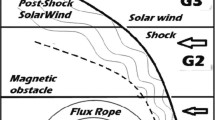
Abstract
We derive fast forward interplanetary (IP) shock speeds and impact angles to study the geoeffectiveness of 461 IP shocks that occurred from January 1995 to December 2013 using ACE and Wind spacecraft data. The geomagnetic activity is inferred from the SuperMAG project data. SuperMAG is a large chain which employs more than 300 ground stations to compute enhanced versions of the traditional geomagnetic indices. The SuperMAG auroral electroject SME index, an enhanced version of the traditional AE index, is used as an auroral power (AP) indicator. AP intensity jumps triggered by shock impacts are correlated with both shock speed and impact angle. It is found that high AP intensity events typically occur when high speed IP shocks impact the Earth’s magnetosphere with the shock normal almost parallel to the Sun-Earth line. This result suggests that symmetric and strong magnetospheric compression leads to favorable conditions for intense auroral power release, as shown previously by simulations and observations. Some potential mechanisms will be discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
B Abraham-Shrauner, Determination of magne-tohydronamic shock normals, J. Geophys. Res. 77(4), 736–739 (1972). doi:10.1029/JA077i004p00736
B. Abraham-Shrauner, S. H. Yun, Inter-planetary shocks seen by Ames Plasma Probe on Pi-oneer 6 and 7, J. Geophys. Res. 81(13), (1976). doi:10.1029/JA081i013p02097
S.-I. Akasofu, J. Chao, Interplanetary shock waves and magnetospheric substorms. Planet. Space Sci. 28(4), 381–385 (1980). doi:10.1016/0032-0633(80)90042-2
L. Bolduc, GIC observations and studies in the Hydro-Québec power system. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 64(16), 1793–1802 (2002). doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00128-1
D.S. Colburn, C.P. Sonett, Discontinuities in the solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 439(A11), 506 (1966). doi:10.1007/BF00240575
J.D. Craven, L.A. Frank, C.T. Russell, E.E. Smith, R.P. Lepping, Global auroral responses to magnetospheric compressions by shocks in the solar wind: two case studies, in Solar Wind-Magnetosphere Coupling, ed. by Y. Kamide, J.A. Slavin (Terra Scientific, Tokyo, Japan, 1986), pp. 367–380
T.N. Davis, M. Sugiura, Auroral elec-trojet activity index AE and its universal time variations. J. Geophys. Res. 71(3), 785–801 (1966). doi:10.1029/JZ071i003p00785
E. Echer, W.D. Gonzalez, L.E.A. Vieira, A.D.L.F.L. Guarnieri, A. Prestes, A.L.C. Gonzalez, N.J. Schuch, Interplanetary shock parameters during solar activity maximum (2000) and minimum (1995-1996). Braz. J. Phys. 33(1), 2301 (2003). doi:10.1590/S0103-97332003000100010
E. Echer, B. Tsurutani, F. Guarnieri, J. Kozyra, Interplanetary fast forward shocks and their geomagnetic effects: CAWSES events. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 73(11-12), 1330–1338 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.09.020
I.A. Erinmez, J.G. Kappenman, W.A. Radasky, Management of the geomagnetically induced current risks on the national grid company’s electric power transmission system. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 63(5–6), 743–756 (2002). doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00036-6
J.W. Gjerloev, A global ground-based magneto-meter initiative. Eos Trans. AGU 90(27), 230–231 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009EO270002
J. W. Gjerloev, The SuperMAG data processing technique, J. Geophys. Res. 117(A09213), 1–19 (2012). doi:10.1029/2012JA017683
W.D. Gonzalez, B.T. Tsurutani, A.L. Clúade Gonzalez, Interplanetary origin of geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 88(3-4), 529–562 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1005160129098
