Abstract
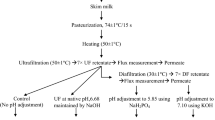
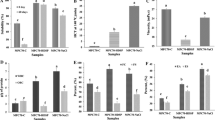
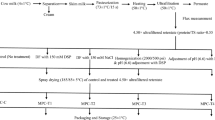
Milk protein concentrate (MPC) powders offer a great potential for use in an array of food applications because of their nutritional and functional values. However, MPC powders with protein content ≥80% (MPC80) exhibit poor solubility and hence restrict their potential use. The objective of this study was to determine the impact of adding salt during the diafiltration stage of MPC80 manufacture on solubility, turbidity, and to compare minerals and protein content of supernatants of ultracentrifuged samples with control sample. Three types of samples were produced: MPC80-C (control) with or without salt treatment, MPC80-Na (150 mM NaCl), and MPC80-K (150 mM KCl). Lower solubility was observed in MPC80-C (53%) as compared to MPC80-Na or MPC80-K (100%). Higher turbidity was observed in MPC80-C (530 NTU) and lower turbidity was observed in samples of MPC80-Na (128 NTU) and MPC80-K (131 NTU). Furthermore, lower protein and calcium contents were observed in supernatants of ultracentrifuged samples of MPC80-C (2.3%; 0.35 mg.mL−1) as compared to MPC80-Na (3.8%; 0.63mg.mL−1) and MPC80-K (3.7%; 0.67 mg.mL−1). The opposite trend was found in reconstituted samples (5% TS). Our results showed that the addition of salt impacted the distribution of minerals and proteins in colloidal and soluble phases of MPC80-Na and MPC80-K. The results from this work will contribute to our understanding of the role that mineral-induced changes (depletion or addition) play in the functionality of MPC80.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Piot M, Rousseau F, Grongnet J, Gaucheron F (2009) Physico-chemical changes in casein micelles of buffalo and cow milks as a function of alkalinisation. Dairy Sci Technol 89:387–403. doi:10.1051/dst/2009020
Altuner E, Alpas H, Erdem Y, Bozoglu F (2006) Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on physicochemical and biochemical properties of milk. Eur Food Res Technol 222:392–396. doi:10.1007/s00217-005-0072-4
Amamcharla JK, Metzger LE (2011) Development of a rapid method for the measurement of lactose in milk using a blood glucose biosensor. J Dairy Sci 94:4800–4809. doi:10.3168/jds.2011-4416
Anema SG, Pinder DN, Hunter RJ, Hemar Y (2006) Effects of storage temperature on the solubility of milk protein concentrate (MPC85). Food Hydrocoll 20:386–393. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2005.03.015
Aoki T, Umeda T, Nakano T (1999) Effect of sodium chloride on the properties of casein micelles. Milchwissenschaft 54:91–93
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (1995) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn., Gaithersburg, MD, USA
Baldwin AJ (2010) Insolubility of milk powder products—a minireview. Dairy Sci Technol 90:169–179
Bhaskar G, Singh H, Blazey N (2001) Milk protein concentrate products and process. International Patent Specification Patent WO01/41578
Carr A, Bhaskar G, Ram S (2002) Monovalent salt enhances solubility of milk protein concentrate. US Patent 0208955
De Castro-Morel M, Harper W (2002) Basic functionality of commercial milk protein concentrates. Milchwissenschaft 57:367–370
Famelart M, Le Graet Y, Raulot K (1999) Casein micelle dispersions into water, NaCl and CaCl2: physicochemical characteristics of micelles and rennet coagulation. Int Dairy J 9:293–297
Farrell H, Kumosinski T, Pulaski P, Thompson M (1988) Calcium-induced associations of the caseins: a thermodynamic linkage approach to precipitation and resolubilization. Arch Biochem Biophys 265:146–158
Griffin M, Lyster R, Price J (1988) The disaggregation of calcium–depleted casein micelles. Eur J Biochem 174:339–343
Gualco SJ (2010) Effect of sodium chloride addition during diafiltration on the solubility of milk protein concentrate. M.Sc. Thesis, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, USA
Havea P (2006) Protein interactions in milk protein concentrate powders. Int Dairy J 16:415–422
Huppertz T, Alting A, Slangen C, Floris R (2010) Milk protein concentrate functionality (oral presentation). http://www.wds2010.com/delegates/presentations/09tue/05-Session3_2-Thom%20Huppertz.pdf. Accessed Sept 9 2012
Huppertz T, Fox P (2006) Effect of NaCl on some physico-chemical properties of concentrated bovine milk. Int Dairy J 16:1142–1148
