Abstract
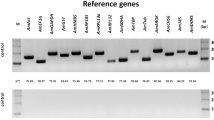
Honey bees are important model organisms for neurobiology, because they display a large array of behaviors. To link behavior with individual gene function, quantitative polymerase chain reaction is frequently used. Comparing gene expression of different individuals requires data normalization using adequate reference genes. These should ideally be expressed stably throughout lifetime. Unfortunately, this is frequently not the case. We studied how well three commonly used reference genes are suited for this purpose and measured gene expression in the brains of honey bees differing in age and social role. Although rpl32 is used most frequently, it only remains stable in expression between newly emerged bees, nurse-aged bees, and pollen foragers but shows a peak at the age of 12 days. The genes gapdh and ef1α-f1, in contrast, are expressed stably in the brain throughout all age groups except newly emerged bees. According to stability software, gapdh was expressed most stably, followed by rpl32 and ef1α-f1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ament, S.A., Corona, M., Pollock, H.S., Robinson, G.E. (2008) Insulin signaling is involved in the regulation of worker division of labor in honey bee colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 4226–4231
Andersen, C.L., Jensen, J.L., Ørntoft, T.F. (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64, 5245–5250
Bagnall, N.H., Kotze, A.C. (2010) Evaluation of reference genes for real-time PCR quantification of gene expression in the Australian sheep blowfly, Lucilia cuprina. Med. Vet. Entomol. 24, 176–181
Ben-Shahar, Y., Leung, H.T., Pak, W.L., Sokolowski, M.B., Robinson, G.E. (2003) cGMP-dependent changes in phototaxis: a possible role for the foraging gene in honey bee division of labor. J. Exp. Biol. 206, 2507–2515
Bloch, G., Toma, D.P., Robinson, G.E. (2001) Behavioral rhythmicity, age, division of labor and period expression in the honey bee brain. J. Biol. Rhythms. 16, 444–456
Bustin, S.A. (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 25, 169–193
Bustin, S.A., Nolan, T. (2004) Pitfalls of quantitative real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. J. Biomol. Tech. 15, 155–166
Bustin, S.A., Benes, V., Garson, J.A., Hellemans, J., Huggett, J., Kubista, M., Mueller, R., Nolan, T., Pfaffl, M.W., Shipley, G.L., Vandesompele, J., Wittwer, C.T. (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 55, 611–622
Chapuis, M.P., Tohidi-Esfahani, D., Dodgson, T., Blondin, L., Ponton, F., Cullen, D., Simpson, S.J., Sword, G.A. (2011) Assessment and validation of a suite of reverse transcription-quantitative PCR reference genes for analyses of density-dependent behavioural plasticity in the Australian plague locust. BMC Mol. Biol. 12, 7
Corona, M., Velarde, R.A., Remolina, S., Moran-Lauter, A., Wang, Y., Hughes, K.A., Robinson, G.E. (2007) Vitellogenin, juvenile hormone, insulin signaling, and queen honey bee longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 104, 7128–7133
Danforth, B.N., Shuqing, J. (1998) Elongation Factor-1α occurs as two copies in bees: implications for phylogenetic analysis of EF-1α sequences in insects. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15(3), 225–235
Grozinger, C.M., Sharabash, N.M., Whitfield, C.W., Robinson, G.E. (2003) Pheromone-mediated gene expression in the honey bee brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100(Suppl 2), 14519–14525
Grubbs, F.E. (1969) Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples. Technometrics 11, 1–21
Hornáková, D., Matousková, P., Kindl, J., Valterová, I., Pichová, I. (2010) Selection of reference genes for real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis in tissues from Bombus terrestris and Bombus lucorum of different ages. Anal. Biochem. 397, 118–120
Huggett, J., Dheda, K., Bustin, S., Zumla, A. (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes. Immun. 6, 279–284
Kubista, M., Andrade, J.M., Bengtsson, M., Forootan, A., Jonák, J., Lind, K., Sindelka, R., Sjöback, R., Sjögreen, B., Strömbom, L., Ståhlberg, A., Zoric, N. (2006) The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Aspects Med. 27, 95–125
Ling, D., Salvaterra, P.M. (2011) Robust RT-qPCR data normalization: validation and selection of internal reference genes during post-experimental data analysis. PLoS One 6(3), e17762
Lord, J.C., Hartzer, K., Toutges, M., Oppert, B. (2010) Evaluation of quantitative PCR reference genes for gene expression studies in Tribolium castaneum after fungal challenge. J. Microbiol. Methods 80, 219–221
Lourenco, A.P., Mackert, A., Cristino, A.S., Simoes, Z.L.P. (2008) Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in the honey bee, Apis mellifera, by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Apidologie 39, 372–385
