Abstract
Purpose
Upregulation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 has been found to be associated with a poor prognosis in many types of cancer and is considered an attractive therapeutic target. As yet, few efforts have been focused on its tumor suppressive activity triggered by its ligand, ephrinA1. Here, we aimed to determine the potential of ephrinA1 as an important player in melanoma metastasis.
Methods
Data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) were analyzed to explore the expression and prognostic implications of EphA2 and ephrinA1 in melanoma. Western blotting, shRNA, colony formation and immunofluorescence assays, as well as two in vivo xenograft models (subcutaneous and metastatic) were used to evaluate the role of EphA2 in melanoma progression. Akt inhibition and ephrinA1-Fc were used to confirm the influence of Akt activation and ephrinA1 levels on the EphA2 effects. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on xenograft and patient melanoma tissues.
Results
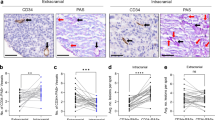
We found that high levels of ephrinA1, but not EphA2, were negatively correlated with melanoma metastasis. The expression levels of EphA2 and ephrinA1 were not correlated. After EphA2 downregulation, colony forming abilities and lung metastatic growth were reduced in melanoma cell lines with a low ephrinA1 expression, but were increased in melanoma cell lines with a high ephrinA1 expression. EphA2-mediated colony formation in EphA2-high/ephrinA1-low cells was found to be Akt-dependent and to be inhibited by the addition of ephrinA1-Fc. IHC staining of primary melanoma specimens revealed that EphA2-high/ephrinA1-low patients exhibited poorer outcomes than EphA2-high/ephrinA1-high patients.
Conclusions
From our data we conclude that evaluation of ephrinA1 levels may be helpful for the application of EphA2-targeted therapies and for prognostic predictions in melanoma patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. Balch, S.J. Soong, M.B. Atkins, A.C. Buzaid, N. Cascinelli, D.G. Coit, I.D. Fleming, J.E. Gershenwald, A. Houghton Jr., J.M. Kirkwood, K.M. McMasters, M.F. Mihm, D.L. Morton, D.S. Reintgen, M.I. Ross, A. Sober, J.A. Thompson, J.F. Thompson, An evidence-based staging system for cutaneous melanoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 54(3), 131–149 (2004) quiz 182 – 134
S.P. Leong, J.E. Gershenwald, S.J. Soong, D. Schadendorf, A.A. Tarhini, S. Agarwala, A. Hauschild, C.W. Soon, A. Daud, M. Kashani-Sabet, Cutaneous melanoma: a model to study cancer metastasis. J Surg Oncol 103(6), 538–549; (2011)
E.B. Pasquale, Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 133(1), 38–52 (2008)
T.T. Ma, L. Wang, J.L. Wang, Y.J. Liu, Y.C. Chen, H.J. He, Y. Song, Hypoxia-Induced cleavage of soluble ephrinA1 from cancer cells is mediated by MMP-2 and associates with angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. OncoTargets Therapy 12, 8491–8499 (2019)
D. Udayakumar, G. Zhang, Z. Ji, C.N. Njauw, P. Mroz, H. Tsao, EphA2 is a critical oncogene in melanoma. Oncogene 30(50), 4921–4929 (2011)
E.B. Pasquale, Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 10(3), 165–180 (2010)
M. Nakamoto, A.D. Bergemann, Diverse roles for the Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases in carcinogenesis. Microsc. Res. Tech. 59(1), 58–67 (2002)
