022-02126-5