Majerowicz, D., Alves-Bezerra, M., Logullo, R., Fonseca-de-Souza, A.L., Meyer-Fernandes, J.R., Braz, G.R., Gondim, K.C. (2011) Looking for reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR experiments in Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 20, 713–722
Mamidala, P., Rajarapu, S.P., Jones, S.C., Mittapalli, O. (2011) Identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in Cimex lectularius. J. Med. Entomol. 48, 947–951
McQuillan, H.J., Nakagawa, S., Mercer, A.R. (2012) Mushroom bodies of the honeybee brain show cell population-specific plasticity in expression of amine-receptor genes. Learn. Mem. 19, 151–158
Mustard, J.A., Blenau, W., Hamilton, I.S., Ward, V.K., Ebert, P.R., Mercer, A.R. (2003) Analysis of two D1-like dopamine receptors from the honey bee Apis mellifera reveals agonist-independent activity. Brain Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 113, 67–77
Navajas, M., Migeon, A., Alaux, C., Martin-Magniette, M., Robinson, G.E., Evans, J., Cros-Arteil, S., Crauser, D., Le Conte, Y. (2008) Differential gene expression of the honey bee Apis mellifera associated with Varroa destructor infection. BMC Genomics 9, 301–301
Pfaffl, M.W. (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 29(9), e45
Pfaffl, M.W., Tichopad, A., Prgomet, C., Neuvians, T.P. (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: Bestkeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 26, 509–515
Ponton, F., Chapuis, M.P., Pernice, M., Sword, G.A., Simpson, S.J. (2011) Evaluation of potential reference genes for reverse transcription-qPCR studies of physiological responses in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect. Physiol. 57, 840–850
Scharlaken, B., de Graaf, D.C., Goossens, K., Brunain, M., Peelman, L.J., Jacobs, F. (2008) Reference gene selection for insect expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR: the head of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, after a bacterial challenge. J. Insect. Sci. 8, 1–10
Sirover, M.A. (1997) Role of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in normal cell function and in cell pathology. J. Cell. Biochem. 66, 133–140
Suzuki, T., Higgins, P.J., Crawford, D.R. (2000) Control selection for RNA quantitation. Biotechniques 29, 332–337
Thellin, O., Zorzi, W., Lakaye, B., De Borman, B., Coumans, B., Hennen, G., Grisar, T., Igout, A., Heinen, E. (1999) Housekeeping genes as internal standards: use and limits. J. Biotechnol. 75, 291–295
Toma, D.P., Bloch, G., Moore, D., Robinson, G.E. (2000) Changes in period mRNA levels in the brain and division of labor in honey bee colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 6914–6919
Van Hiel, M.B., Van Wielendaele, P., Temmerman, L., Van Soest, S., Vuerinckx, K., Huybrechts, R., Broeck, J.V., Simonet, G. (2009) Identification and validation of housekeeping genes in brains of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria under different developmental conditions. BMC Mol. Biol. 10, 56–56
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., Speleman, F. (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3(7), RESEARCH0034
Walldorf, U., Hovemann, B.T. (1990) Apis mellifera cytoplasmic elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1α) is closely related to Drosophila melanogaster EF-1α. FEBS Lett. 267(2), 245–249
Winnebeck, E.C., Millar, C.D., Warman, G.R. (2010) Why does insect RNA look degraded? J. Insect. Sci. 10, 159–159
Yamazaki, Y., Shirai, K., Paul, R.K., Fujiyuki, T., Wakamoto, A., Takeuchi, H., Kubo, T. (2006) Differential expression of HR38 in the mushroom bodies of the honeybee brain depends on the caste and division of labor. FEBS Lett. 580, 2667–2670
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Benedikt Polaczek for assistance in beekeeping. This work was supported by grants from the German Research Foundation (DFG) to RS (SCH1573/2-1, SCH1573/4-1) and WB (BL469/7-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript editor: Stan Schneider
Possibilité d’utiliser trois gènes de référence communs pour une PCR quantitative en temps réel chez les abeilles
Expression génique / PCR quantitative / gène de référence / programme de stabilité / Apis mellifera
Untersuchung von drei häufig verwendeten Referenzgenen für quantitative Echtzeit-PCR in Honigbienen
Genexpression / quantitative PCR / Referenzgene / Stabilitätsprogramme / Apis mellifera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reim, T., Thamm, M., Rolke, D. et al. Suitability of three common reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in honey bees. Apidologie 44, 342–350 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0184-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-012-0184-3