C.W. Menges, D.J. McCance, Constitutive activation of the Raf-MAPK pathway causes negative feedback inhibition of Ras-PI3K-AKT and cellular arrest through the EphA2 receptor. Oncogene 27(20), 2934–2940 (2008)
H. Miao, D.Q. Li, A. Mukherjee, H. Guo, A. Petty, J. Cutter, J.P. Basilion, J. Sedor, J. Wu, D. Danielpour, A.E. Sloan, M.L. Cohen, B. Wang, EphA2 mediates ligand-dependent inhibition and ligand-independent promotion of cell migration and invasion via a reciprocal regulatory loop with Akt. Cancer Cell 16(1), 9–20 (2009)
A. Barquilla, E.B. Pasquale, Eph receptors and ephrins: therapeutic opportunities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 55, 465–487 (2015)
H. Miao, E. Burnett, M. Kinch, E. Simon, B. Wang, Activation of EphA2 kinase suppresses integrin function and causes focal-adhesion-kinase dephosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2(2), 62–69 (2000)
Zhou Y., Yamada N., Tanaka T., Hori T., Yokoyama S., Hayakawa Y., Yano S., Fukuoka J., Koizumi K., Saiki I., Sakurai H. Crucial roles of RSK in cell motility by catalysing serine phosphorylation of EphA2. Nat. Commun. 6:7679 (2015)
H. Guo, H. Miao, L. Gerber, J. Singh, M.F. Denning, A.C. Gilliam, B. Wang, Disruption of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase leads to increased susceptibility to carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Cancer Res. 66(14), 7050–7058 (2006)
B. Miao, Z. Ji, L. Tan, M. Taylor, J. Zhang, H.G. Choi, D.T. Frederick, R. Kumar, J.A. Wargo, K.T. Flaherty, N.S. Gray, H. Tsao, EPHA2 is a mediator of vemurafenib resistance and a novel therapeutic target in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 5(3), 274–287 (2015)
G. Zhuang, D.M. Brantley-Sieders, D. Vaught, J. Yu, L. Xie, S. Wells, D. Jackson, R. Muraoka-Cook, C. Arteaga, J. Chen, Elevation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy. Cancer Res. 70(1), 299–308 (2010)
K.R. Amato, S. Wang, L. Tan, A.K. Hastings, W. Song, C.M. Lovly, C.B. Meador, F. Ye, P. Lu, J.M. Balko, D.C. Colvin, J.M. Cates, W. Pao, N.S. Gray, J. Chen, EPHA2 Blockade Overcomes Acquired Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 76(2), 305–318 (2016)
D. Vaught, J. Chen, D.M. Brantley-Sieders, Regulation of mammary gland branching morphogenesis by EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Biol. Cell 20(10), 2572–2581 (2009)
D.P. Zelinski, N.D. Zantek, J.C. Stewart, A.R. Irizarry, M.S. Kinch, EphA2 overexpression causes tumorigenesis of mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 61(5), 2301–2306 (2001)
W. Song, Y. Hwang, V.M. Youngblood, R.S. Cook, J.M. Balko, J. Chen, D.M. Brantley-Sieders, Targeting EphA2 impairs cell cycle progression and growth of basal-like/triple-negative breast cancers. Oncogene 36(40), 5620–5630 (2017)
J. Mo, B. Sun, X. Zhao, Q. Gu, X. Dong, Z. Liu, Y. Ma, N. Zhao, Y. Liu, J. Chi, R. Sun, The in-vitro spheroid culture induces a more highly differentiated but tumorigenic population from melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res. 23(4), 254–263 (2013)
L. Deng, J. Sun, X. Chen, L. Liu, D. Wu, Nek2 augments sorafenib resistance by regulating the ubiquitination and localization of beta-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.: CR 38(1), 316 (2019)
T. Schatton, G.F. Murphy, N.Y. Frank, K. Yamaura, A.M. Waaga-Gasser, M. Gasser, Q. Zhan, S. Jordan, L.M. Duncan, C. Weishaupt, R.C. Fuhlbrigge, T.S. Kupper, M.H. Sayegh, M.H. Frank, Identification of cells initiating human melanomas. Nature 451(7176), 345–349 (2008)