R.A. Gummow, P. Eng, GIC effects on pipeline corrosion and corrosion control systems. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 64(16), 1755–1764 (2002). doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00125-6
X.-C. Guo, Y.-Q. Hu, C. Wang, Earth’s magnetosphere impinged by interplanetary shocks of different orientations. Chin. Phys. Lett. 22(12), 3221–3224 (2005). doi:10.1088/0256-307X/22/12/067
A.J. Halford, S.L. McGregor, K.R. Murphy, R.M. Millan, M.K. Hudson, L.A. Woodger, C.A. Cattel, A.W. Breneman, I.R. Mann, W.S. Kurth, G.B. Hospodarsky, M. Gkioulidou, J.F. Fennell, BARREL observations of an ICME-shock impact with the magnetosphere and the resultant radiation belt electron loss. J. Geophys. Res. 120(4), 2557–2570 (2015). doi:10.1002/2014JA020873
J. Kappenman, Geomagnetic storms and their impacts on the US power grid, Tech. rep (Metatech Corp, Goleta, 2010)
K. Kawasaki, S.-I. Akasofu, F. Yasuhara, C.-I. Meng, Storm sudden commencements and polar magnetic substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 6781–6789 (1971). doi:10.1029/JA076i028p06781
S. Kokubun, R.L. McPherron, C.T. Russell, Triggering of substorms by solar wind discontinuities. J. Geophys. Res. 82(1), 74–86 (1977). doi:10.1029/JA082i001p00074
K. Liou, P. T. Newell, C.-I. Meng, C.-C. Wu, R. P. Lepping, Investigation of external triggering of substorms with Polar ultraviolet imager observations, J. Geophys. Res. 108(A10), (2003). doi:10.1029/2003JA009984
J.-J. Liu, H.-Q. Hu, D.-S. Han, Z.-Y. Xing, Z.-J. Hu, D.-H. Huang, H.-G. Yang, Response of nightside aurora to interplanetary shock from ground optical observation. Chin. J. Geophys 56(5), 598–611 (2013). doi:10.1002/cjg2.20056
A.T.Y. Lui, R.E. Lopez, S.M. Krimigis, R.W. McEntire, L.J. Zanetti, T.A. Potemra, A case study of magnetotail current sheet disruption and diversion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 15(7), 721–724 (1988). doi:10.1029/GL015i007p00721
A.T.Y. Lui, A. Mankofsky, C.-L. Chang, K. Papadopoulos, C.S. Wu, A current disruption mechanism in the neutral sheet: a possible trigger for substorm expansions. J. Geophys. Res. 17(6), 745–748 (1990). doi:10.1029/GL017i006p00745
L.R. Lyons, A new theory for magnetospheric substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 100(A10), 19,069–19,081 (1995). doi:10.1029/95JA01344
L.R. Lyons, Substorms: fundamental observational features, distinction from other disturbances, and external triggering. J. Geophys. Res. 101(A6), 13,011–13,025 (1996). doi:10.1029/95JA01987
P.T. Newell, G. W. Gjerloev, SuperMAG-based partial ring current indices. J. Geophys. Res. 117(A05215), 1–19 (2012). doi:10.1029/2012JA017586
P. T. Newell, J. W. Gjerloev, Evaluation of SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices as indicators of substorms and auroral power. J. Geophys. Res. 116(A12211), 1–12 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011JA016779
P. T. Newell, J. W. Gjerloev, Substorm and magnetosphere characteristic scales inferred from the SuperMAG auroral electrojet indices, J. Geophys. Res. 116(A12211), 1–12 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011JA016936
P.T. Newell, J.W. Gjerloev, Local geomagnetic indices and the prediction of auroral power. J. Geophys. Res. 119(12), 9790–9803 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014JA020524
S.Y. Oh, Y. Yi, Y.H. Kim, Solar cycle variation of the interplanetary forward shock drivers observed at 1 AU. Sol. Phys. 245(2), 391–410 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11207-007-9042-2
D. M. Oliveira, A study of interplanetary shock geoeffectiveness controlled by impact angles using simulations and observations, Ph.D. thesis, University of New Hampshire (2015)
