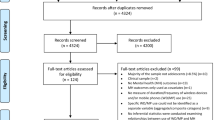
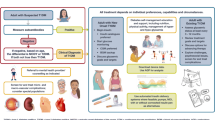
Abstract
Since the “2007 summary report of child and adolescent overweight and obesity treatment” published by Barlow, many obesity intervention studies have been conducted in pediatric ambulatory care. Although several meta-analyses have been published in the interim, many studies were excluded because of the focus and criteria of these meta-analyses. Therefore, the primary goal of this article was to identify randomized case–control trials conducted in the primary care setting and to report on treatment approaches, challenges, and successes. We have developed four themes for our discussion and provide a brief summary of our findings. Finally, we identified major gaps and potential solutions and describe several urgent key action items.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011–2012. JAMA. 2014;311(8):806–14.
Lakshman R, Elks CE, Ong KK. Childhood obesity. Circulation. 2012;126(14):1770–9.
Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309(1):71–82.
Danaei G, Ding EL, Mozaffarian D, et al. The preventable causes of death in the United States: comparative risk assessment of dietary, lifestyle, and metabolic risk factors. Hales S, ed. PLoS Med. 2009;6(4):e1000058.
Story MT, Neumark-Stzainer DR, Sherwood NE, et al. Management of child and adolescent obesity: attitudes, barriers, skills, and training needs among health care professionals. Pediatrics. 2002;110:210–4.
Nelson JM, Vos MB, Walsh SM, O’Brien LA, Welsh JA. Weight management-related assessment and counseling by primary care providers in an area of high childhood obesity prevalence: current practices and areas of opportunity. Child Obes. 2015;11(2):194–201.
Shadix K, Bell-Wilson JA. Finding your niche—certification options for the RD. Today’s Dietitian. 2007;9(3):40. http://www.todaysdietitian.com/newarchives/tdmar2007pg40.shtml.
Commission of Dietetic Registration (CDR), the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND): board certification as a specialist in pediatric nutrition: eligibility application instructions. Last accessed 27 Nov 2015: https://admin.cdrnet.org/vault/2459/web/files/Pediatric%20Specialty%20ApplicationBooklet%206-2014.pdf.
Kyle T. ConscienHealth. Oral abstract presentation at: The Obesity Society Annual Meeting at ObesityWeekSM 2015; November 2–6, 2015; Los Angeles, CA. www.obesityweek.com.
Lesser LI, Krist AH, Kamerow DB, Bazemore AW. Comparison between US Preventive Services Task Force recommendations and Medicare coverage. Ann Fam Med. 2011;9:44–9.
Barlow SE, Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics. 2007;(Suppl 4):S164-92.
Kris-Etherton PM, Akabas SR, Bales CW, Bistrian B, Braun L, Edwards MS, et al. The need to advance nutrition education in the training of health care professionals and recommended research to evaluate implementation and effectiveness. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5):1153S–66.
Whitlock EP, O’Connor EA, Williams SB, Beil TL, Lutz KW. Effectiveness of weight management interventions in children: a targeted systematic review for the USPSTF. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):e396–418.
Bryce J, Coitinho D, Darnton-Hill I, Pelletier D, Pinstrup-Andersen P, Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. Maternal and child undernutrition: effective action at national level. Lancet. 2008;371:510–26.
Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013;382(9890):427–51.
Bocca G, Corpeleijn E, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Results of a multidisciplinary treatment program in 3-year-old to 5-year-old overweight or obese children: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166(12):1109–15.
Stark LJ, Spear S, Boles R, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of a clinic and home-based behavioral intervention to decrease obesity in preschoolers. Obesity. 2011;19:134–41.
Taveras EM, Gortmaker SL, Hohman KH, Horan CM, Kleinman KP, Mitchell K, et al. Randomized controlled trial to improve primary care to prevent and manage childhood obesity: the high five for kids study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2011;165(8):714–22.
Foster BA, Farragher J, Parker P, Sosa ET. Treatment interventions for early childhood obesity: a systematic review. Acad Pediatr. 2015;15(4):353–61.