L. Li, J. Chen, J. Wang, D. Cai, Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with overweight/obese in Guangdong province, China. Primary care diabetes 9(3), 191–195 (2015)
A. Kassambara, C. Gourzones-Dmitriev, S. Sahota, T. Reme, J. Moreaux, H. Goldschmidt, A. Constantinou, P. Pasero, D. Hose, B. Klein, A DNA repair pathway score predicts survival in human multiple myeloma: the potential for therapeutic strategy. Oncotarget 5(9), 2487–2498 (2014)
M. Macrae, R.M. Neve, P. Rodriguez-Viciana, C. Haqq, J. Yeh, C.R. Chen, J.W. Gray, F. McCormick, A conditional feedback loop regulates Ras activity through EphA2. Cancer Cell 8(2), 111–118 (2005)
O. Straume, L.A. Akslen, Importance of vascular phenotype by basic fibroblast growth factor, and influence of the angiogenic factors basic fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 and ephrin-A1/EphA2 on melanoma progression. Am. J. Pathol. 160(3), 1009–1019 (2002)
E. Wiedemann, S. Jellinghaus, G. Ende, A. Augstein, R. Sczech, B. Wielockx, S. Weinert, R.H. Strasser, D.M. Poitz, Regulation of endothelial migration and proliferation by ephrin-A1. Cell. Signal 29, 84–95 (2017)
X. Li, L. Wang, J.W. Gu, B. Li, W.P. Liu, Y.G. Wang, X. Zhang, H.N. Zhen, Z. Fei, Up-regulation of EphA2 and down-regulation of EphrinA1 are associated with the aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis of malignant glioma. Tumour biology: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 31(5), 477–488 (2010)
J. Wykosky, W. Debinski, The EphA2 receptor and ephrinA1 ligand in solid tumors: function and therapeutic targeting. Mol. Cancer Res.: MCR 6(12), 1795–1806 (2008)
K.H. Paraiso, M. Das Thakur, B. Fang, J.M. Koomen, I.V. Fedorenko, J.K. John, H. Tsao, K.T. Flaherty, V.K. Sondak, J.L. Messina, E.B. Pasquale, A. Villagra, U.N. Rao, J.M. Kirkwood, F. Meier, S. Sloot, G.T. Gibney, D. Stuart, H. Tawbi, K.S. Smalley, Ligand-independent EPHA2 signaling drives the adoption of a targeted therapy-mediated metastatic melanoma phenotype. Cancer Discov. 5(3), 264–273 (2015)
W.B. Fang, D.M. Brantley-Sieders, M.A. Parker, A.D. Reith, J. Chen, A kinase-dependent role for EphA2 receptor in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 24(53), 7859–7868 (2005)
K.R. Amato, S. Wang, A.K. Hastings, V.M. Youngblood, P.R. Santapuram, H. Chen, J.M. Cates, D.C. Colvin, F. Ye, D.M. Brantley-Sieders, R.S. Cook, L. Tan, N.S. Gray, J. Chen, Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of EPHA2 promotes apoptosis in NSCLC. J. Clin. Invest. 124(5), 2037–2049; (2014)
Y. Sheng, J. Wei, Y. Zhang, X. Gao, Z. Wang, J. Yang, S. Yan, Y. Zhu, Z. Zhang, D. Xu, C. Wang, Y. Zheng, Q. Dong, L. Qin, Mutated EPHA2 is a target for combating lymphatic metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 144(10), 2440–2452 (2019)
D. Kiewlich, J. Zhang, C. Gross, W. Xia, B. Larsen, R.R. Cobb, S. Biroc, J.M. Gu, T. Sato, D.R. Light, T. Heitner, J. Willuda, D. Vogel, F. Monteclaro, A. Citkowicz, S.R. Roffler, D.A. Zajchowski, Anti-EphA2 antibodies decrease EphA2 protein levels in murine CT26 colorectal and human MDA-231 breast tumors but do not inhibit tumor growth. Neoplasia 8(1), 18–30 (2006)
M. Ishikawa, R. Miyahara, M. Sonobe, M. Horiuchi, T. Mennju, E. Nakayama, M. Kobayashi, R. Kikuchi, J. Kitamura, N. Imamura, C.L. Huang, H. Date, Higher expression of EphA2 and ephrin-A1 is related to favorable clinicopathological features in pathological stage I non-small cell lung carcinoma. Lung cancer 76(3), 431–438 (2012)
