Abstract
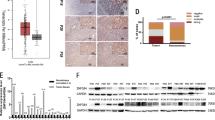
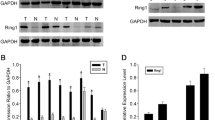
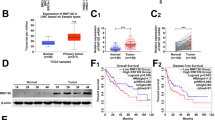
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cause of malignancy-related deaths. Recently, RING-finger protein 5 (RNF5), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, was revealed to be associated with the development of several human cancers. However, the clinical implication and functional role of RNF5 in HCC are poorly understood. We analysed RNF5 expression in HCC samples and observed that both the mRNA and protein levels of RNF5 were significantly increased in HCC tissues. RNF5 upregulation was markedly associated with larger tumour size, more satellite foci, and higher alpha fetoprotein (AFP) level, indicating poor prognosis in patients with HCC. Knockdown and overexpression experiments demonstrated that RNF5 promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells in vitro. Moreover, RNF5 facilitated HCC growth in vivo. Our findings indicated that RNF5 was an oncogene of HCC progression and could be used as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for patients with HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Propst A, Propst T, Waldenberger P, Judmaier G, Vogel W. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2006;10(2):339–51.
Hsu CY, Liu PH, Hsia CY, Lee YH, Nagaria TS, Lee RC, et al. Surgical resection is better than transarterial chemoembolization for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the milan criteria: a prognostic Nomogram study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(3):994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4929-x.
Zhang J, Zhou ZG, Huang ZX, Yang KL, Chen JC, Chen JB, et al. Prospective, single-center cohort study analyzing the efficacy of complete laparoscopic resection on recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Cancer. 2016;35(5):229–35.
Limor B, Irina K, Christine D, Anindita B, Benjamin P, Ze’Ev R. The LIM domain protein UNC-95 is required for the assembly of muscle attachment structures and is regulated by the RING finger protein RNF-5 in C. elegans. J Cell Biol. 2004;165(6):857–67.
Christine D, Limor B, Anindita B, Sharon I, Shoichi T, Koh N, et al. RNF5, a RING finger protein that regulates cell motility by targeting paxillin ubiquitination and altered localization. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(15):5331–45.
Delaunay A, Bromberg KD, Hayashi Y, Mirabella M, Burch D, Kirkwood B, et al. The ER-bound RING finger protein 5 (RNF5/RMA1) causes degenerative myopathy in transgenic mice and is deregulated in inclusion body myositis. PLoS ONE. 2008;3(2):e1609. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001609.
Jeon YJ, Khelifa S, Ratnikov B, Scott DA, Feng Y, Parisi F, et al. Regulation of glutamine carrier proteins by RNF5 determines breast cancer response to ER stress-inducing chemotherapies. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(3):354–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.006.
Bromberg KD, Kluger HM, Delaunay A, Abbas S, DiVito KA, Krajewski S, et al. Increased expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 is associated with decreased survival in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(17):8172–9. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0045.
Pitarresi JR, Liu X, Avendano A, Thies KA, Sizemore GM, Hammer AM, et al. Disruption of stromal hedgehog signaling initiates RNF5-mediated proteasomal degradation of PTEN and accelerates pancreatic tumor growth. Life Sci Alliance. 2018;1(5):e201800190. https://doi.org/10.26508/lsa.201800190.
Gao Y, Xuan C, Jin M, An Q, Zhuo B, Chen X, et al. Ubiquitin ligase RNF5 serves an important role in the development of human glioma. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):4659–66. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10801.
Wang C, Wan X, Yu T, Huang Z, Shen C, Qi Q, et al. Acetylation stabilizes phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase by disrupting the interaction of E3 Ligase RNF5 to promote breast tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2020;32(6):108021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108021.
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Li B. Six genes as potential diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma through data mining. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):9787–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27664.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers: 81871963, 81871961 and 81572335) and Medical and Health Key project of Xiamen (3502Z20191106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Ethical standards
The use of specimens was approved by the institutional research ethics committee of Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University (number: 2015–02-08). All animal experiments were approved by the ethical committee of Xiamen University and under the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by NIH.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Li, J., Chen, H. et al. RING-finger protein 5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and predicts poor prognosis. Human Cell 34, 530–538 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00460-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-020-00460-5