Arauz Boudreau AD, Kurowski DS, Gonzalez WI, Dimond MA, Oreskovic NM. Latino families, primary care, and childhood obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Prev Med. 2013;44(3 Suppl 3):S247–57.
Ball G, Mackenzie-Rife KA, Newton MS, Alloway CA, Slack JM, Plotnikoff RC, et al. One-on-one lifestyle coaching for managing adolescent obesity: findings from a pilot, randomized controlled trial in a real-world, clinical setting. Paediatr Child Health. 2011;16(6):345–50.
McCallum Z, Wake M, Gerner B, Baur LA, Gibbons K, Gold L, et al. Outcome data from the LEAP (Live, Eat and Play) trial: a randomized controlled trial of a primary care intervention for childhood overweight/mild obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007;31(4):630–6.
Boutelle KN, Norman GJ, Rock CL, Rhee KE, Crow SJ. Guided self-help for the treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics. 2013;131(5):e1435–42.
Davis AM, Sampilo M, Gallagher KS, Dean K, Saroja MB, Yu Q, et al. Treating rural pediatric obesity through telemedicine: outcomes from a small randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38(9):932–43.
Debarr LL, Stevens VJ, Perrin N, Wu P, Pearson J, Yarborough BJ, et al. A primary care-based, multicomponent lifestyle intervention for overweight adolescent females. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e611–20.
Diaz RG, Esparaza-Romero J, Moya-Camarena SY, Robles-Sardin AE, Valencia ME. Lifestyle intervention in primary care settings improves obesity parameters among Mexican youth. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010;110(2):285–90.
Golley RK, Magarey AM, Baur LA, Steinbeck KS, Daniels LA. Twelve-month effectiveness of a parent-led, family-focused weight-management program for prepubertal children: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2007;119(3):517–25.
Hofsteenge GH, Chinapaw MJM, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, Weijs PJM. Long-term effect of the Go4it group treatment for obese adolescents: a randomised controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2014;33(3):385–91.
Lloyd-Richardson EE, Jelalian E, Sato AF, Hart CN, Mehlenbeck R, Wing RR. Two-year follow-up of an adolescent behavioral weight control intervention. Pediatrics. 2012;130(2):e281–8.
Looney SM, Raynor HA. Examining the effect of three low-intensity pediatric obesity interventions: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2014;53(14):1367–74.
Magarey AM, Perry RA, Baur LA, Steinbeck KS, Sawyer M, Hills AP, et al. A parent-led family-focused treatment program for overweight children aged 5 to 9 years: the PEACH RCT. Pediatrics. 2011;127(2):214–22.
O’Connor TM, Hilmers A, Watson K, Baranowski T, Giardino AP. Feasibility of an obesity intervention for paediatric primary care targeting parenting and children: helping HAND. Child Care Health Dev. 2013;39(1):141–9.
Quattrin T, Roemmich JN, Paluch R, Yu J, Epstein LH, Ecker MA. Treatment outcomes of overweight children and parents in the medical home. Pediatrics. 2014;134(2):290–7.
Raynor HA, Osterhold KM, Hart CN, Jelalian E, Vivier P, Wing RR. Efficacy of U.S. pediatric obesity primary care guidelines: two randomized trials. Pediatr Obes. 2012;7(1):28–38.
Resnicow K, McMaster F, Bocian A, Harris D, Zhou Y, Snetselaar L, et al. Motivational interviewing and dietary counseling for obesity in primary care: an RCT. Pediatrics. 2015;135(4):649–57. This study highlights the importance of contact time and support staff to lead to improvements in weight status.
Small L, Bonds-McClain D, Melnyk B, Vaughan L, Gannon AM. The preliminary effects of a primary care-based randomized treatment trial with overweight and obese young children and their parents. J Pediatr Health Care Off Publ Natl Assoc Pediatr Nurse Assoc Pract. 2014;28(3):198–207.
Stovitz SD, Berge JM, Wetzsteon RJ, Sherwood NE, Hannah PJ, Himes JH. Stage 1 treatment of pediatric overweight and obesity: a pilot and feasibility randomized controlled trial. Child Obes. 2014;10(1):50–7.
