Abstract
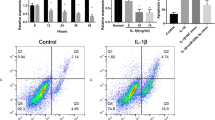
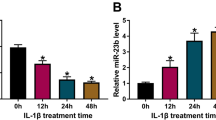
In recent years, some studies have been made on the effects of circular RNA (circRNA) in osteoarthritis (OA) and so on; however, its mechanisms remain to be further explored. Studies have shown that tumor necrosis factor-alpha can inhibit hsa_circ_0045714 expression in chondrocytes so as to upregulate miR-193b expression. Dual-luciferase reporter assay showed that insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) is a key target gene of miR-193b. Hsa_circ_0045714 over-expression does not influence miR-193b expression, but can inhibit its transcriptional activity, thereby upregulating IGF1R expression. Hsa_circ_0045714 can promote the expression of type II collagen and aggrecan, and upregulate chondrocyte proliferation, while its linear sequences cannot. IGF1R has similar function, while miR-193b can inhibit the expression of type II collagen and aggrecan, and downregulate chondrocyte proliferation but enhance their apoptosis. IGF1R overexpression can reverse the effect of miR-193b, while miR-193b mimics or IGF1R siRNA can inhibit the function of hsa_circ_0045714. Therefore, hsa_circ_0045714 can regulate extracellular matrix synthesis as well as proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. The findings will provide new proofs for studies on the applications of circRNA in OA and other orthopedic diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association CO. Diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2010;2:1–6.
Xia B, Chen D, Zhang J, Hu S, Jin H, Tong P. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: a review of molecular mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;95:495–505.
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 2016;2016:1–11.
Cortés-López M, Miura P. Emerging functions of circular RNAs. Yale J Biol Med. 2016;89:527–37.
Dou C, Cao Z, Yang B, et al. Changing expression profiles of lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs during osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21499.
Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Circular RNA related to the chondrocyte ECM regulates MMP13 expression by functioning as a MiR-136 ‘sponge’ in human cartilage degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572.
Thomas LF, Sætrom P. Circular RNAs are depleted of polymorphisms at microRNA binding sites. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:2243–6.
Cong L, Zhu Y, Tu G. A bioinformatic analysis of microRNAs role in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2017;25(8):1362–71. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2017.03.012.
Ukai T, Sato M, Akutsu H, Umezawa A, Mochida J. MicroRNA-199a-3p, microRNA-193b, and microRNA-320c are correlated to aging and regulate human cartilage metabolism. J Orthop Res. 2012;30:1915–22.
Zhang Y, Moerkens M, Ramaiahgari S, et al. Elevated insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling induces antiestrogen resistance through the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling routes. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:R52.
Zhang M, Zhou Q, Liang QQ, et al. IGF-1 regulation of type II collagen and MMP-13 expression in rat endplate chondrocytes via distinct signaling pathways. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2009;17:100–6.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–8.
Wang Y, Cheng Z, Elalieh HZ, et al. IGF-1R signaling in chondrocytes modulates growth plate development by interacting with the PTHrP/Ihh pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:1437–46.
Hou C, Yang Z, Kang Y, et al. MiR-193b regulates early chondrogenesis by inhibiting the TGF-beta2 signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2015;589:1040–7.
Takada Y, Takada YK, Fujita M. Crosstalk between insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor and integrins through direct integrin binding to IGF1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;34:67–72.
Hu W, Zhang W, Li F, Guo F, Chen A. miR-139 is up-regulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte proliferation and migration possibly via suppressing EIF4G2 and IGF1R. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474:296–302.
Suh HS, Zhao ML, Derico L, Choi N, Lee SC. Insulin-like growth factor 1 and 2 (IGF1, IGF2) expression in human microglia: differential regulation by inflammatory mediators. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10:37.
Martel-Pelletier J, Di Battista JA, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JP. IGF/IGFBP axis in cartilage and bone in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Inflamm Res. 1998;47:90–100.
Higgins TF, Johnson BD. Effect of exogenous IGF-1 on chondrocyte apoptosis in a rabbit intraarticular osteotomy model. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:125–30.
Doré S, Abribat T, Rousseau N, et al. Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production by human osteoarthritic chondrocytes is not dependent on growth hormone action. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:413–9.
Wang L, Shao YY, Ballock RT. Thyroid hormone-mediated growth and differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes involves IGF-1 modulation of beta-catenin signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25:1138–46.
Gagarina V, Gabay O, Dvir-Ginzberg M, et al. SirT1 enhances survival of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes by repressing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and activating the insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1383–92.
Loeser RF, Shanker G. Autocrine stimulation by insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor 2 mediates chondrocyte survival in vitro. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1552–9.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No.: 2015A030313611).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Bf., Zhang, Y., Xiao, J. et al. Hsa_circ_0045714 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. Human Cell 30, 311–318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0177-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0177-7