D.M. Oliveira, J. Raeder, Impact angle control of interplanetary shock geoeffectiveness. J. Geophys. Res. 119(10), 8188–8201 (2014). doi:10.1002/2014JA020275
D.M. Oliveira, J. Raeder, Impact angle control of interplanetary shock geoeffectiveness: a statistical study. J. Geophys. Res. 120(6), 4313–4323 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015JA021147
K. Papadopoulos, The role of microturbulence on collisionless reconnection, in Dynamics of the Magnetosphere, ed. by S.-I. Akasofu, Astrophysics and Space Science Library 78, (Springer Netherlands, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979), pp. 289-309, doi:10.1007/978-94-009-9519-214
V.J. Pizzo, The evolution of corotating stream fronts near the ecliptic plane in the inner solar system: 2.Three-dimensional tilted-dipole fronts. J. Geophys. Res. 96(A4), 5405–5420 (1991). doi:10.1029/91JA00155
J. Raeder. Global Magnetohydrodynamics: a Tutorial Review, in Space Plasma Simulation, ed. by J. Buchner, C. T. Dum, and M. Scholer, (Springer Verlag, Berlin Heilderberg, New York, 2003), pp. 1–20. doi:10.1007/3-540-36530-311
A.K. Richter, K.C. Hsieh, A.H. Luttrell, E. Marsch, R. Schwenn, Review of interplanetary shock phenomena near and within 1 AU, in Collisionless Shocks in the Heliosphere: Reviews of Current Research, in Geophys. Monogr. Ser. 35, ed. by B.T. Tsurutani, R.G. Stone (American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., 1985), pp. 33–50. doi:10.1029/GM035p0033
A.A. Samsonov, Numerical MHD modeling of the Earth’s magnetosheath for different IMF orientations. Adv. Space Res. 36, 1652–1656 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.031
A. A. Samsonov, Propagation of inclined inter-planetary shock through the magnetosheath, J. Atmos.Sol. Terr. Phys. 73, 1–9 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.031
A. A. Samsonov, D. G. Sibeck, J. Imber, MHD simulation for the interaction of an interplanetary shock with the Earth’s magnetosphere, J. Geophys. Res. 112(A12220), 1–9 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JA012627
A.A. Samsonov, V.A. Sergeev, M.M. Kuznetsova, D.G. Sibeck, Asymmetric magnetospheric compressions and expansions in response to impact of inclined interplanetary shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42(12), 4716–4722 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL064294
J. Schieldge, G. Siscoe, A correlation of the occurrence of simultaneous sudden magnetospheric compressions and geomagnetic bay onsets with selected geophysical indices. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 32(11), 1819–1830 (1970). doi:10.1016/0021-9169(70)90139-X
C.J. Schrijver, R. Dobbins, W. Murtagh, S.M. Petrinec, Assessing the impact of space weather on the electric power grid based on insurance claims for industrial electrical equipment. Space Weather (2014). doi:10.1002/2014SW001066
G.L. Siscoe, Three-dimensional aspects of interplanetary shock waves. J. Geophys. Res. 81(34), 6235–6241 (1976). doi:10.1029/JA081i034p06235
E.J. Smith, J.A. Slavin, R.D. Zwickl, S.J. Bame, Shocks and storm sudden commencements, in Solar Wind and Magnetosphere Coupling, ed. by Y. Kamide, J.A. Slavin (Terra Scientific, Tokyo, 1986), p. 345
T. Takeuchi, C.T. Russell, T. Araki, Effect of the orientation of interplanetary shock on the geomagnetic sudden commencement. J. Geophys. Res. 107(A12), 1423 (2002). doi:10.1029/2002JA009597
B. Tsurutani, G. Lakhina, O. Verkhoglyadova, W. Gonzalez, E. Echer, F. Guarnieri, A review of interplanetary discontinuities and their geomagnetic effects. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 73(1), 5–19 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.04.001