Wake M, Baur LA, Gerner B, Gibbons K, Gold L, Gunn J, et al. Outcomes and costs of primary care surveillance and intervention for overweight or obese children: the LEAP 2 randomised controlled trial. BMJ Br Med J. 2009;339:b3308.
Berkowitz RI, Rukstalis MR, Bishop-Gilyard CT, Moore RH, Gehrman CA, Xanthapoulous MS, et al. Treatment of adolescent obesity comparing self-guided and group lifestyle modification programs: a potential model for primary care. J Pediatr Psychol. 2013;38(9):978–86.
Wright JA, Phillips BD, Watson BL, Newby PK, Norman GJ, Adams WG. Randomized trial of a family-based, automated, conversational obesity treatment program for underserved populations. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013;21(9):E369–78.
Boodai SA, McColl JH, Reilly JJ. National Adolescent Treatment Trial for Obesity in Kuwait (NATTO): project design and results of a randomised controlled trial of a good practice approach to treatment of adolescent obesity in Kuwait. Trials. 2014;15:234.
Danielsen YS, Nordhus IH, Júlíusson PB, Mæhle M, Pallesen S. Effect of a family-based cognitive behavioural intervention on body mass index, self-esteem and symptoms of depression in children with obesity (aged 7–13): a randomised waiting list controlled trial. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013;7(2):e116–28.
Kalvainen MP, Korppi MO, Nuutinen OM. Clinical efficacy of group-based treatment for childhood obesity compared with routinely given individual counseling. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007;31(10):1500–8.
Kalvainen M, Utrianien P, Vanninen E, Korppi M, Nuutinen O. Impact of childhood obesity treatment on body composition and metabolic profile. World J Pediatr. 2012;8(1):31–7.
Marlid S, Gronowitz E, Forsell C, Dahlgren J, Friberg P. A controlled study of lifestyle treatment in primary care for children with obesity. Pediatr Obes. 2013;8(3):207–17.
Pakpour AH, Gellert P, Dombrowski SU, Fridlund B. Motivational interviewing with parents for obesity: an RCT. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):e644–52.
Stark LE, Clifford LM, Towner EK, Filigno SS, Zion C, Bolling C, et al. A pilot randomized controlled trial of a behavioral family-based intervention with and without home visits to decrease obesity in preschoolers. J Pediatr Psychol. 2014;39(9):1001–12.
Taveras EM, Marshall R, Kleinman KP, Gillman MW, Hacker K, Horan CM, et al. Comparative effectiveness of childhood obesity interventions in pediatric primary care: a cluster-randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(6):535–42. Taveras et al. presented a very well designed study showing that a weight loss intervention in the primary care office and led by primary care physicians is unlikely to lead to clinically significant weight status improvements.
Wake M, Lycett K, Clifford SA, Sabin MA, Gunn J, Gibbons K, et al. Shared care obesity management in 3–10 year old children: 12 month outcomes of HopSCOTCH randomised trial. BMJ Br Med J. 2013;346:f3092.
Savoye M, Shaw M, Dziura J, Tamborlane WV, Rose P, Guandalini C, et al. Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297(24):2697–704.
Savoye M, Nowicka P, Shaw M, Yu S, Dziura J, Chavent G, et al. Long-term results of an obesity program in an ethnically diverse pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):402–10.
Martinez-Andrade GO, Cespedes EM, Rifas-Shiman SL, Romero-Quechol G, Gonzalez-Unzaga MA, Benitez-Trejo MA, et al. Feasibility and impact of Creciendo Sanos, a clinic-based pilot intervention to prevent obesity among preschool children in Mexico City. BMC Pediatr. 2014;14:77.
Kalarchian MA, Levine MD, Arslanian SA, Ewing LJ, Houck PR, Cheng Y, et al. Family-based treatment of severe pediatric obesity: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1060–8.
Banks J, Sharp DJ, Hunt LP, Shield JP. Evaluating the transferability of a hospital-based childhood obesity clinic to primary care: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Gen Pract. 2012;62(594):e6–12.
van der Baan-Slootweg O, Benninga MA, Beelen A, van der Palen J, Tamminga-Smeulders C, Tijssen JG, et al. Inpatient treatment of children and adolescents with severe obesity in the Netherlands: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2014;168(9):807–14.
