Abstract
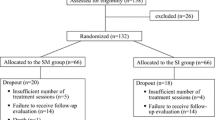
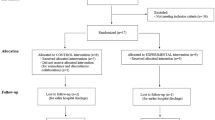
Dysphagia is one of the common findings in children with cerebral palsy (CP). Electrical stimulation (ES) has been demonstrated to positively contribute to swallowing functions, particularly in adult patients with various neurological disorders. Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the effects of sensory-level ES treatment combined with conventional dysphagia rehabilitation in pediatric age group CP patients who had any oropharyngeal dysphagia symptoms and/or findings. Participants were randomly assigned to either the experimental group (Group 1, n = 52) who underwent intermittent galvanic stimulation to bilateral masseter muscles for 5 days/week, for 4 weeks combined with conventional dysphagia rehabilitation or the control group (Group 2, n = 50) who received sham stimulation with conventional dysphagia rehabilitation. The experimental group achieved significantly more improvement in swallowing functions including drooling, tongue movements, chewing, eating large food ability, feeding duration, as well as dysphagia screen test and dysphagia level, compared to control group. This study suggested that sensory-level ES might be a useful and safe therapeutic modality to improve oropharyngeal symptoms, symptom severity and dysphagia level in children with CP and dysphagia. Further research is needed to determine the long-term effects of ES on dysphagia, especially in different neurological disorders such as CP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hutton JL (2006) Cerebral palsy life expectancy. Clin Perinatol 33(2):545–555
Strauss D, Shavelle R (1998) Life expectancy of adults with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 40(6):369–375
Fung EB, Samson-Fang L, Stallings VA, Conaway M, Liptak G, Henderson RC (2002) Feeding dysfunction is associated with poor growth health status in children with cerebral palsy. J Am Diet Assoc 102:361–368
Himuro N, Mishima R, Seshimo T, Morishima T, Kosaki K, Ibe S et al (2018) Change in mobility function and its causes in adults with cerebral palsy by Gross Motor Function Classification System level: a cross-sectional questionnaire study. NeuroRehabilitation. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-172340(Epub ahead of print)
Van den Engel-Hoek L, Harding C, van Gerven M, Cockerill H (2017) Pediatric feeding and swallowing rehabilitation: An overview. J Pediatr Rehabil Med 10(2):95–105
Benfer KA, Weir KA, Bell KL, Ware RS, Davies PSW, Boyd RN (2017) Oropharyngeal dysphagia and cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 140(6)
Morgan AT, Dodrill P, Ward EC (2012) Interventions for oropharyngeal dysphagia in children with neurological impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD009456. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009456.pub2
Arvedson JC (2013) Feeding children with cerebral palsy and swallowing difficulties. Eur J Clin Nutr 67(Suppl 2):S9–S12
Christiaanse ME, Mabe B, Russell G, Simeone TL, Fortunato J, Rubin B (2011) Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is no more effective than usual care for the treatment of primary dysphagia in children. Pediatr Pulmonol 46(6):559–565
Rice KL (2012) Neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the early intervention population: a series of five case studies. Internet J Allied Health Sci Pract 10(3):1e7
Song WJ, Park JH, Lee JH, Kim MY (2015) Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on swallowing functions in children with cerebral palsy: a pilot randomised controlled trial. HKJOT 25:1e6
Umay E, Unlu E, Cakci A (2014) Psychological status and quality of life of caregivers of children with dysphagic cerebral palsy. Res J 1:768–776
Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, Russell D, Wood E, Galuppi B (1997) Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 39(4):214–223
Serel Arslan S, Demir N, Karaduman AA, Belafsky PC (2017) The pediatric version of the eating assessment tool: a caregiver administered dyphagia-specific outcome instrument for children. Disabil Rehabil 5:1–5
Dziewas R, Warnecke T, Olenberg S, Teismann I, Zimmermann J, Kramer C et al (2008) Towards a basic endoscopic assessment of swallowing in acute stroke development and evaluation of a simple dysphagia score. Cerebrovasc Dis 26:41–47
Karaca Umay E, Yaylaci A, Saylam G, Gundogdu I, Gurcay E, Akcapinar D et al (2017) The effect of sensory-level electrical stimulation of the masseter muscle in early stroke patients with dysphagia: a randomized controlled study. Neurol India 64(4):734–742
Sheppard JJ (2008) Using motor learning approaches for treating swallowing and feeding disorders: a review. Lang Speech Hear Ser 39(2):227–236
Gow D, Hobson AR, Furlong P, Hamdy S (2004) Characterising the central mechanisms of sensory modulation in human swallowing motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 115(10):2382–2390
Steele CM, Miller AJ (2010) Sensory input pathways and mechanisms in swallowing: a review. Dysphagia 25(4):323–333
Arvedson J, Clark H, Lazarus C, Schooling T, Frymark T (2010) The effects of oral-motor exercises on swallowing in children: an evidence-based systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 52(11):1000–1013
Scott S (2014) Classifying eating and drinking ability in people with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 56(3):201
Dodrill P, Gosa MM (2015) Pediatric dysphagia: physiology, assessment, and management. Ann Nutr Metab 66(suppl 5):24–31
Harding C, Cockerill H (2015) Managing eating and drinking difficulties (dysphagia) with children who have learning disabilities: What is effective? Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 20(3):395–405
Jayasekeran V, Singh S, Tyrrell P, Michou E, Jefferson S, Mistry S et al (2010) Adjunctive functional pharyngeal electrical stimulation reverses swallowing disability after brain lesions. Gastroenterology 138(5):1737–1746
Permsirivanich W, Tipchatyotin S, Wongchai M, Leelamanit V, Setthawatcharawanich S, Sathirapanya P et al (2009) Comparing the effects of rehabilitation swallowing therapy vs. neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy among stroke patients with persistent pharyngeal dysphagia: a randomized controlled study. J Med Assoc Thai 92(2):259–265
Xia W, Zheng C, Lei Q, Tang Z, Hua Q, Zhang Y et al (2011) Treatment of post-stroke dysphagia by vitalstim therapy coupled with conventional swallowing training. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci 31(1):73–76
Li L, Li Y, Huang R, Yin J, Shen Y, Shi J (2015) The value of adding transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation (VitalStim) to traditional therapy for post-stroke dysphagia: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 51(1):71–78
Sproson L, Pownall S, Enderby P, Freeman J (2018) Combined electrical stimulation and exercise for swallow rehabilitation post-stroke: a pilot randomized control trial. Int J Lang Commun Disord 53(2):405–417
Merrill DR (2009) Review of electrical stimulation in cerebral palsy and recommendations for future directions. Dev Med Child Neurol 51(Suppl 4):154–165
Pernambuco Lde A, Silva HJ, Lima LM, Cunha RA, Santos Vda S, Cunha DA et al (2011) Electrical activity of masseter muscle in young adults during swallowing of liquid. J Soc Bras Fonoaudiol 23(3):214–219
Ludlow CL, Humbert I, Saxon K, Poletto C, Sonies B, Crujido L (2007) Effects of surface electrical stimulation both at rest and during swallowing in chronic pharyngeal. Dysphagia Dysphagia 22(1):1–10
Funding
There is no funding source in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict interest among the authors. Author EU declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author EG declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author EO declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author EUA declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the caregivers of all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umay, E., Gurcay, E., Ozturk, E.A. et al. Is sensory-level electrical stimulation effective in cerebral palsy children with dysphagia? A randomized controlled clinical trial. Acta Neurol Belg 120, 1097–1105 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-01071-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-018-01071-6