Hussain R, Gaiani C, Aberkane L, Scher J (2011) Characterization of high-milk-protein powders upon rehydration under various salt concentrations. J Dairy Sci 94:14–23. doi:10.3168/jds.2010-3323
Laemmli U (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mao X, Tong P, Gualco S, Vink S (2012) Effect of NaCl addition during diafiltration on the solubility, hydrophobicity, and disulfide bonds of 80% milk protein concentrate powder. J Dairy Sci 95:3481–3488
Mimouni A, Deeth H, Whittaker A, Gidley M, Bhandari B (2010) Rehydration of high-protein-containing dairy powder: slow- and fast-dissolving components and storage effects. Dairy Sci Technol 90:335–344
Mistry V, Hassan H (1991a) Delactosed, high milk protein powder. 1. Manufacture and composition. J Dairy Sci 74:1163–1169
Mistry V, Hassan H (1991b) Delactosed, high milk protein powder. 2. Physical and functional properties. J Dairy Sci 74:3716–3723
Morr CV, German B, Kinsella JE, Regenstein JM, Buren JPV, Kilara A et al. (1985) A Collaborative Study to Develop a Standardized Food Protein Solubility Procedure. J Food Sci 50:1715–1718. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1985.tb10572.x
Rose D (1968) Relation between micellar and serum casein in bovine milk. J Dairy Sci 51:1897–1902
Schmidt DG (1982) Association of caseins and casein micelle structure. In: Fox P (ed) Developments in dairy chemistry, vol 1. Applied Science Publishers Ltd, London, pp 61–86
Schokker E, Church J, Mata J, Gilbert E, Puvanenthiran A, Udabage P (2011) Reconstitution properties of micellar casein powder: effects of composition and storage. Int Dairy J 21:877–886
Schrader K, Buchheim W, Morr CV (1997) High pressure effects on the colloidal calcium phosphate and the structural integrity of micellar casein in milk. Part 1. High pressure dissolution of colloidal calcium phosphate in heated milk systems. Food/Nahrung 41:133–138. doi:10.1002/food.19970410303
Schuck P, Briard V, Mejean S, Piot M, Famelart M, Maubois J (1999) Dehydration by desorption and by spray drying of dairy proteins: influence of the mineral environment. Dry Technol 17:1347–1357
Schuck P, Davenel A, Mariette F, Briard V, Méjean S, Piot M (2002) Rehydration of casein powders: effects of added mineral salts and salt addition methods on water transfer. Int Dairy J 12:51–57
Schuck P, Mejean S, Dolivet A, Gaiani C, Banon S, Scher J, Jeantet R (2007) Water transfer during rehydration of micellar casein powders. Lait 87:425–432
Sikand V, Tong P, Roy S, Rodriguez-Saona L, Murray B (2011) Solubility of commercial milk protein concentrates and milk protein isolates. J Dairy Sci 94:6194–6202
Sikand V, Tong P, Vink S, Walker J (2012) Effect of powder source and processing conditions on the solubility of milk protein concentrates 80. Milchwissenschaft 67:300–303
Singh H (2007) Interactions of milk proteins during the manufacture of milk powders. Lait 87:413–423
Udabage P, Mckinnon IR, Augustin MA (2000) Mineral and casein equilibria in milk: effects of added salts and calcium-chelating agents. J Dairy Res 67:361–370
Vaia B, Smiddy MA, Kelly AL, Huppertz T (2006) Solvent-mediated disruption of bovine casein micelles at alkaline pH. J Agric Food Chem 54:8288–8293
Ward BR, Goddard SJ, Augustin MANN, Mckinnon I (1997) EDTA-induced dissociation of casein micelles and its effect on foaming properties of milk. J Dairy Res 64:495–504
Zwijgers A (1992) Outline of milk protein concentrate. Int Food Ingred 3:18–23
Acknowledgments
Financial support of this work by Dairy Research Institute (Rosemont, IL) and California Dairy Research Foundation (Davis, CA) is appreciated. The authors would like to thank Dr. Lloyd Metzger, South Dakota State University, and Dr. Chao Wu, Hilmar Ingredients (Hilmar, CA) for technical lab analyses support. In addition, the authors would like to thank Dr. Frédéric Gaucheron, French National Institute for Agricultural Research (Rennes, France), and Dr. Harjinder Singh, Massey University (Palmerston North, New Zealand) for their helpful insight and comments on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sikand, V., Tong, P.S. & Walker, J. Effect of adding salt during the diafiltration step of milk protein concentrate powder manufacture on mineral and soluble protein composition. Dairy Sci. & Technol. 93, 401–413 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-013-0110-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13594-013-0110-0