Campbell KJ, Lioret S, McNaughton SA, Crawford DA, Salmon J, Ball K, et al. A parent-focused intervention to reduce infant obesity risk behaviors: a randomized trial. Pediatrics. 2013;131(4):652–60.
Wen LM, Baur LA, Simpson JM, Rissel C, Wardle K, Flood VM. Effectiveness of home based early intervention on children’s BMI at age 2: randomised controlled trial. BMJ Br Med J. 2012;344, e3732.
Wen LM, Baur LA, Simpson JM, Xu H, Hayes AJ, Hardy LL, et al. Sustainability of effects of an early childhood obesity prevention trial over time: a further 3-year follow-up of the healthy beginnings trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(6):543–51. This is a well-designed study with long-term follow up showing the need for additional interventions in order to maintain weight loss.
Daniels LA, Mallan KM, Nicholson JM, Thorpe K, Nambiar S, Mauch CE, et al. An early feeding practices intervention for obesity prevention. Pediatrics. 2015;136(1):e40–9.
Mustila T, Raitanen J, Keskinen P, Saari A, Luoto R. Lifestyle counselling targeting infant’s mother during the child’s first year and offspring weight development until 4 years of age: a follow-up study of a cluster RCT. BMJ Open. 2012;2(1), e000624.
Norman G, Huang J, Davila EP, Kolodziejczyk JK, Carlson J, Covin JR, et al. Outcomes of a 1-year randomized controlled trial to evaluate a behavioral ‘stepped-down’ weight loss intervention for adolescent patients with obesity. Pediatr Obes. 2015. doi:10.1111/ijpo.12013.
Epstein LH, Valoski A, Wing RR, McCurley J. Ten-year follow-up of behavioral, family-based treatment for obese children. JAMA. 1990;264(19):2519–23.
Skelton JA, Irby MB, Geiger AM. A systematic review of satisfaction and pediatric obesity treatment: new avenues for addressing attrition. J Healthc Qual Off Publ Natl Assoc Healthc Qual. 2014;36(4):5–22.
Centers for Disease Control and Preventions. Last accessed at http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/cdc_charts.htm.
Lycett K, Wittert G, Gun J, Huton C, Clifford SA, Wake M. The challenges of real-world implementation of web-based shared care software: the HopSCOTCH shared care obesity trail in children. BMC Med Inf Decis Making. 2014;14:61.
Tershakovec AM, Kuppler K. Ethnicity, insurance type, and follow-up in a pediatric weight management program. Obes Res. 2003;11(1):17–20.
Zeller M, Kirk S, Claytor R, Khoury P, Grieme J, Santangelo M, et al. Predictors of attrition from a pediatric weight management program. J Pediatr. 2004;144(4):466–70.
Davis AM, Daldalian MC, Mayfield CA, Dean K, Black WR, Sampilo ML. Outcomes from an urban pediatric obesity program targeting minority youth: the healthy Hawks program. Child Obes. 2013;9(6):492–500.
Dhaliwal J, Nosworthy NM, Holt NL, Zwaigenbaum L, Avis JL, Rasquinha A, et al. Attrition and the management of pediatric obesity: an integrative review. Child Obes. 2014;10(6):461–73.
Ehrmann DE, Sallinen BJ, IglayReger HB, Gordon PM, Woolford SJ. Slow and steady: readiness, pretreatment weekly strengthening activity, and pediatric weight management program completion. Child Obes. 2013;9(3):193–9.
Cole TJ, Faith MS, Pietrobelli A, Heo M. What is the best measure of adiposity change in growing children: BMI, BMI%, BMI z-score or BMI centile? Euro J Clin Nutr. 2005;59:419–25.
Woo JG. Using body mass index Z-score among severely obese adolescents: a cautionary note. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2009;4(4):405–10.
