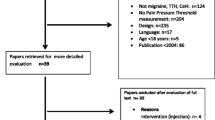
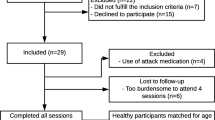
Abstract
We investigated if dynamic pressure pain sensitivity in the symptomatic area is associated with pressure sensitivity in local and distant pain-free areas in cluster headache (CH). A pressure algometry set consisting of 8 rollers with fixed pressure levels ranging from 500 to 5300 g was used to assess dynamic pressure pain sensitivity in men with episodic CH. Each roller was moved from an anterior-to-posterior direction over the temporalis muscle. The load level of the first painful roller was considered the dynamic pain threshold (DPT). Further, pain elicited during DPT (roller evoked pain) was also assessed. We used a pressure algometer to determine pressure pain thresholds (PPTs) over the temporalis muscle, C5/C6 joint, second metacarpal, and tibialis anterior. Patients were assessed in an asymptomatic (remission) phase, at least 6 months after their last cluster period and without taking pharmacological treatment. Forty men with episodic CH (mean age 42 years) were included. Both outcomes, DPTs (r = 0.781, P < 0.001) and roller-evoked pain (r = 0.586; P < 0.001) were bilaterally correlated. Further, DPT, but not roller-evoked pain, was moderately associated with PPTs measured at the symptomatic (temporalis: r = 0.665, P < 0.001) and distant pain-free (C5–C6 joint: r = 0.389, P = 0.013; second metacarpal: r = 0.551, P < 0.001; and, tibialis anterior: r = 0.308, P = 0.035) points. Dynamic pressure sensitivity in the trigeminal area was correlated to pressure pain sensitivity at both symptomatic and distant pain-free areas in men with CH supporting the use of roller pressure algometry. Dynamic pressure algometry may be a new tool for assessing the status of sensitization in primary headaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischera M, Marziniak M, Gralow I, Evers S (2008) The incidence and preva-lence of cluster headache: a meta-analysis of population-based studies. Cephalalgia 28:614–618
Buture A, Boland JW, Dikomitis L, Ahmed F (2019) Update on the pathophysiology of cluster headache: imaging and neuropeptide studies. J Pain Res 12:269–281
Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Ortega-Santiago R, Cuadrado ML, López-de-Silanes C, Pareja JA (2011) Bilateral widespread mechanical pain hypersensitivity as sign of central sensitization in patients with cluster headache. Headache 51:384–391
Gil-Martínez A, Navarro-Fernández G, Mangas-Guijarro M, Díaz-de-Terán J (2019) Hyperalgesia and central sensitization signs in patients with cluster headache: A cross-sectional study. Pain Med (Epub ahead of print)
Rolke R, Baron R, Maier C, Tölle TR, Treede RD, Beyer A, Binder A, Birbaumer N, Birklein F, Bötefür IC, Braune S, Flor H, Huge V, Klug R, Landwehrmeyer GB, Magerl W, Maihöfner C, Rolko C, Schaub C, Scherens A, Sprenger T, Valet M, Wasserka B (2006) Quantitative sensory testing in the German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain (DFNS): standardized protocol and reference values. Pain 123:231–243
Finocchietti S, Graven-Nielsen T, Arendt-Nielsen L (2015) Dynamic mechanical assessment of muscle hyperalgesia in humans: the dynamic algometer. Pain Res Manag 20:29–34
Guerrero-Peral AL, Ruíz M, Barón J, Palacios-Ceña M, Arendt-Nielsen L, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C (2018) Roller pressure algometry as a new tool for assessing dynamic pressure sensitivity in migraine. Cephalalgia 38:1257–1266
Palacios-Ceña M, Wang K, Castaldo M, Guerrero-Peral Á, Caminero AB, Fernández-de-las-Peñas C, Arendt-Nielsen L (2017) Assessment of deep dynamic mechanical sensitivity in individuals with tension-type headache: the dynamic pressure algometry. Eur J Pain 21:1451–1460
ICHD-III Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society: The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3 edition (2018). Cephalalgia 38:1–211
Nie H, Arendt-Nielsen L, Andersen H, Graven-Nielsen T (2005) Temporal summation of pain evoked by mechanical stimulation in deep and superficial tissue. J Pain 6:348–355
Walton DM, Macdermid JC, Nielson W, Teasell RW, Chiasson M, Brown L (2011) Reliability, standard error, and minimum detectable change of clinical pressure pain threshold testing in people with and without acute neck pain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 41:644–650
Chesterson LS, Sim J, Wright CC, Foster N (2007) Inter-rater reliability of algometry in measuring pressure pain thresholds in healthy humans, using multiple raters. Clin J Pain 23:760–766
Dancey CP, Reidy J (2004) Statistics without maths for psychology: using SPSS for Windows. Prentice Hall, New York
Hübscher M, Moloney N, Leaver A, Rebbeck T, McAuley JH, Refshauge K (2013) Relationship between quantitative sensory testing and pain or disability in people with spinal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 154:1497–1504
Racine M, Tousignant-Laflamme Y, Kloda LA, Dion D, Dupuis G, Choinière M (2012) A systematic literature review of 10 years of research on sex/gender and experimental pain perception—part 1: are there really differences between women and men? Pain 153:602–618
Acknowledgements
The Shionogi Science Program.
Funding
No funds were obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study concept and design. MLC and CFdlP did the statistical analysis and interpretation of data. AGP, VGM and DGA contributed to draft the paper. All authors provided administrative, technical, and material support. LAN and MLC supervised the study. All authors have read, revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ángel Guerrero-Peral, Víctor Gómez-Mayordomo, David García-Azorín, Nuria González-García, César Fernández-de-las-Peñas, Lars Arendt-Nielsen, María L. Cuadrado declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerrero-Peral, Á., Gómez-Mayordomo, V., García-Azorín, D. et al. Association of dynamic and widespread mechanical sensitivity in cluster headache. Acta Neurol Belg 120, 1265–1270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01450-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01450-y