B. T. Tsurutani, X. Y. Zhou, Interplane-tary shock triggering of substorms: Wind and Polar, Adv. Space Res. 31(4), 1063–1067 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00796-2
C. Wang, Z. H. Huang, Y. Q. Hu, X. C. Guo, 3D global simulation of the interaction of interplanetary shocks with the magnetosphere, in 4th Annual IGPP In-ternational Astrophysics Conference on the Physics of Collisionless Shocks, edited by G. Li, G. Zank, and C. T. Russell, (AIP Conference Proceedings, Am. Inst. of Phys., Washington, D.C., 2005) pp. 320-324. doi:10.1063/1.2032716
C. Wang, C. X. Li, Z. H. Huang, J. D. Richardson, Effect of interplanetary shock strengths and orientations on storm sudden commencement rise times, Geophys. Res. Lett. 33(L14104), 1–3 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006GL025966
C. Yue, Q. G. Zong, H. Zhang, Y. F. Wang, C. J. Yuan, Z. Y. Pu, S. Y. Fu, A. T. Y. Lui, B. Yang, C. R. Wang, Geomagnetic activity triggered by interplanetary shocks, J. Geophys. Res. 115(A00I05), 1–13 (2010). doi:10.1029/2010JA015356
X. Zhou, B.T. Tsurutani, Interplanetary shock triggering of nightside geomagnetic activity: substorms, pseudobreakups, and quiescent events. J. Geophys. Res. 106(A9), 18,957–18,967 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000JA003028
X.-Y. Zhou, B.T. Tsurutani, Rapid intensification and propagation of the dayside aurora: large scale interplanetary pressure pulses (fast shocks). Geophys. Res. Lett. 26(8), 1097–1100 (1999). doi:10.1029/1999GL900173
Q.-G. Zong, X.-Z. Zhou, Y. F. Wang, X. Li, P. Song, D. N. Baker, T. A. Fritz, P. W. Daly, M. Dunlop, A. Pedersen, Energetic electron response to ULF waves induced by interplanetary shocks in the outer radiation belt, J. Geophys. Res. 114(A10204), 1–11 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009JA014393
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant AGS-1143895 from the National Science Foundation and grant FA-9550-120264 from the Air Force Office of Sponsored Research. We thank the Wind and ACE teams for the solar wind data and CDAWeb interface for data availability. We thank Dr. C. W. Smith, the ACE team, and Dr. J. C. Kasper for their list compilations. For the ground magnetometer data, we gratefully acknowledge: Intermagnet; USGS, Jeffrey J. Love; CARISMA, PI Ian Mann; CANMOS; The S-RAMP Database, PI K. Yumoto and Dr. K. Shiokawa; The SPIDR database; AARI, PI Oleg Troshichev; The MACCS program, PI M. Engebretson, Geomagnetism Unit of the Geological Survey of Canada; GIMA; MEASURE, UCLA IGPP and Florida Institute of Technology; SAMBA, PI Eftyhia Zesta; 210 Chain, PI K. Yumoto; SAMNET, PI Farideh Honary; The institutes who maintain the IMAGE magnetometer array, PI Eija Tanskanen; PENGUIN; AUTUMN, PI Martin Conners; DTU Space, PI Dr. J¨urgen Matzka; South Pole and McMurdo Magnetometer, PI’s Louis J. Lanzarotti and Alan T. Weatherwax; ICESTAR; RAPIDMAG; PENGUIn; British Artarctic Survey; McMac, PI Dr. Peter Chi; BGS, PI Dr. Susan Macmillan; Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radio Wave Propagation (IZMIRAN); GFZ, PI Dr. J¨urgen Matzka; MFGI, PI B. Heilig; IGFPAS, PI J. Reda; University of L’Aquila, PI M. Vellante; SuperMAG, PI Jesper W. Gjerloev. D.M.O. thanks the SuperMAG PI J. W. Gjerloev for the straightforward SuperMAG website for its convenience of data visualization and download.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, D.M., Raeder, J., Tsurutani, B.T. et al. Effects of Interplanetary Shock Inclinations on Nightside Auroral Power Intensity. Braz J Phys 46, 97–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-015-0389-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-015-0389-9