Abstract
Objective
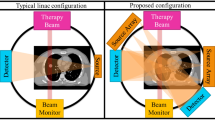
Radionuclides with various types of radiation are frequently used for brachytherapy. For example, iridium-192 (192Ir) has been widely used as high-dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy source, housed in a remote after-loading unit. With its average energy of 380 keV, the photons emitted from 192Ir are generally considered unsuitable for usage as transmission-based external imaging sources. Using Monte Carlo simulations, we have previously showed that 192Ir indeed can be used as an external source to image the breast in the forms of fan-beam computed tomography (FBCT) and cone-beam computer tomography (CBCT). In this study, we designed and built an imaging assembly in a physical laboratory setting to prove and validate this new imaging method. The goal of this study is to demonstrate the feasibility of building a robust dual-function platform that can carry out both image-guided target localization and radiation treatment through a single HDR source.
Methods
In this study, a microSelectron HDR 192Ir source was used as the external imaging source and the amorphous-silicon imaging panel on a Simulix Evolution™ radiotherapy simulator as the imaging detector. A breast phantom with cystic lesions was situated on a custom-made rotary stage whose center was aligned along the pathway between the radiation source and the center of the imaging panel. Plain radiographic images were obtained at every 3° intervals from 0° to 360° around the center of the rotary stage. The CBCT images were subsequently reconstructed.
Results
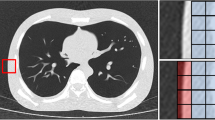
A 3D data set of 192Ir CBCT images was reconstructed. Compared with the images obtained from a conventional thin-slice CT scanner, the cystic lesions inside the breast phantom can be clearly identified. Despite multiple sources of scattering and resultant noise, the quality of images demonstrated sufficient clarity for the purpose of target localization.
Conclusion
The 192Ir radionuclide can be used as a possible external radiation source for breast imaging. This study provides the evidence that building a new imaging/therapy dual-function platform using a single 192Ir source is feasible.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A, Kramer JL, Smith RA, Jemal A (2016) Breast cancer statistics, 2015: convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):31–42
Hamid S, Rocchio K, Arthur D, Vera R, Sha S, Jolly M, Cavanaugh S, Wooten E, Benda R, Greenfield B, Prestidge B (2012) A multi-institutional study of feasibility, implementation, and early clinical results with noninvasive breast brachytherapy for tumor bed boost. Int J Radiat Oncol 83(5):1374–1380
Fang J, Wu X, Yang Y, Zhao W (2016) A new imaging/therapy platform by using external radionuclide (192Ir), part 1: Monte Carlo FBCT and CBCT simulation for breast imaging. J Radiat Oncol. doi:10.1007/s13566-016-0252-9
Dawson LA, Jaffray DA (2007) Advances in image-guided radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol 25(8):938–946
Davis SD, Parker W, Evans MD (2013) Using mean dose rate to compare relative dosimetric efficiency with respect to source type and source change schedules for HDR brachytherapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 14(6). doi:10.1120/jacmp.v14i6.4239
Pérez-Calatayud J, Granero D, Ballester F, Puchades V, Casal E, Soriano A, Crispín V (2005) A dosimetric study of Leipzig applicators. Int J Radiat Oncol 62(2):579–584
Reniers B, Verhaegen F (2011) Technical note: cone beam CT imaging for 3D image guided brachytherapy for gynecological HDR brachytherapy. Med Phys 38(5):2762–2767
Sinha A, Singh N, Gurjar OP, Bagdare P (2015) Acceptance testing and quality assurance of Simulix Evolution radiotherapy simulator. Radiat Prot Environ 38(3):102–108
Hsieh J (2003) Computed tomography: principles, design, artifacts, and recent advances. SPIE Press, Bellingham
The MathWorks, Inc. (2016) Wiener2, 2-D adaptive noise-removal filtering. The MathWorks, Inc. http://www.mathworks.com/help/images/ref/wiener2.html. Accessed 28 April 2016
Feldkamp LA, Davis LC, Kress JW (1984) Practical cone-beam algorithm. JOSA A 1(6):612–619
Lee SW, Lee CL, Cho HM, Park HS, Kim DH, Choi YN, Kim HJ (2011) Effects of reconstruction parameters on image noise and spatial resolution in cone-beam computed tomography. J Korean Phys Soc 59(4):2825–2832
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Innovative Cancer Institute, South Miami, FL, for making its CT scanner available for the study and to the Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL, for the use of its HDR and simulator facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding support is associated with this study.
Conflict of Interest
Jian Fang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xiaodong Wu declares that he has filed a US patent application for the design of this study under the names of Xiaodong Wu and Beatriz Amendola. Yidong Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Charles Shang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jeremy Cole declares that he has no conflict of interest. Weizhao Zhao declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Wu, X., Yang, Y. et al. A new imaging/therapy platform by using external radionuclide (192Ir) part 2: data acquisition and analysis for breast imaging. J Radiat Oncol 5, 317–322 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-016-0265-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-016-0265-4