Inokuchi M, Matsuo N, Takayama JI, Hasegawa T. BMI z-score is the optimal measure of annual adiposity change in elementary school children. Ann Hum Biol. 2011;38(6):747–51.
Kakinami L, Henderson M, Chiolero A, Cole TJ, Paradis G. Identifying the best body mass index metric to assess adiposity change in children. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99(11):1020–4.
Manning S, Pucci A, Finer N. Pharmacotherapy for obesity: novel agents and paradigms. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2014;5:135–48.
Roche N, Reddel H, Martin R, Brusselle G, Papi A, Thomas M, et al. Quality standards for real-world research focus on observational database studies of comparative effectiveness. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014;11(S2):S99–104.
Braet C, Mervielde J, VanderEyken W. Psychological aspects of childhood obesity: a controlled study in a clinical and non-clinical sample. J Pediatr Psychol. 1997;22:59–71.
Perez A, Holt N, Gokiert R, et al. Why don’t families initiate treatment? A qualitative multicentre study investigating parents’ reasons for declining paediatric weight management. Paediatr Child Health. 2015;20(4):179–84.
Skelton JA, Beech BM. Attrition in paediatric weight management: a review of the literature and new directions. Obes Rev. 2011;12(501):e273–81.
Kitscha CE, Brunet K, Farmer A, Mager DR. Reasons for non-return to a pediatric weight management program. Can J Diet Pract Res. 2009;70:89–94.
Wright DR, Taveras EM, Gillman MW, et al. The cost of a primary care-based childhood obesity prevention intervention. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:44.
Cawley J. The economics of childhood obesity. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010;29(3):364–71.
Adams KM, Kohlmeier M, Zeisel SH. Nutrition education in U.S. medical schools: latest update of a national survey. Acad Med. 2010;85(9):1537–42.
Adams KM, Butsch WS, Kohlmeier M. The state of nutrition education at US medical schools. J Biomed Educ. 2015;2015(Article ID 357627):1–7.
Kushner RF, Van Horn L, Rock CL, Edwards MS, Bales CW, Kohlmeier M, et al. Nutrition education in medical school: a time of opportunity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5 Suppl):1167S–73.
Lenders CM, Deen DD, Bistrian B, Edwards MS, Seidner DL, McMahon MM, et al. Residency and specialties training in nutrition: a call for action. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5 Suppl):1174S–83.
DiMaria-Ghalili RA, Mirtallo JM, Tobin BW, Hark L, Van Horn L, Palmer CA. Challenges and opportunities for nutrition education and training in the health care professions: intraprofessional and interprofessional call to action. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(5):1184S–93.
Jortberg BT, Fleming MO. Registered dietitian nutritionists bring value to emerging health care delivery models. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2014;114(12):2017–22.
Silberberg M, Carter-Edwards L, Murphy G, et al. Treating pediatric obesity in the primary care setting to prevent chronic disease: perceptions and knowledge of providers and staff. N C Med J. 2012;73(1):9–14.
Eneli I, Norwood V, Hampl S, Ferris M, Hibbeln T, Patterson K, et al. Perspectives on obesity programs at Children’s Hospitals: insights from senior program administrators. Pediatrics. 2011;128(sup 2):S86–90.
Lee JS, Sheer JLO, Lopez N, Rosenbaum S. Coverage of obesity treatment: a state by state analysis of medicaid and state insurances laws. Public Health Rep. 2010;125:596–604.
Dietz WH, Solomon LS, Pronk N, Ziegenhorn SK, Standish M, Longjohn MM, et al. An integrated framework for the prevention and treatment of obesity and its related chronic diseases. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015;34(9):1456–63.
Acknowledgments
The NFL program receives funding support from the New Balance foundation and mentoring from the Boston Nutrition Obesity Research Center (P30 DK46200) for education and research activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Carine M. Lenders, Aaron J. Manders, Joanna E. Perdomo, Kathy A. Ireland, and Sarah E. Barlow declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Obesity Treatment
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lenders, C.M., Manders, A.J., Perdomo, J.E. et al. Addressing Pediatric Obesity in Ambulatory Care: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?. Curr Obes Rep 5, 214–240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-016-0210-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-016-0210-2