M. Locard-Paulet, L. Lim, G. Veluscek, K. McMahon, J. Sinclair, A. van Weverwijk, J.D. Worboys, Y. Yuan, C.M. Isacke, C. Jorgensen, Phosphoproteomic analysis of interacting tumor and endothelial cells identifies regulatory mechanisms of transendothelial migration. Sci. Signal. 9(414), ra15 (2016)
T. Tawadros, M.D. Brown, C.A. Hart, N.W. Clarke, Ligand-independent activation of EphA2 by arachidonic acid induces metastasis-like behaviour in prostate cancer cells. Brit. J. Cancer 107(10), 1737–1744 (2012)
U. Gopal, J.E. Bohonowych, C. Lema-Tome, A. Liu, E. Garrett-Mayer, B. Wang, J.S. Isaacs, A novel extracellular Hsp90 mediated co-receptor function for LRP1 regulates EphA2 dependent glioblastoma cell invasion. PloS one 6(3), e17649 (2011)
R. Leveque, C. Corbet, L. Aubert, M. Guilbert, C. Lagadec, E. Adriaenssens, J. Duval, P. Finetti, D. Birnbaum, N. Magne, V. Chopin, F. Bertucci, X. Le Bourhis, R.A. Toillon, ProNGF increases breast tumor aggressiveness through functional association of TrkA with EphA2. Cancer Lett. 449, 196–206 (2019)
M. De Robertis, L. Loiacono, C. Fusilli, M.L. Poeta, T. Mazza, M. Sanchez, L. Marchionni, E. Signori, G. Lamorte, A.L. Vescovi, J. Garcia-Foncillas, V.M. Fazio, Dysregulation of EGFR Pathway in EphA2 Cell Subpopulation Significantly Associates with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(1), 159–170 (2017)
M. Tandon, S.V. Vemula, S.K. Mittal, Emerging strategies for EphA2 receptor targeting for cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 15(1), 31–51 (2011)
H.M. Kluger, A.Z. Dudek, C. McCann, J. Ritacco, N. Southard, L.B. Jilaveanu, A. Molinaro, M. Sznol, A phase 2 trial of dasatinib in advanced melanoma. Cancer 117(10), 2202–2208 (2011)
Y. Kaibori, Y. Saito, Y. Nakayama, EphA2 phosphorylation at Ser897 by the Cdk1/MEK/ERK/RSK pathway regulates M-phase progression via maintenance of cortical rigidity. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 33(4), 5334–5349 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81572872).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Baocun Sun and Jing Mo conceived and designed the study. Xiulan Zhao, Xueyi Dong, Tieju Liu, Nan Zhao, Danfang Zhang, Wei Wang and Yanhui Zhang performed the experiments. Xiulan Zhao, Jing Mo and Xueyi Dong performed cell culture, H&E and IHC. Jing Mo, Tieju Liu, Nan Zhao, Danfang Zhang and Wei Wang conducted Western blotting and animal experiments. Jing Mo and Yanhui Zhang performed immunofluorescence assays. Baocun Sun and Jing Mo interpreted and analyzed the data. Jing Mo wrote and Baocun Sun reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to declare.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocol was approved by the Tianjin Medical University Ethical Committee Board, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China. Written informed consent to participate in the study was obtained from all individual participants or their guardians.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, J., Zhao, X., Dong, X. et al. Effect of EphA2 knockdown on melanoma metastasis depends on intrinsic ephrinA1 level. Cell Oncol. 43, 655–667 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00511-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00511-x