Abstract
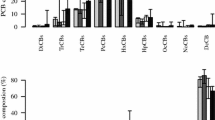
Information on human exposure to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL-PCBs) via dust ingestion is scarce. Concentrations of PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs were determined in house dust collected from Korea, to investigate the occurrence and human exposure to these contaminants. The concentrations of total toxic equivalents (TEQs) in our samples ranged from 0.22 to 11.6 (median: 1.73) pg TEQ/g dry weight, which were lower than those found in other countries. The predominant homologue or congener was octachlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and furan (OCDD/F) in all the samples, suggesting a possibility of multiple sources (e.g. combustion process, textiles and cigarette smoke) of PCDD/Fs in indoor environments. Estimated daily intakes (EDIs) of total TEQs via dust ingestion were 0.056 pg TEQ/day for adults (>20 years) and 0.14 pg TEQ/day for toddlers (<2 years), which were 2–3 orders of magnitude lower than the EDIs of total TEQs via seafood consumption. Our results suggest that dust ingestion could be negligible to the total TEQ exposures for the Korean population. This is the first study on human exposure of PCDD/Fs and DL-PCBs via dust ingestion in the Korean population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng, G. J., Leung, A. O. W., Jiao, L. P. & Wong, M. H. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans pollution in China: Sources, environmental levels and potential human health impacts. Environ. Int. 34, 1050–1061 (2008).
Erikson, M. D. & Kaley II, R. G. Applications of polychlorinated biphenyls. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 18, 135–151 (2011).
Baccarelli, A. et al. Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-dependent pathway and toxic effects of TCDD in humans: A population-based study in Seveso, Italy. Toxicol. Let. 149, 287–293 (2004).
Schecter, A., Birnbaum, L., Ryan, J. J. & Constable, J. D. Dioxins: An overview. Environ. Res. 101, 419–428 (2006).
Wang, L. et al. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and their association with cancer mortality among workers in one automobile foundry factory. Sci. Total Environ. 443, 104–111 (2013).
Fromme, H. et al. Intake and body burden of dioxinlike compounds in Germany: The INES Study. Chemosphere 76, 1457–1463 (2009).
Windal, I. et al. Dietary intake of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs of the Belgian population. Chemosphere 79, 334–340 (2010).
Arisawa, K. et al. Dietary patterns and blood levels of PCDDs, PCDFs, and dioxin-like PCBs in 1656 Japanese individuals. Chemosphere 82, 656–662 (2011).
Sirot, V. et al. Dietary exposure to polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans and polychlorinated biphenyls of the French population: Results of the Second French Total Diet Study. Chemosphere 88, 492–500 (2012).
Zhang, L. et al. Dietary intake of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs from the Chinese diet study in 2007. Chemosphere 90, 1625–1630 (2013).
Domingo, J. L. & Bocio, A. Levels of PCDD/PCDF and PCBs in edible marine species and human intake: A literature review. Environ. Int. 33, 397–405 (2007).
Moon, H.-B. & Choi, H.-G. Human exposure to PCDDs, PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs associated with seafood consumption in Korea from 2005 to 2007. Environ. Int. 35, 279–284 (2009).
Law, R. J. et al. Levels and trends of HBCD and BDEs in the European and Asian environments, with some information for other BFRs. Chemosphere 73, 223–241 (2008).
Harrad, S. & Abdallah, M. A. E. Brominated flame retardants in dust from UK cars-Within-vehicle spatial variability, evidence for degradation and exposure implications. Chemosphere 82, 1240–1245 (2011).
Lee, S., Kannan, K. & Moon, H.-B. Assessment of exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) via seafood consumption and dust ingestion in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 443, 24–30 (2013).
Deziel, N. C. et al. Determinants of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in house dust samples from four areas of the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 433, 516–522 (2012).
Paustenbach, D. J. & Kerger, B. D. The University of Michigan dioxin exposure study: Estimating residential soil and house dust exposures to young children. Chemosphere 91, 200–204 (2013).
Ma, J. et al. Concentrations, profiles, and estimated human exposures for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from electronic waste recycling facilities and a chemical industrial complex in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 8252–8259 (2008).
Tue, N. M. et al. Evaluation of dioxin-like activities in settled house dust from Vietnamese e-waste recycling sites: Relevance of polychlorinated/brominated dibenzo-p-dioxin/furans and dioxin-like PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 9195–9200 (2010).
Leung, A. O. W. et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in surface dust at an e-waste processing site in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 5775–5782 (2011).
Kang, Y., Cheung, K. C., Cai, Z. W. & Wong, M. H. Chemical and bioanalytical characterization of dioxins in indoor dust in Hong Kong. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 74, 947–952 (2011).
Moon, H.-B., Yoon, S.-P., Jung, R.-H. & Choi, M. Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) as a source of sediment contamination by toxic organic contaminants and fecal sterols in a semi-enclosed bay in Korea. Chemosphere 73, 880–889 (2008).
Moon, H.-B., Choi, H.-G., Lee, P.-Y. & Ok, G. Congenerspecific characterization and sources of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediments from industrialized bays of Korea. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27, 323–333 (2008).
Van den Berg, M. et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 93, 223–241 (2006).
Jones-Otazo, H. A. et al. Is house dust the missing exposure pathway for PBDEs? An analysis of the urban fate and human exposure to PBDEs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 5121–5130 (2005).
Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW). in Report on 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey(MOHW, Seoul, Korea, 2002). (in Korean)
Takigami, H., Suzuki, G., Hirai, Y. & Sakai, S.-I. Brominated flame retardants and other polyhalogenated compounds in indoor air and dust from two houses in Japan. Chemosphere 76, 270–277 (2009).
Saito, K. et al. Extraction and cleanup methods of dioxins in house dust from two cities in Japan using accelerated solvent extraction and a disposable multi-layer silica gel catridge. Chemosphere 53, 137–142 (2003).
Suzuki, G. et al. Dioxin-like activity in Japanese indoor dusts evaluated by means of in vitro bioassay and instrumental analysis: Brominated dibenzofurans are an important contributor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 8330–8336 (2010).
Ma, J. et al. Polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil, vegetation, workshop-floor dust, and electronic shredder residue from an electronic waste recycling facility and in soils from a chemical industrial complex in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 7350–7356 (2009).
Moon, H.-B., Choi, M., Choi, H.-G. & Kannan, K. Severe pollution of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in sediments from Lake Shihwa, Korea: Tracking the source. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 64, 2357–2363 (2012).
Lu, Y. et al. Occurrence of synthetic musks in indoor dust from China and implication for human exposure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 60, 182–189 (2011).
Moon, H.-B. et al. Concentrations and accumulation features of PCDDs, PCDFs and dioxin-like PCBs in cetaceans from Korean coastal waters. Chemosphere 79, 733–739 (2010).
Van Leeuwen, F. X. R. & Younes, M. M. Assessment of the health risk of dioxins: re-evaluation of the tolerable daily intake (TDI). Food Addit. Contam. 17, 223–240 (2000).
Scientific Committee on Food (SCF). in Opinion of the scientific committee on food on the risk assessment of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs in food (SCF, Brussels, Belgium, 2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Moon, HB. Occurrence and human exposure of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in house dust from Busan, Korea: Comparison with seafood consumption. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 5, 155–162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-013-0169-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-013-0169-2